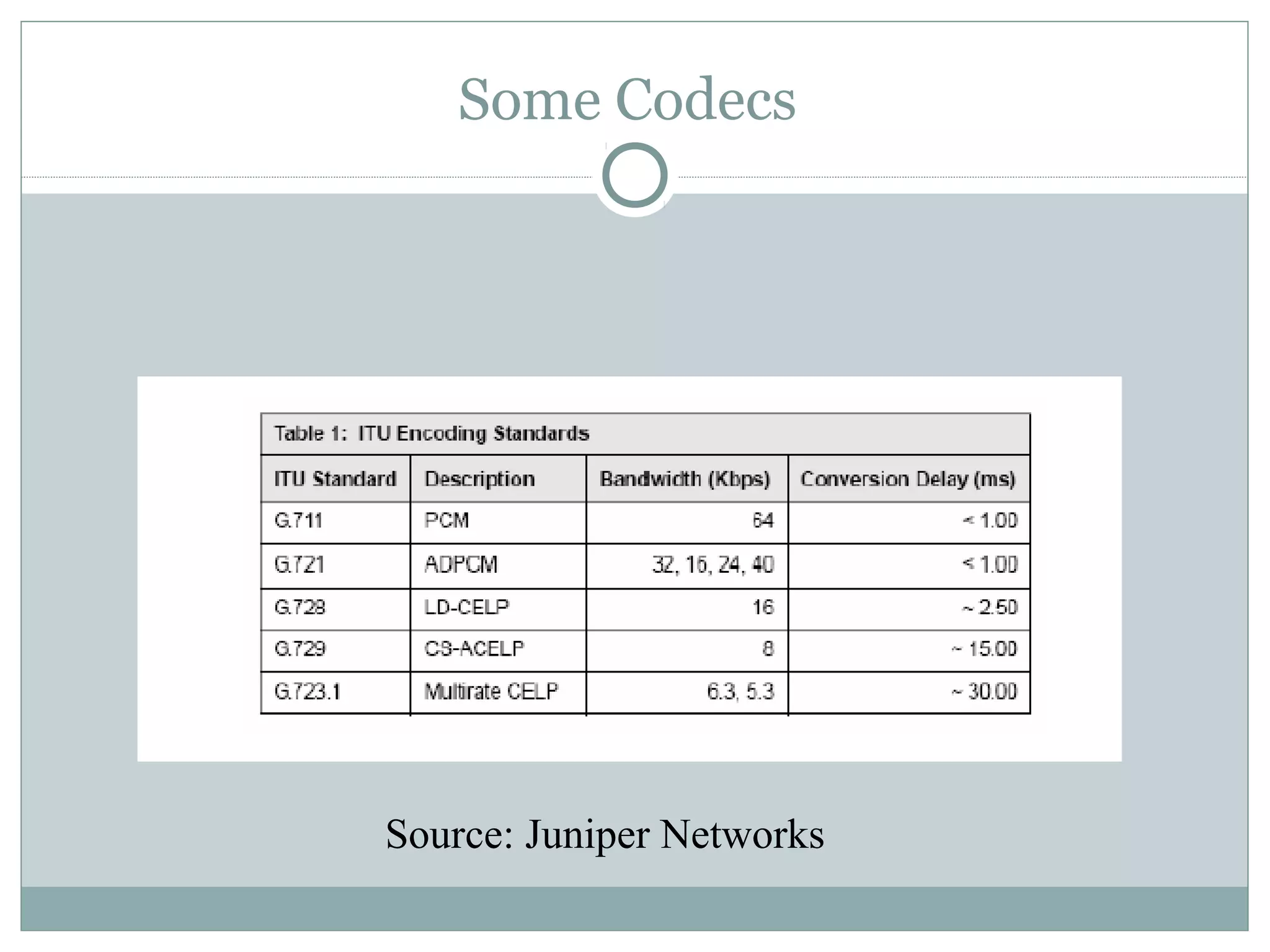
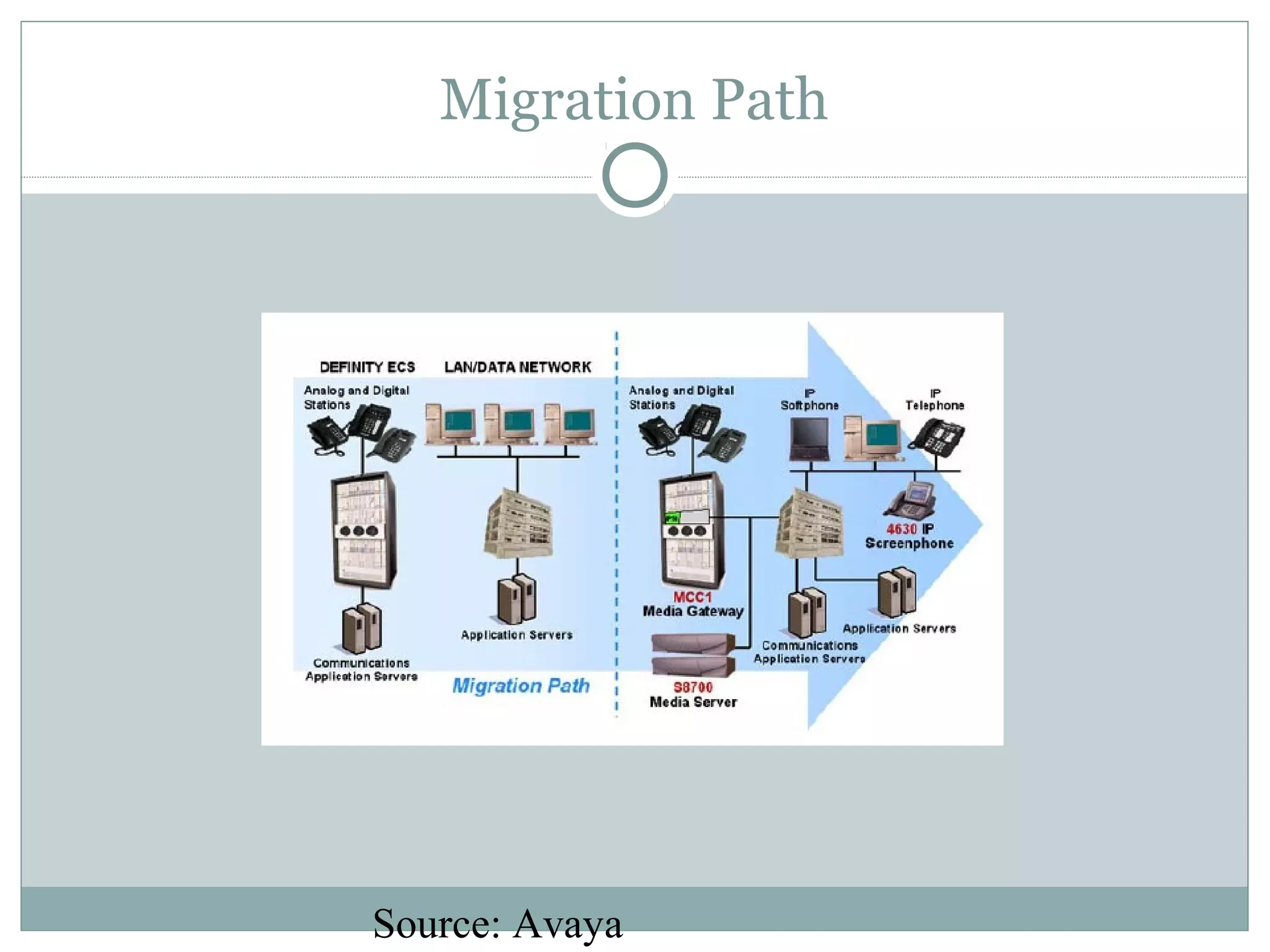
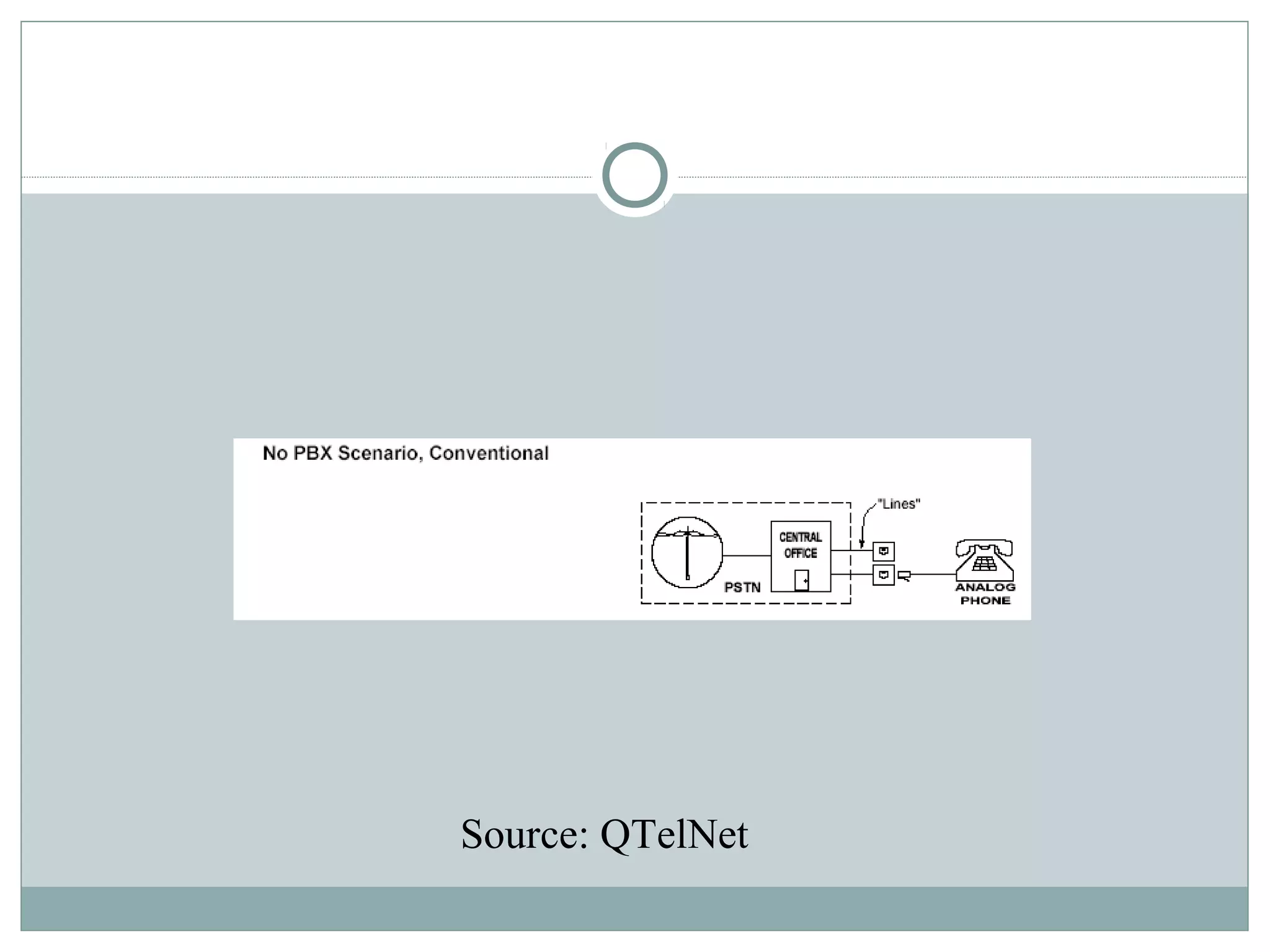
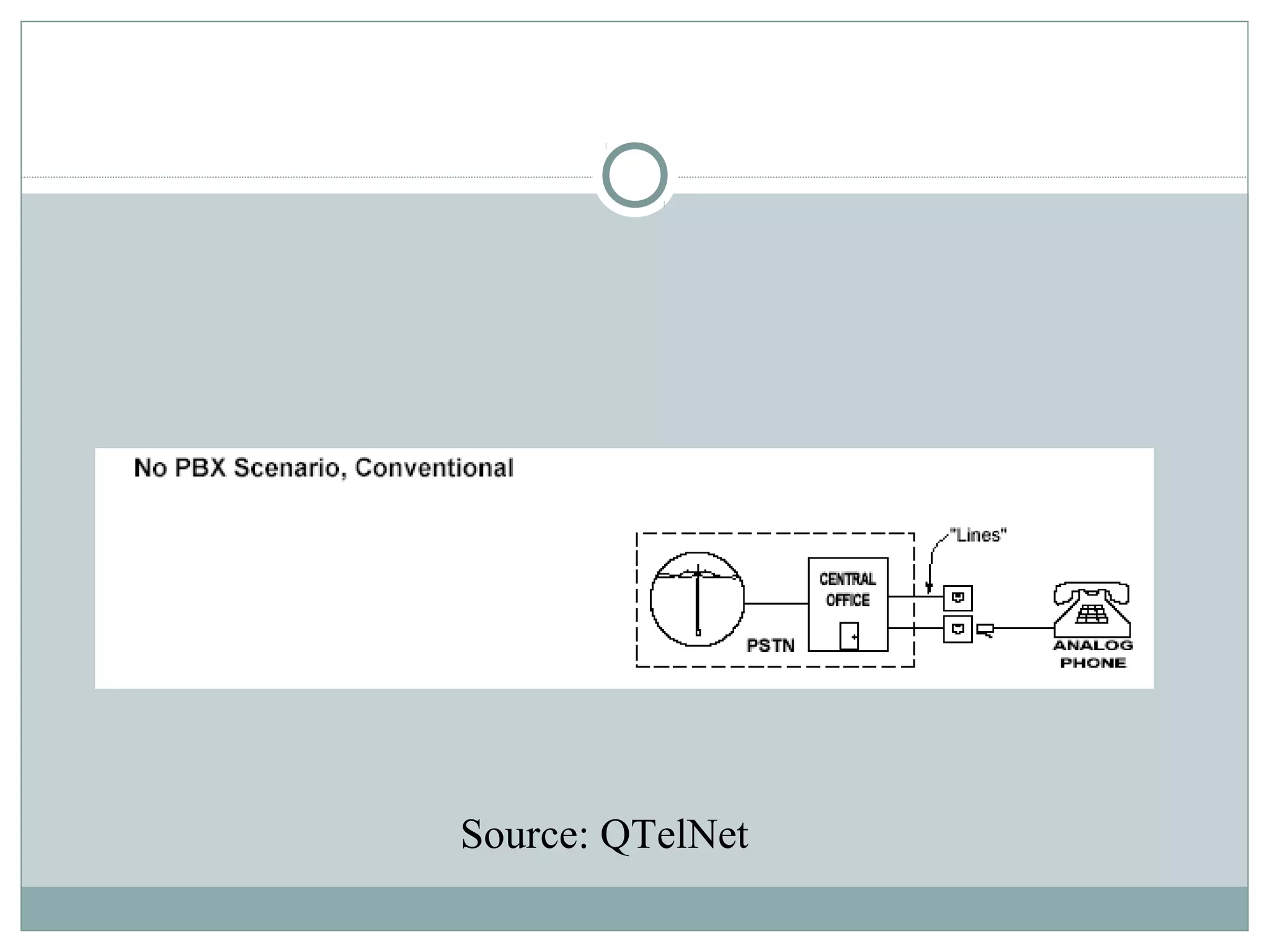
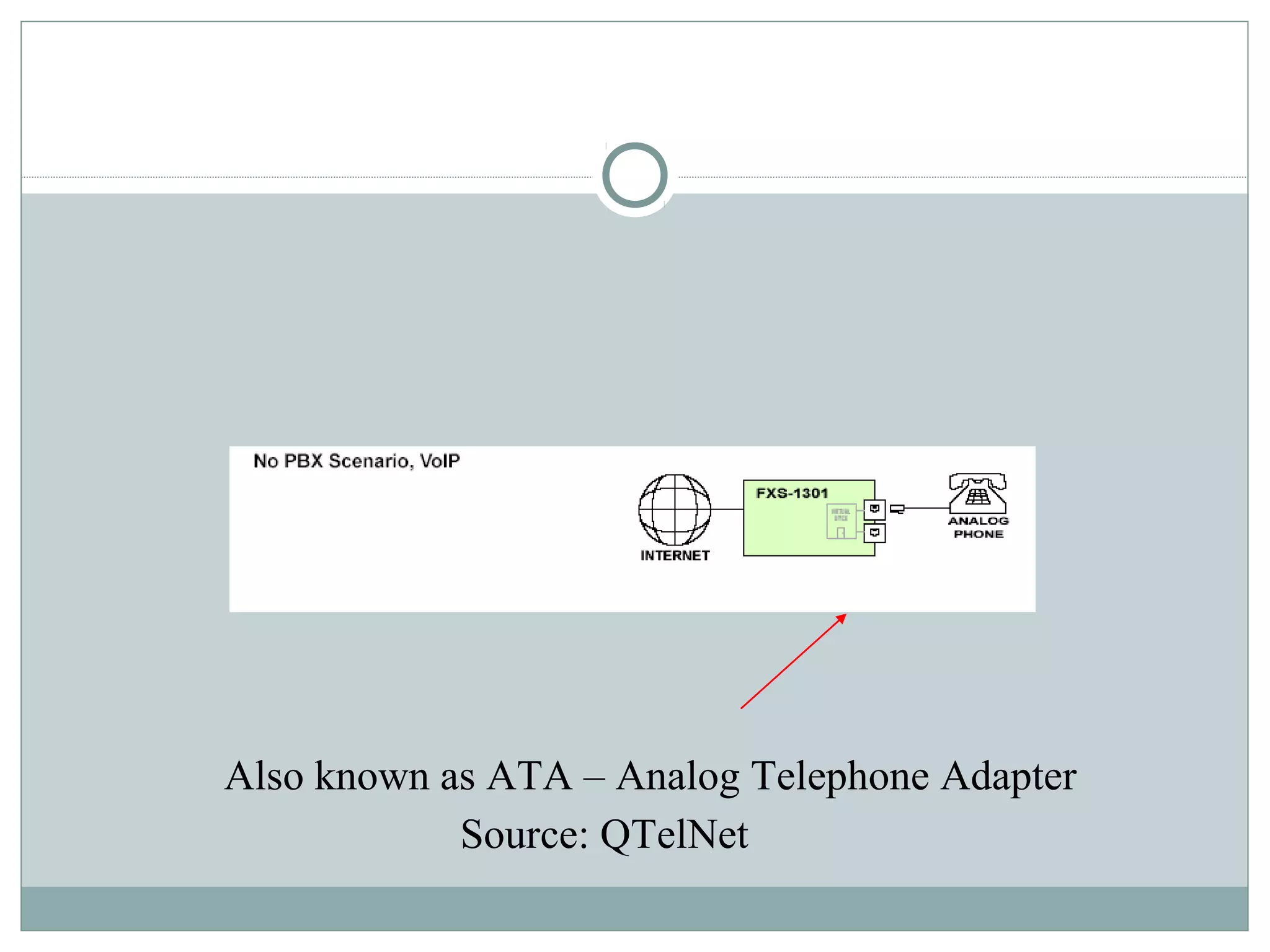
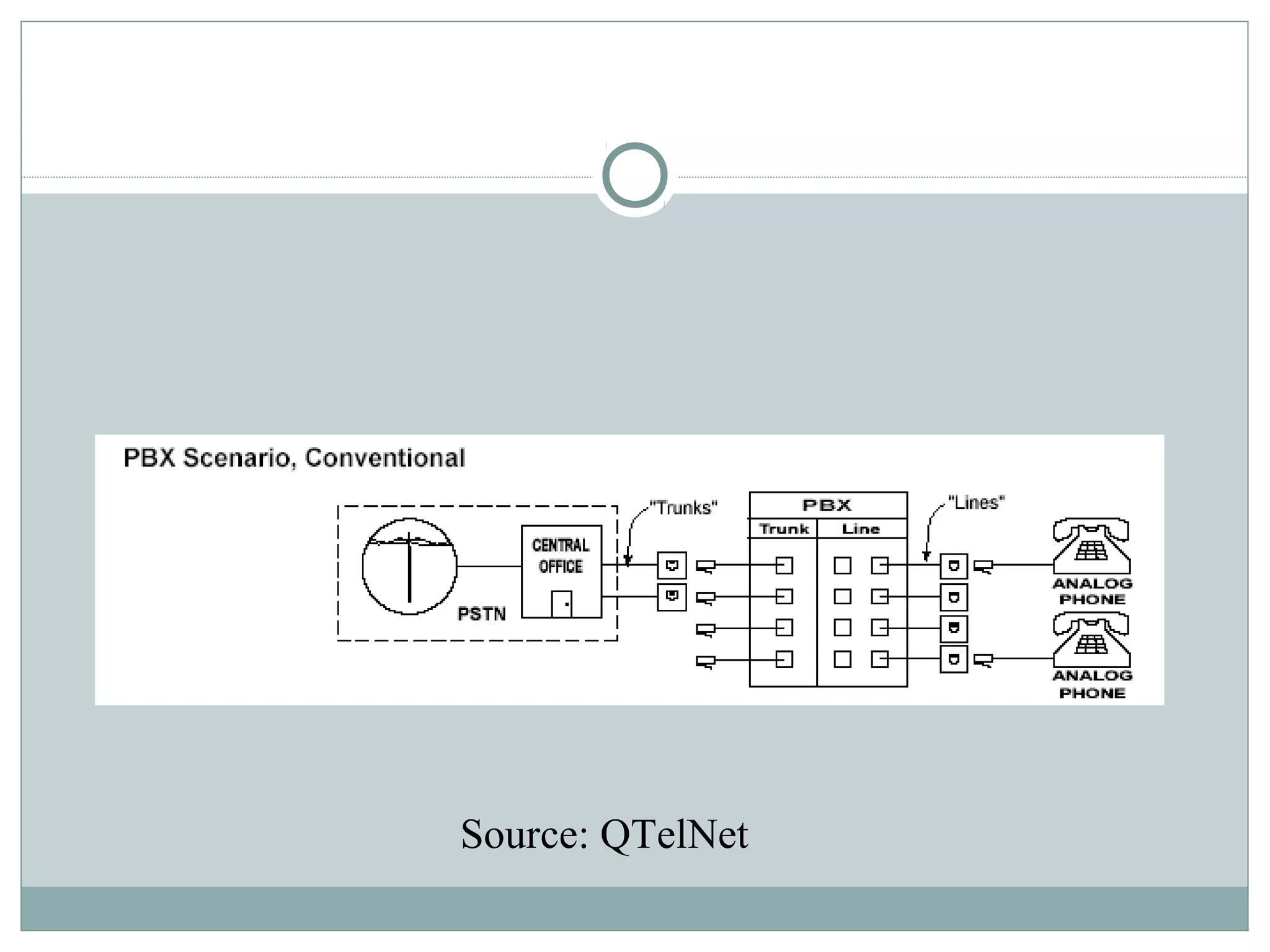
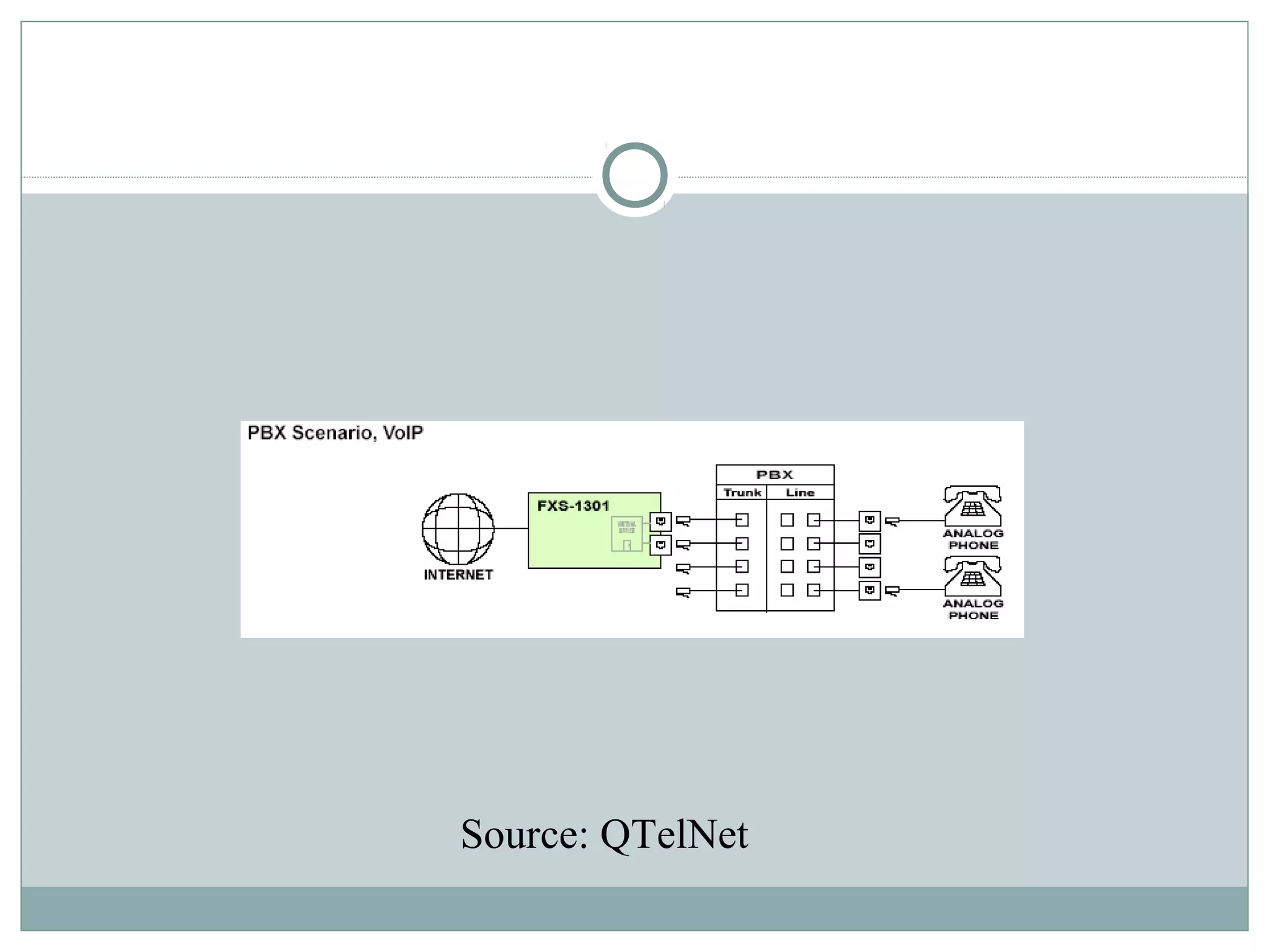
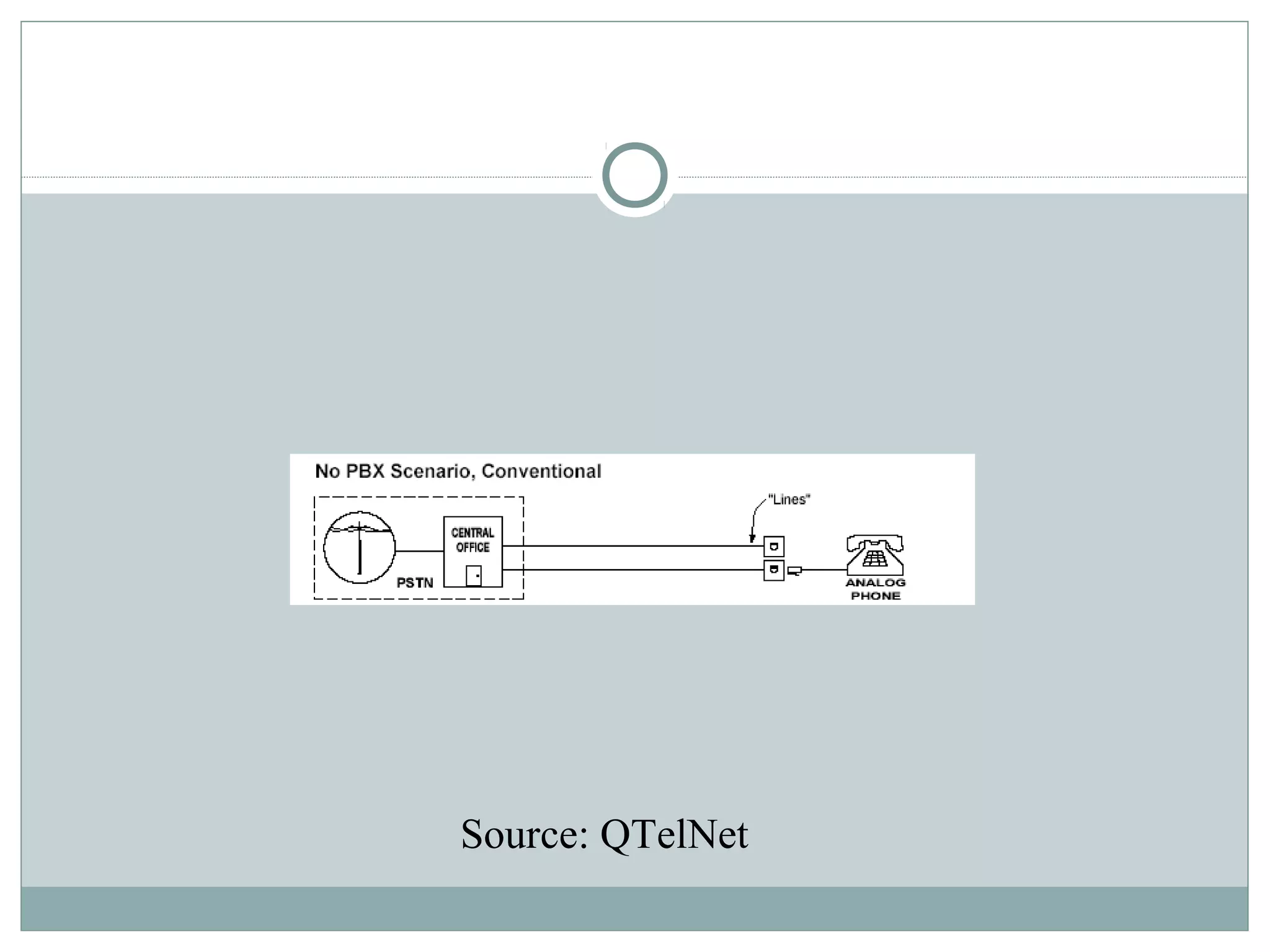
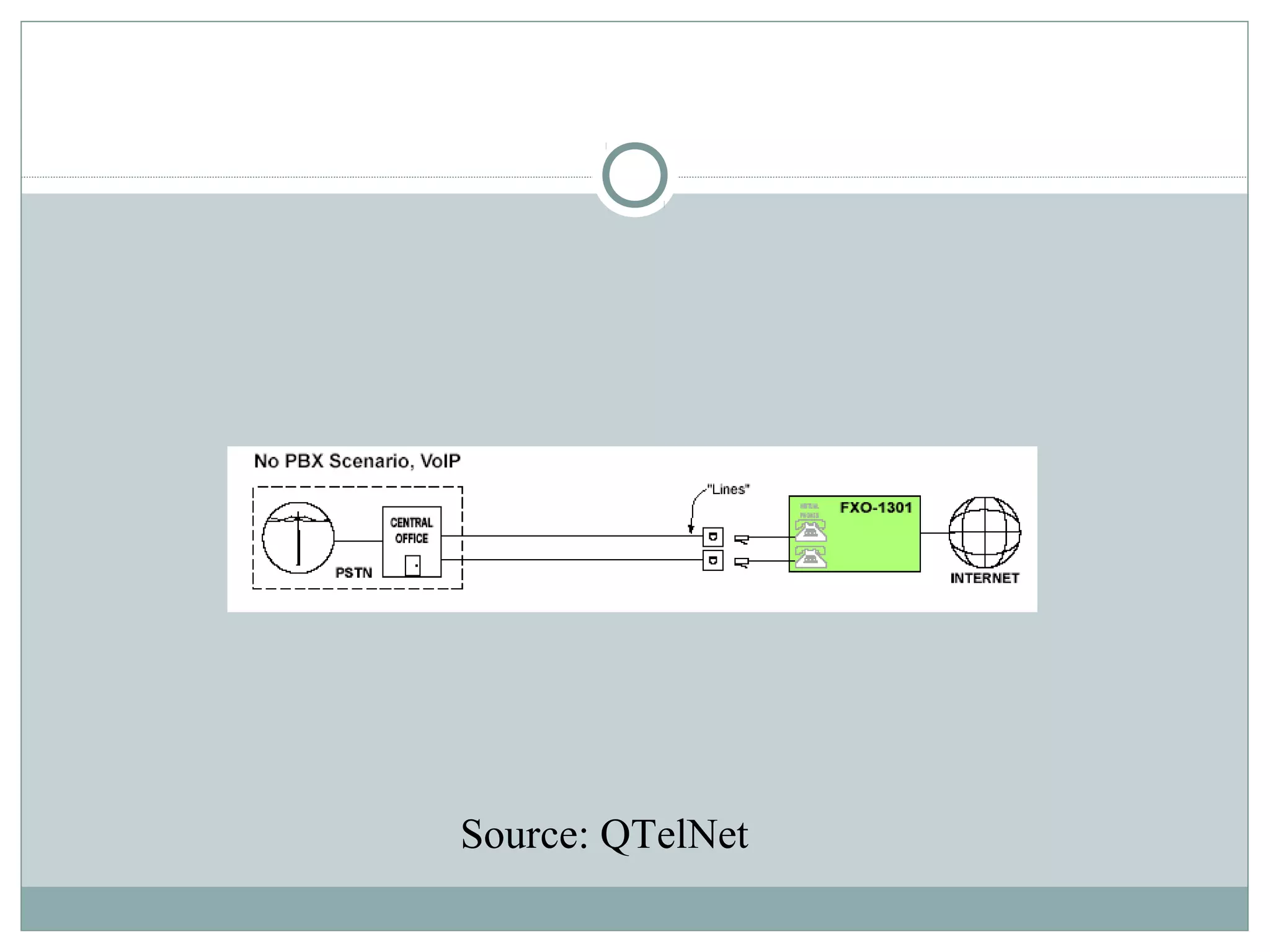
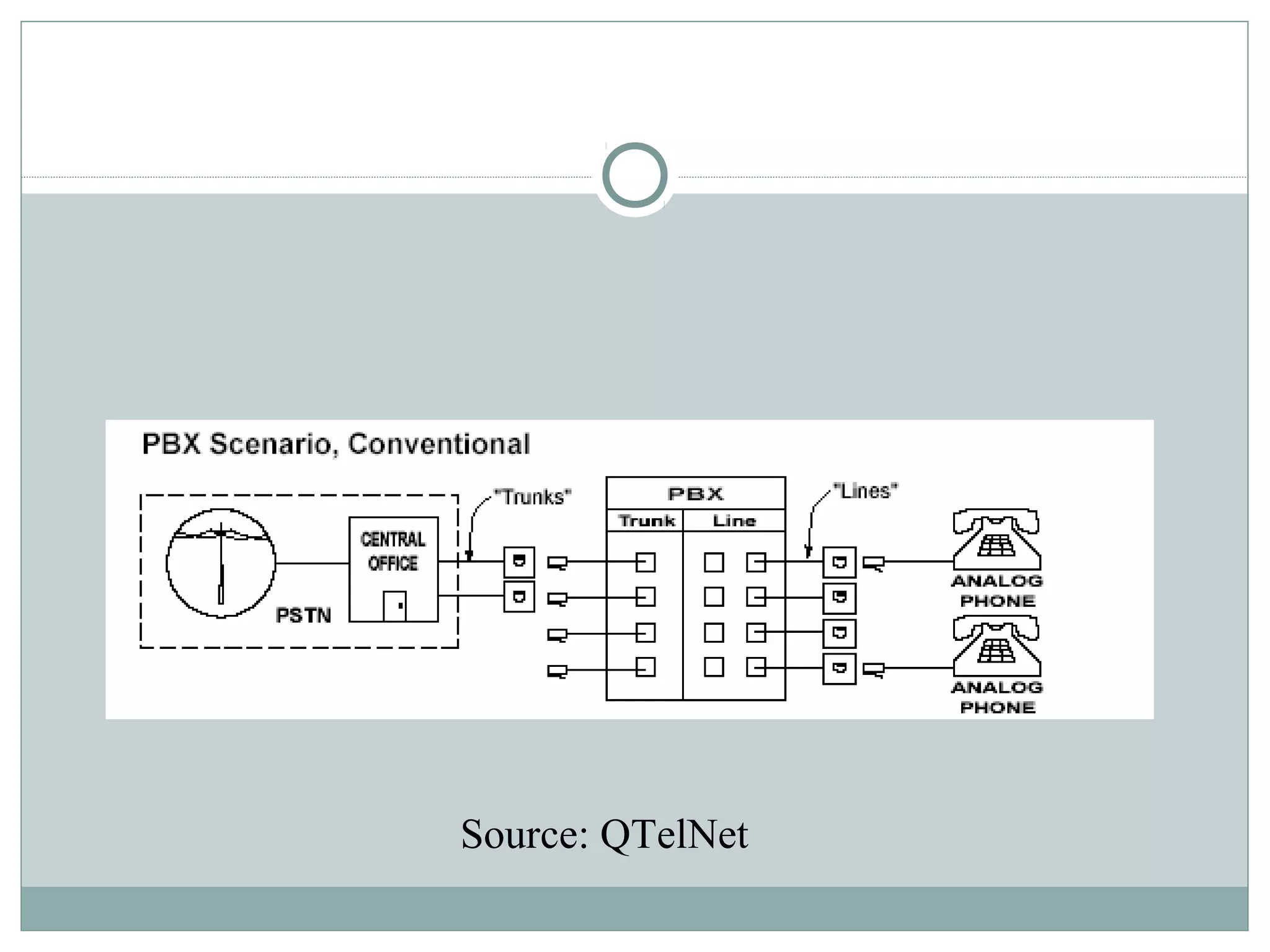
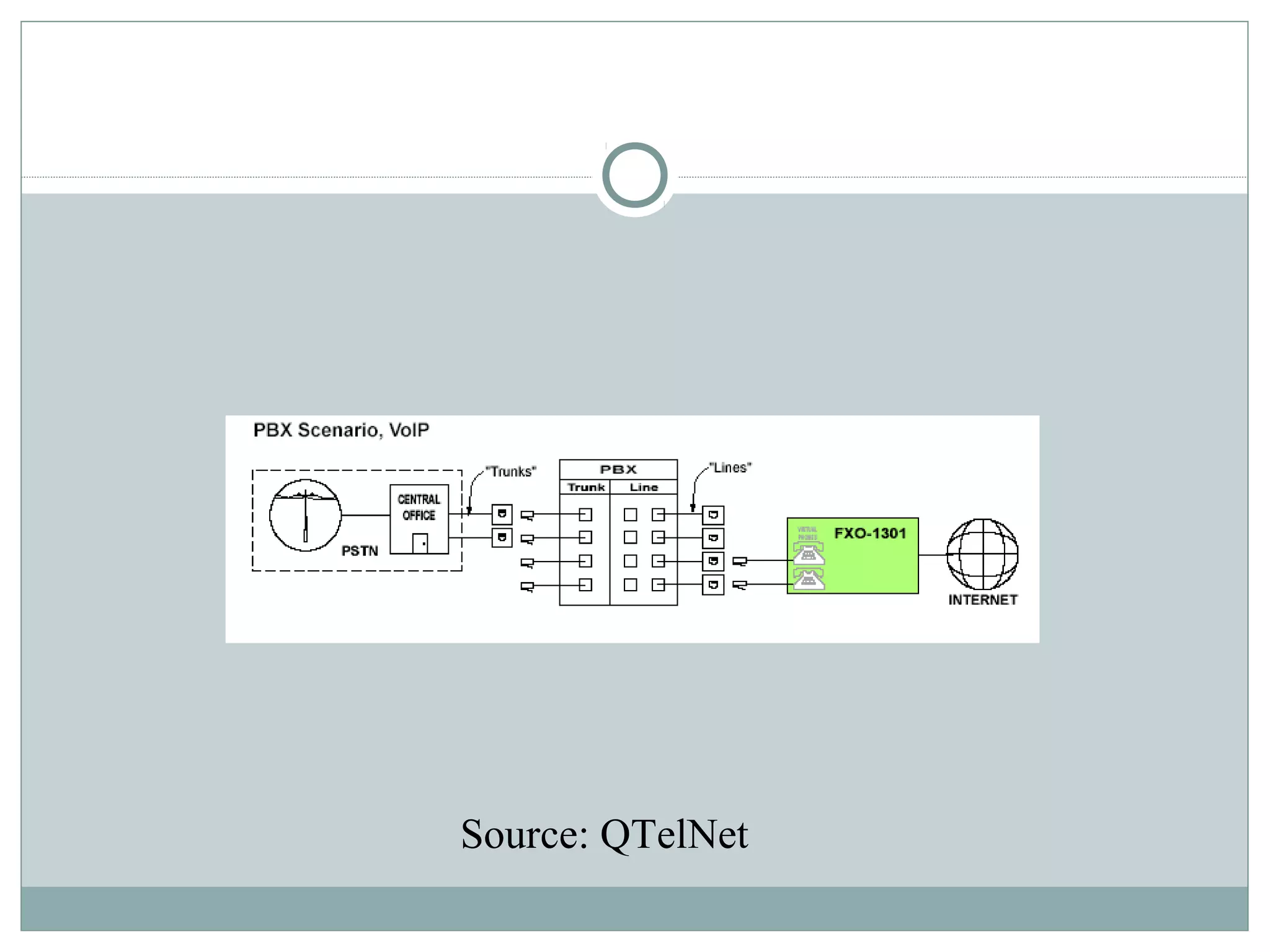
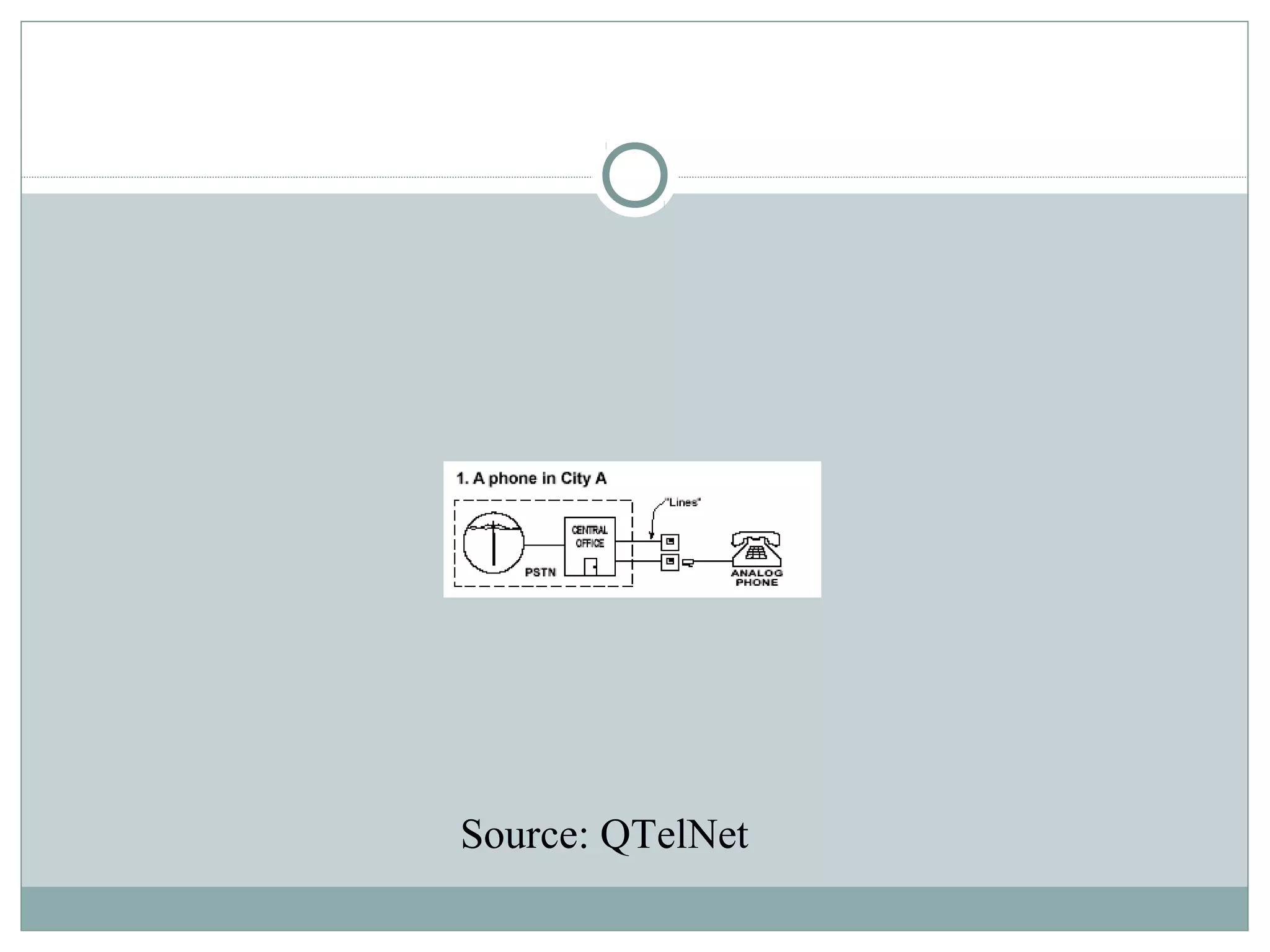
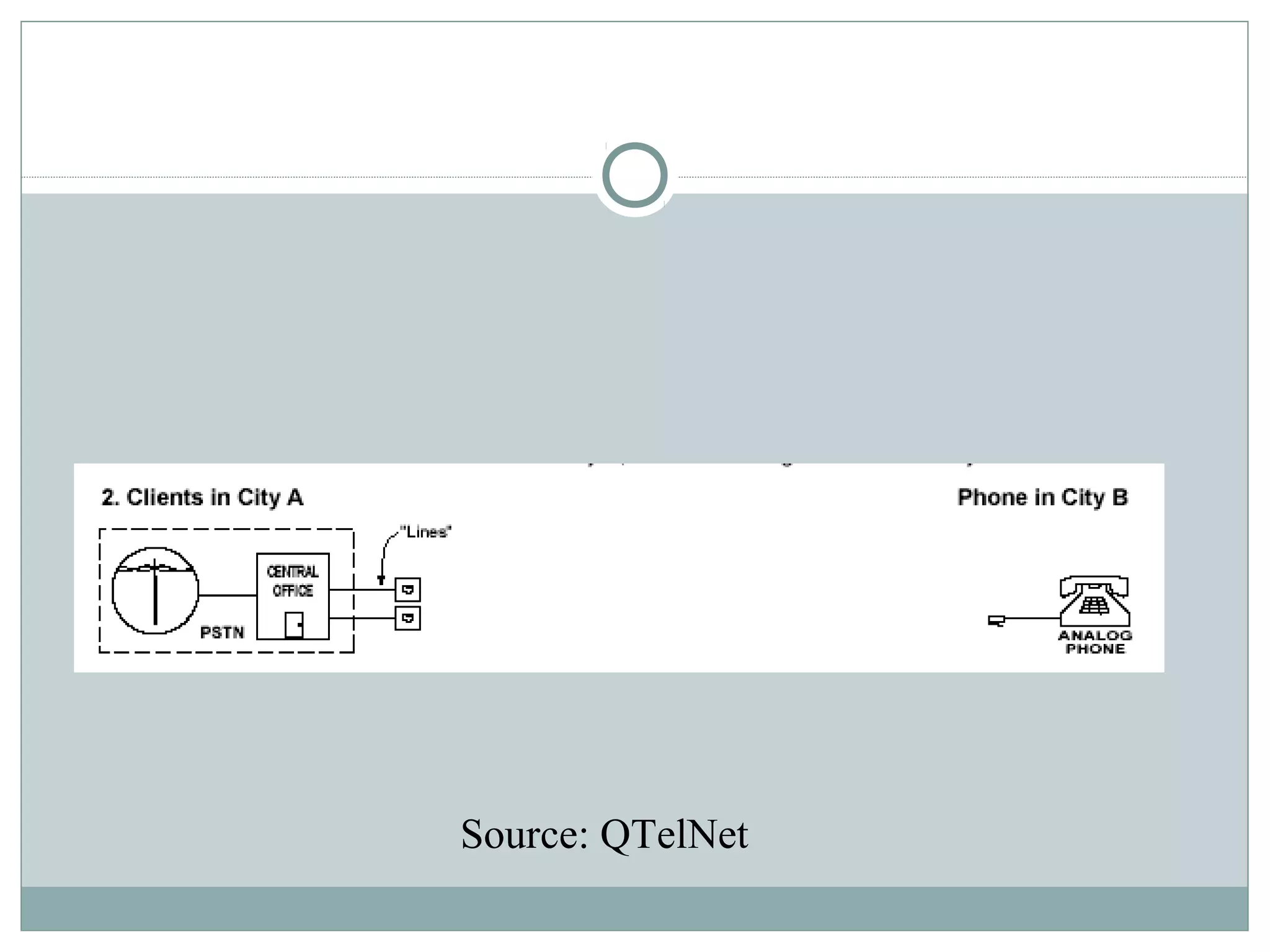
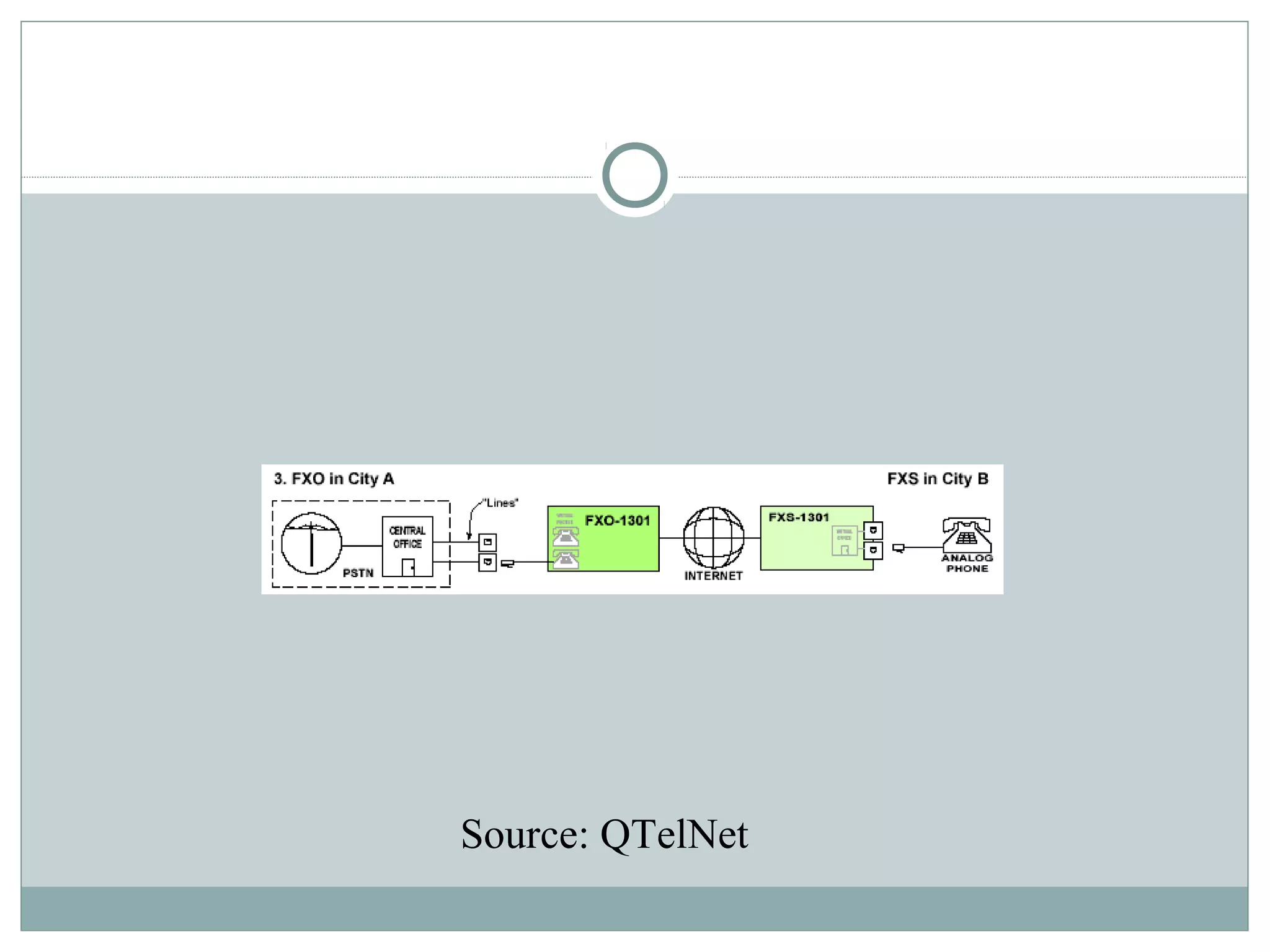
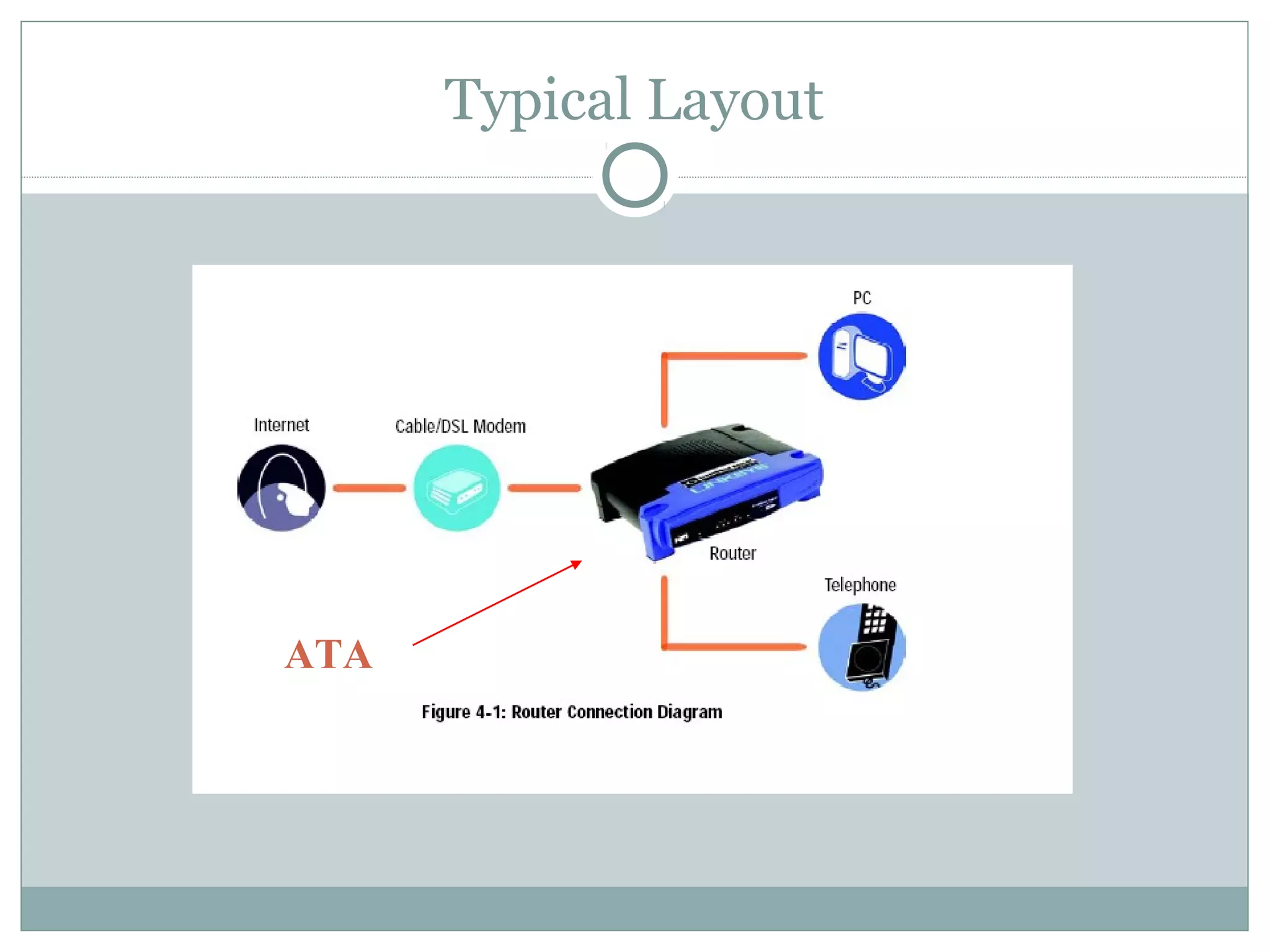
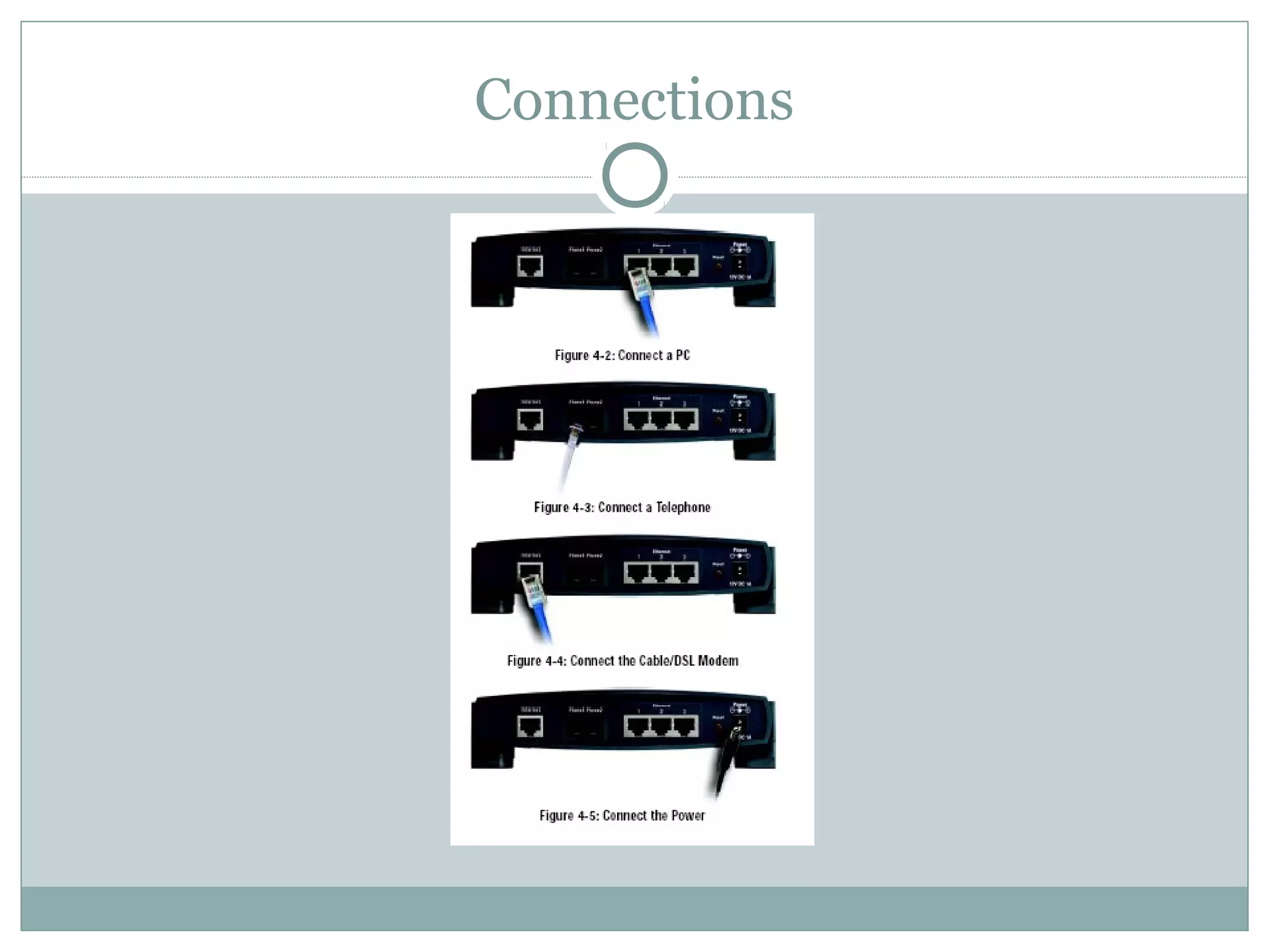
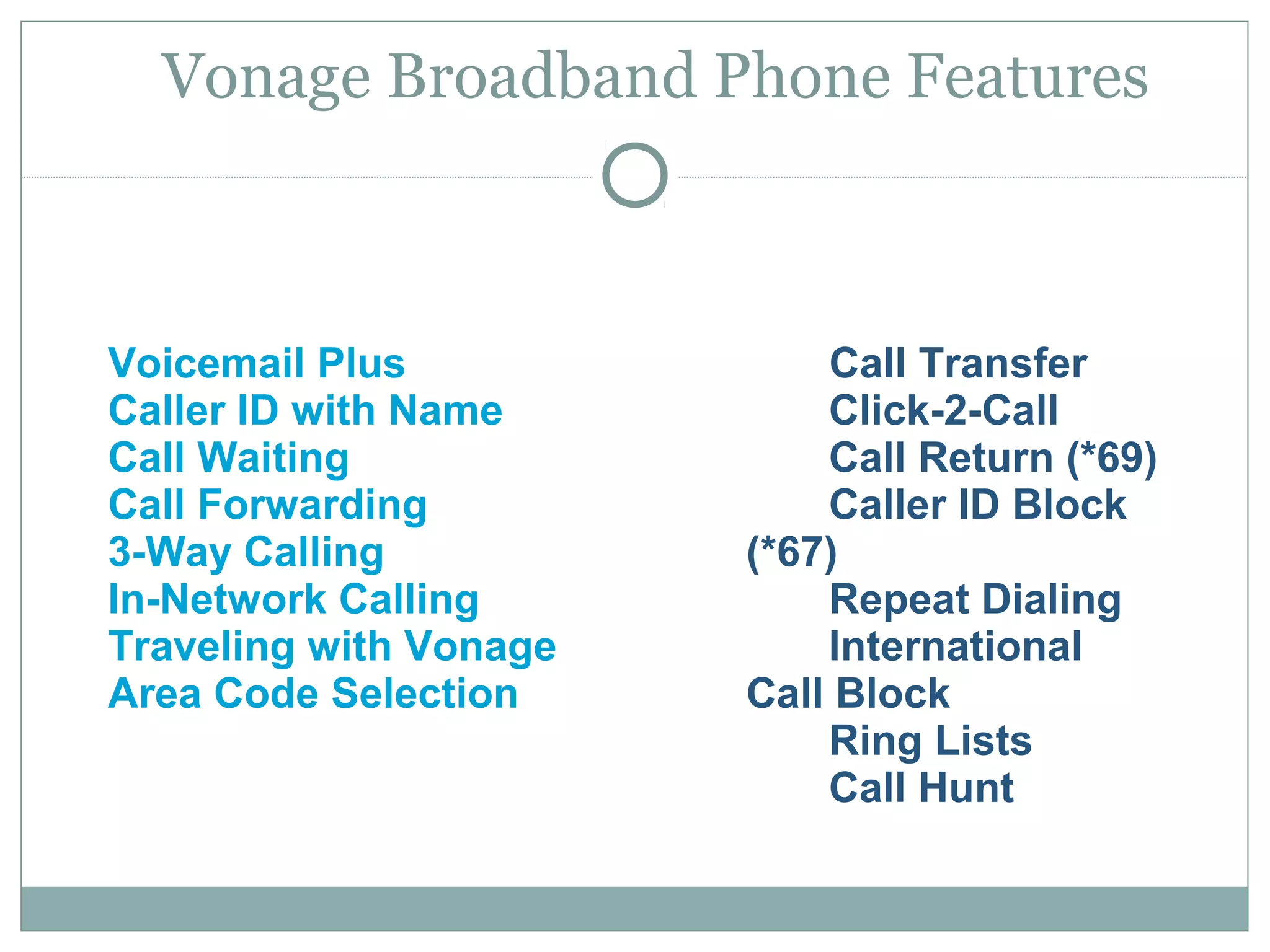
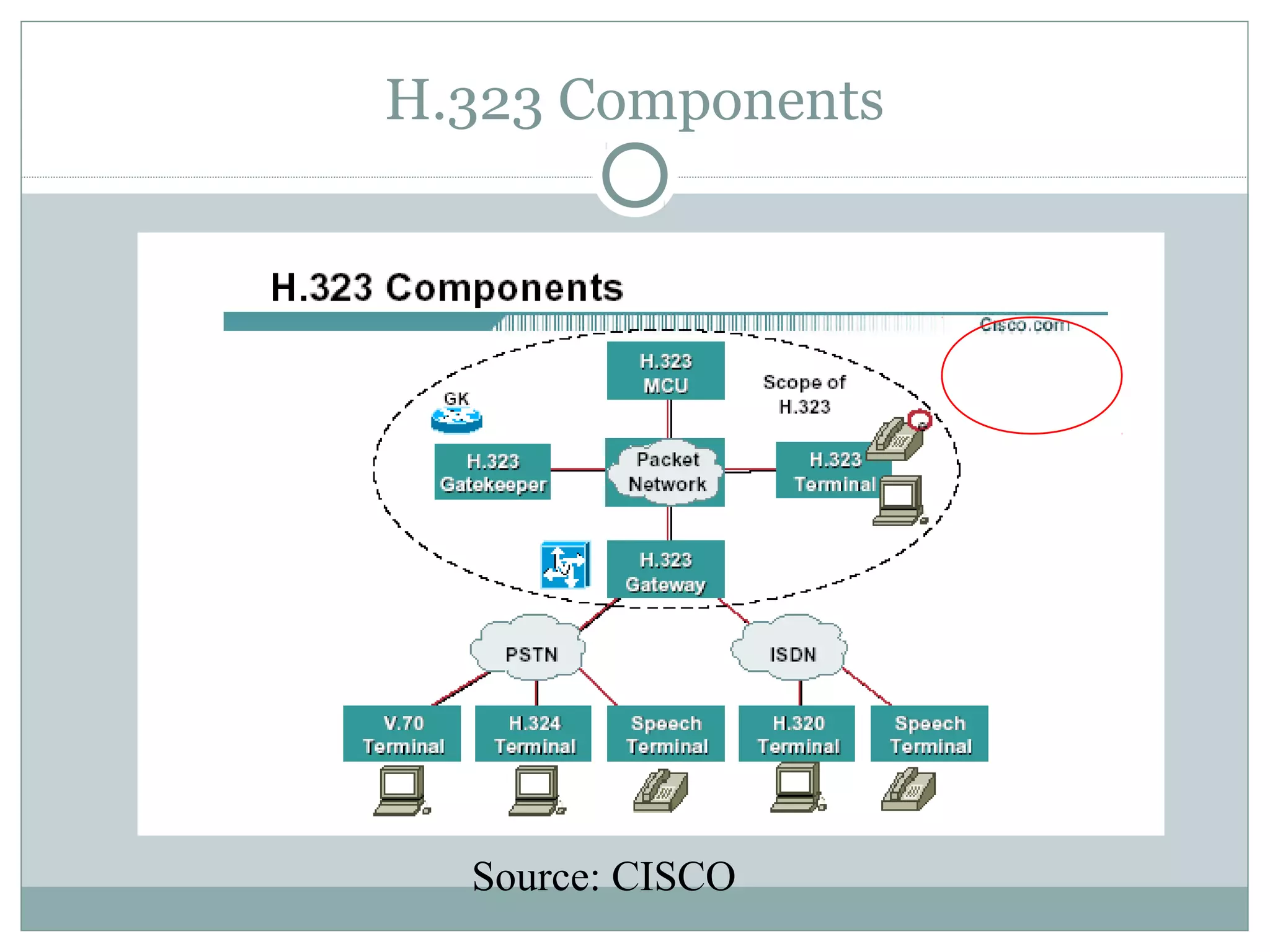
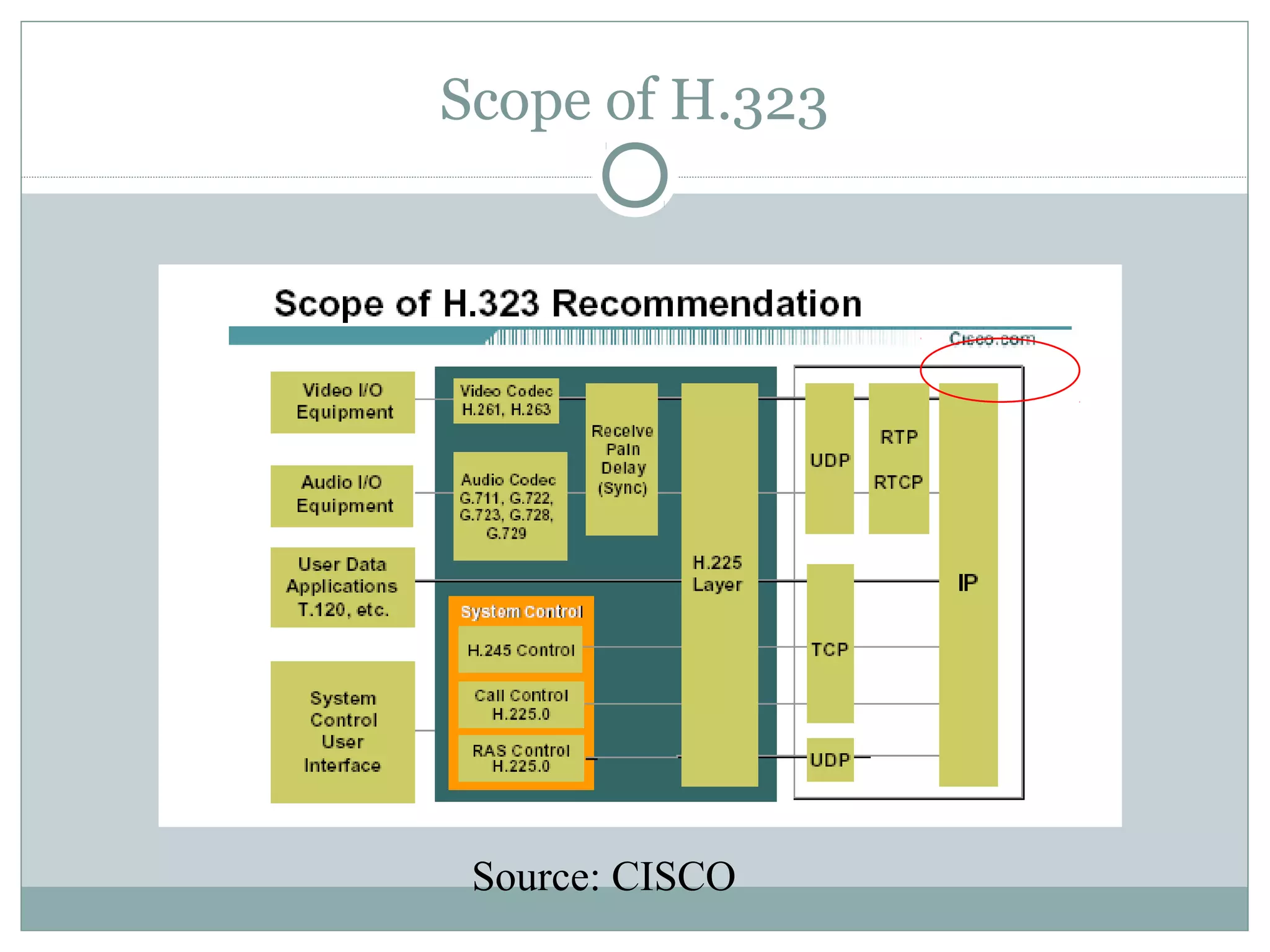
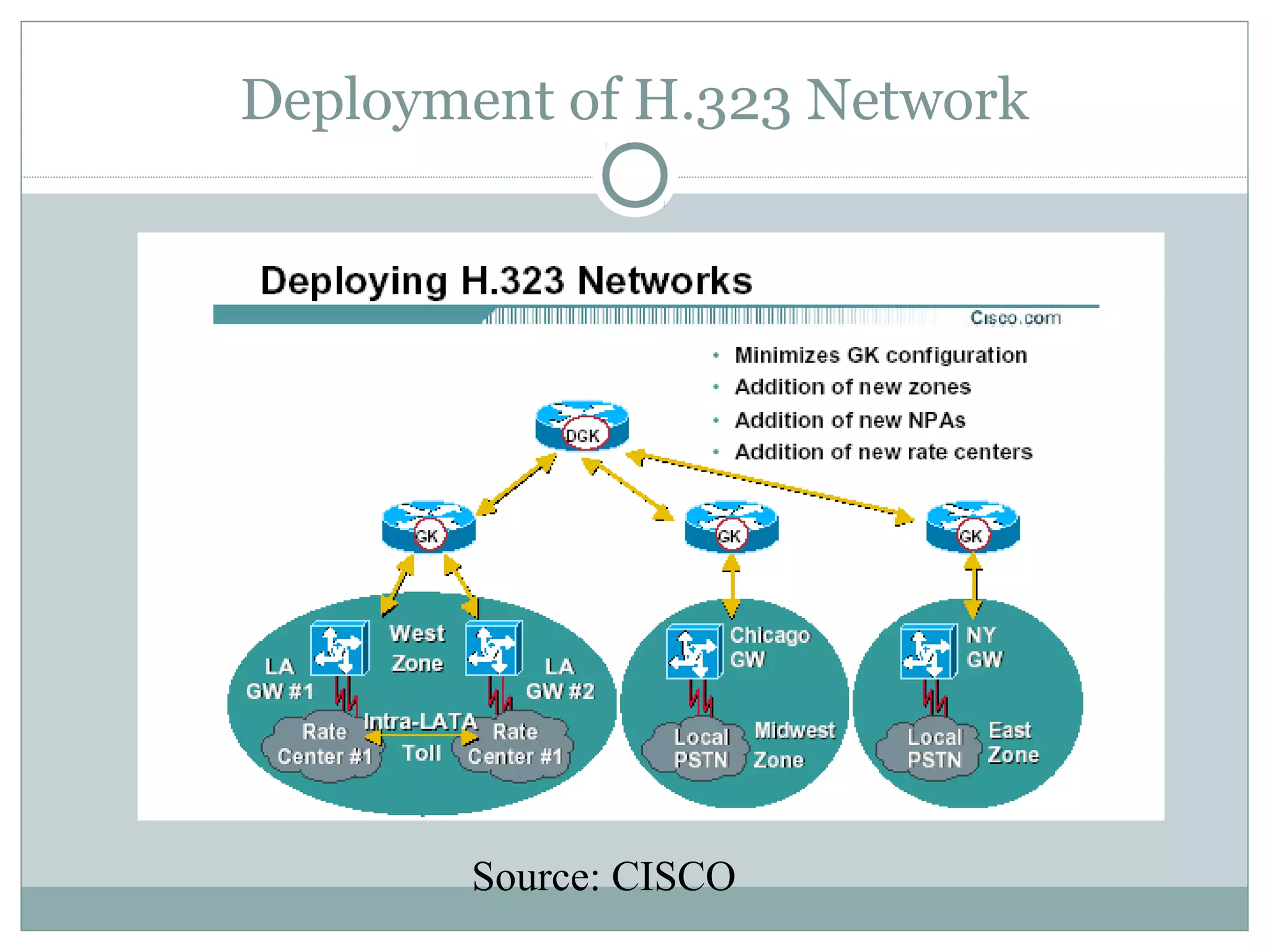
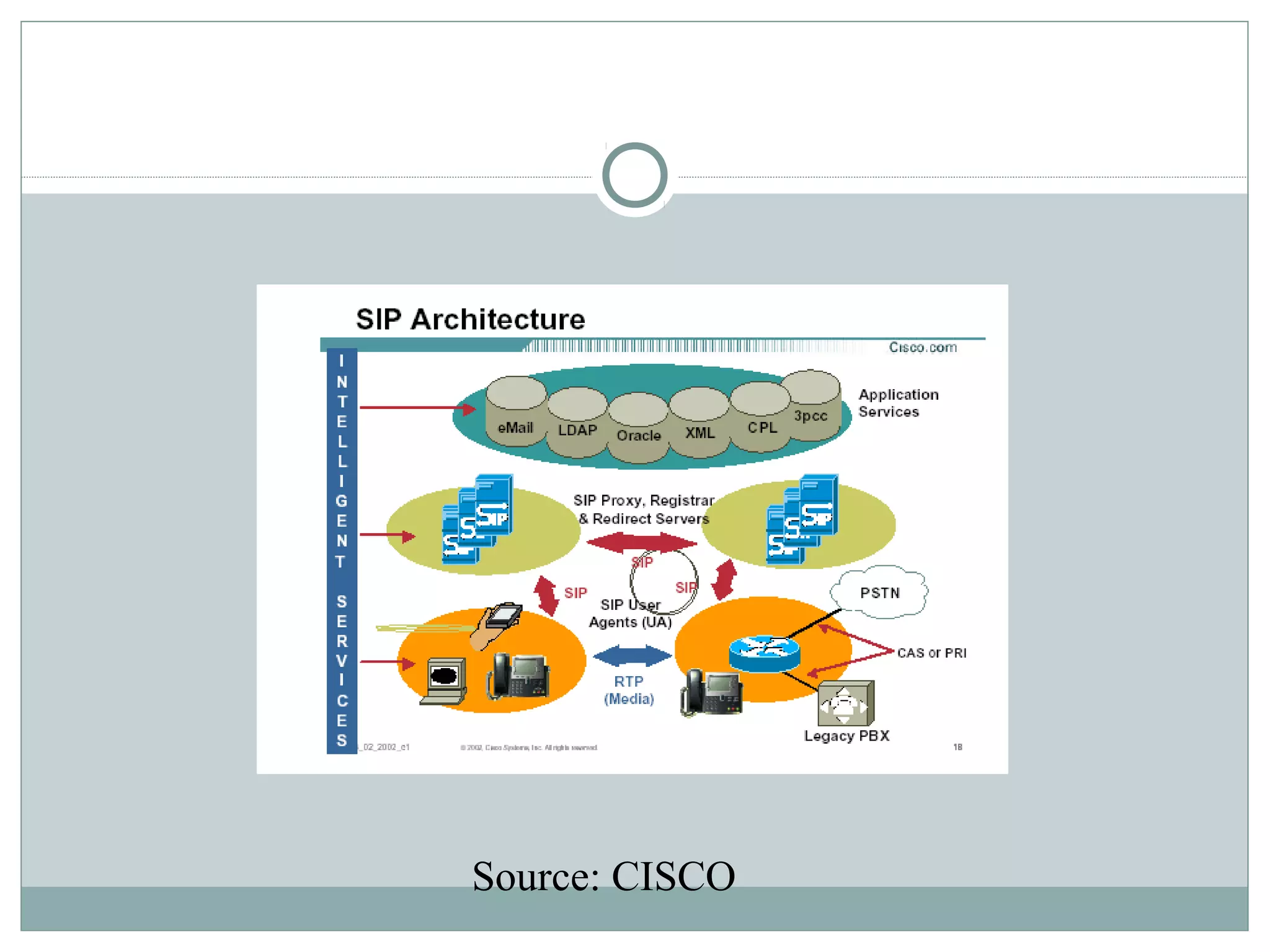
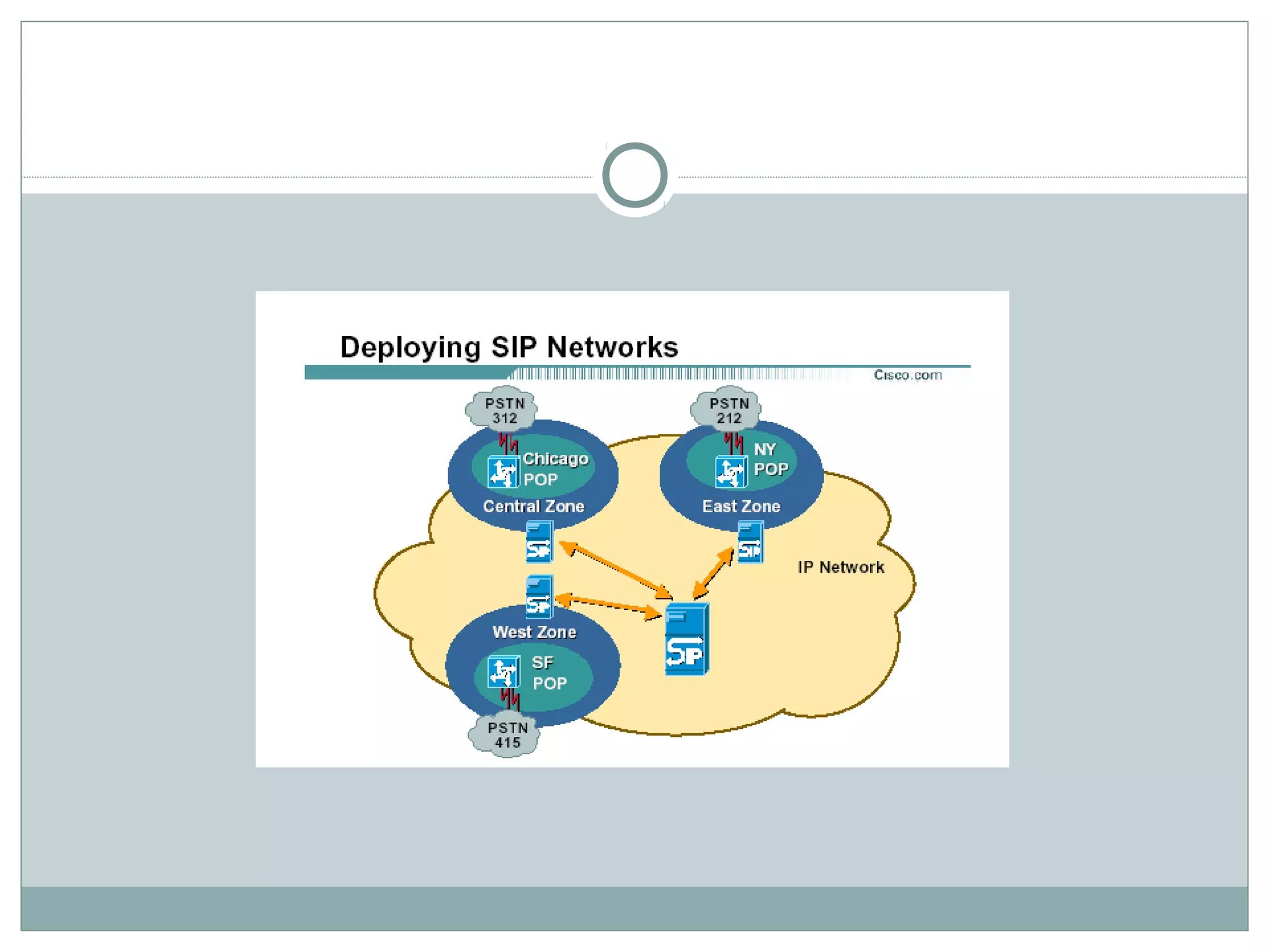
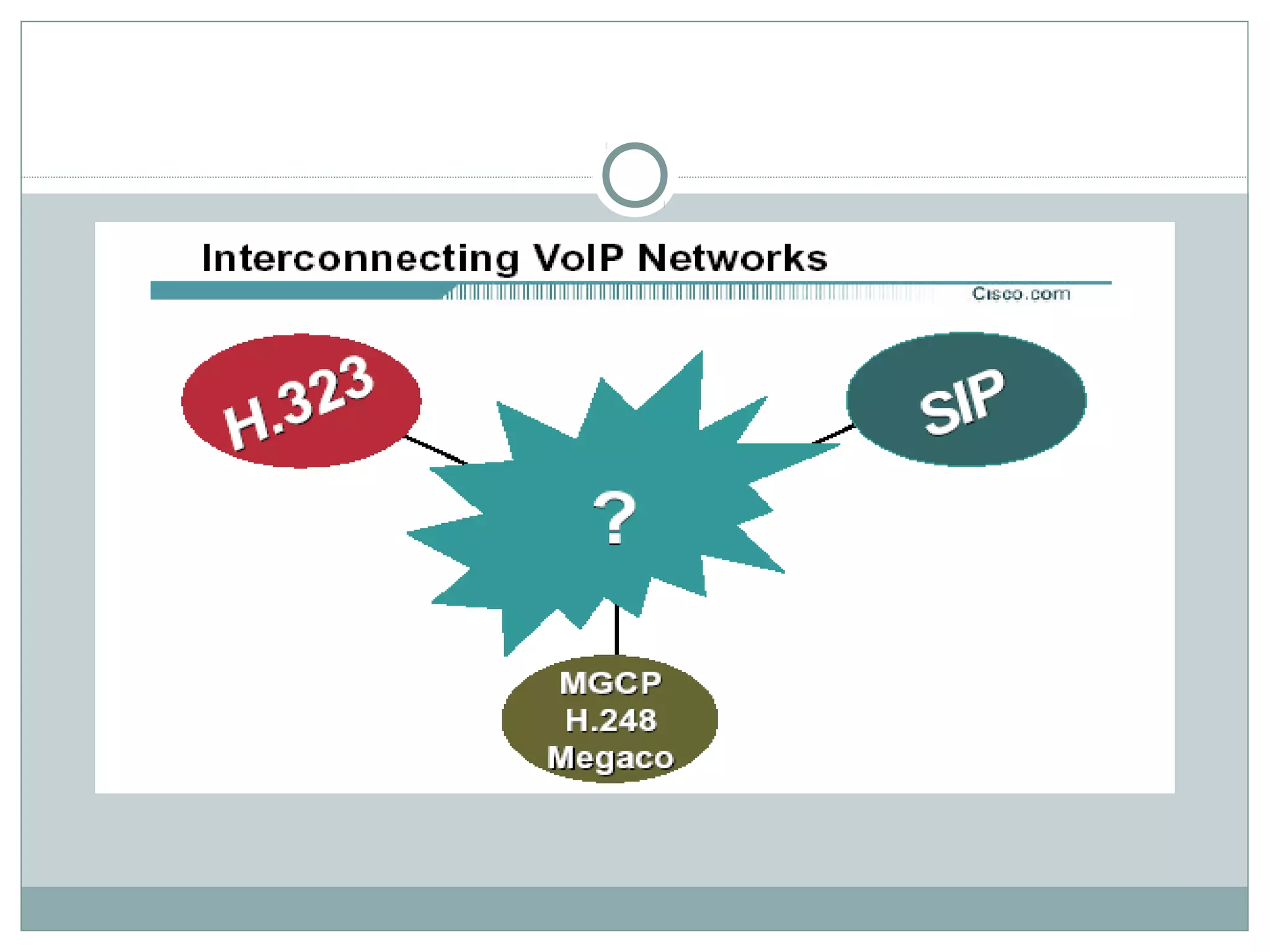
VoIP allows transmission of voice calls over IP networks like the internet. It works by encoding voice input and transmitting it as digital audio packets rather than traditional circuit-switched telephone networks. Key challenges include latency, jitter, bandwidth, packet loss, reliability, and security. Standards like H.323, SIP, and MGCP help address these and ensure interoperability between VoIP systems from different vendors. Components include servers, end-point devices, media gateways, and the IP network itself.