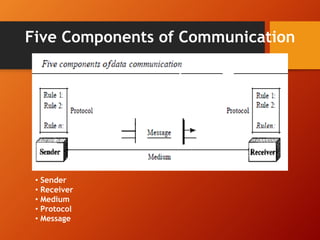
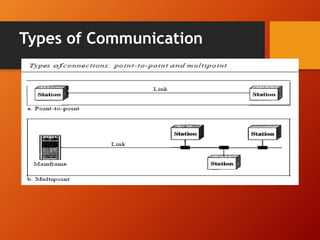
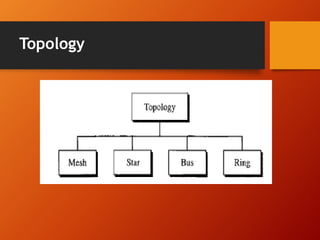
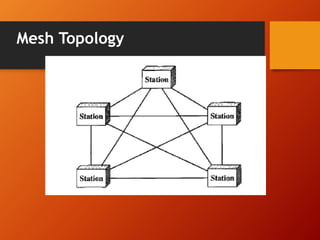
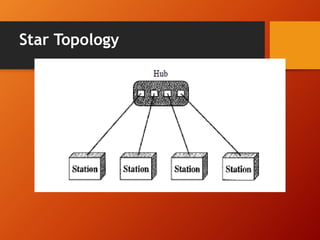
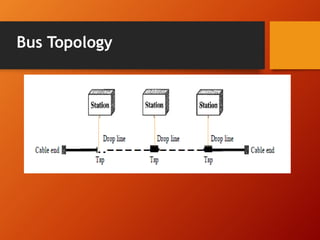
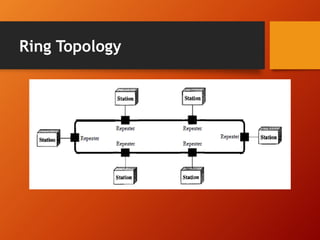
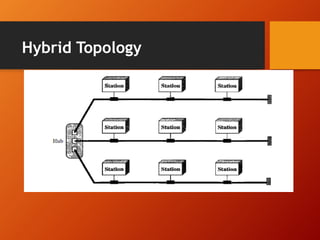
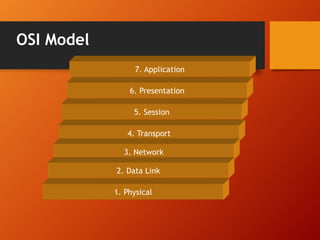
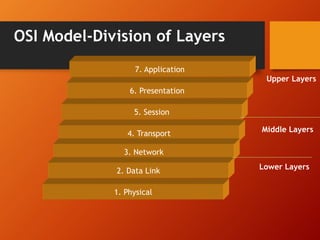
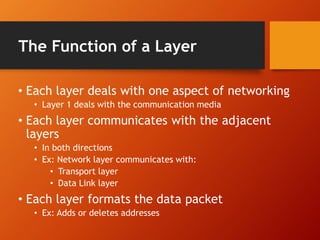
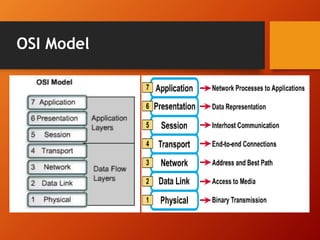
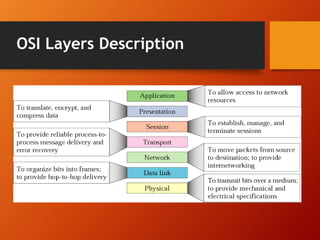
The document provides an overview of networking basics and Cisco systems. It defines what a network is and describes different network types like LAN, WAN, and MAN. It also outlines the five components of communication, different network topologies, and the OSI model. The document then discusses commonly used network devices before focusing on Cisco systems. It provides a brief history of Cisco and describes its products which include routers, switches, security solutions and more.