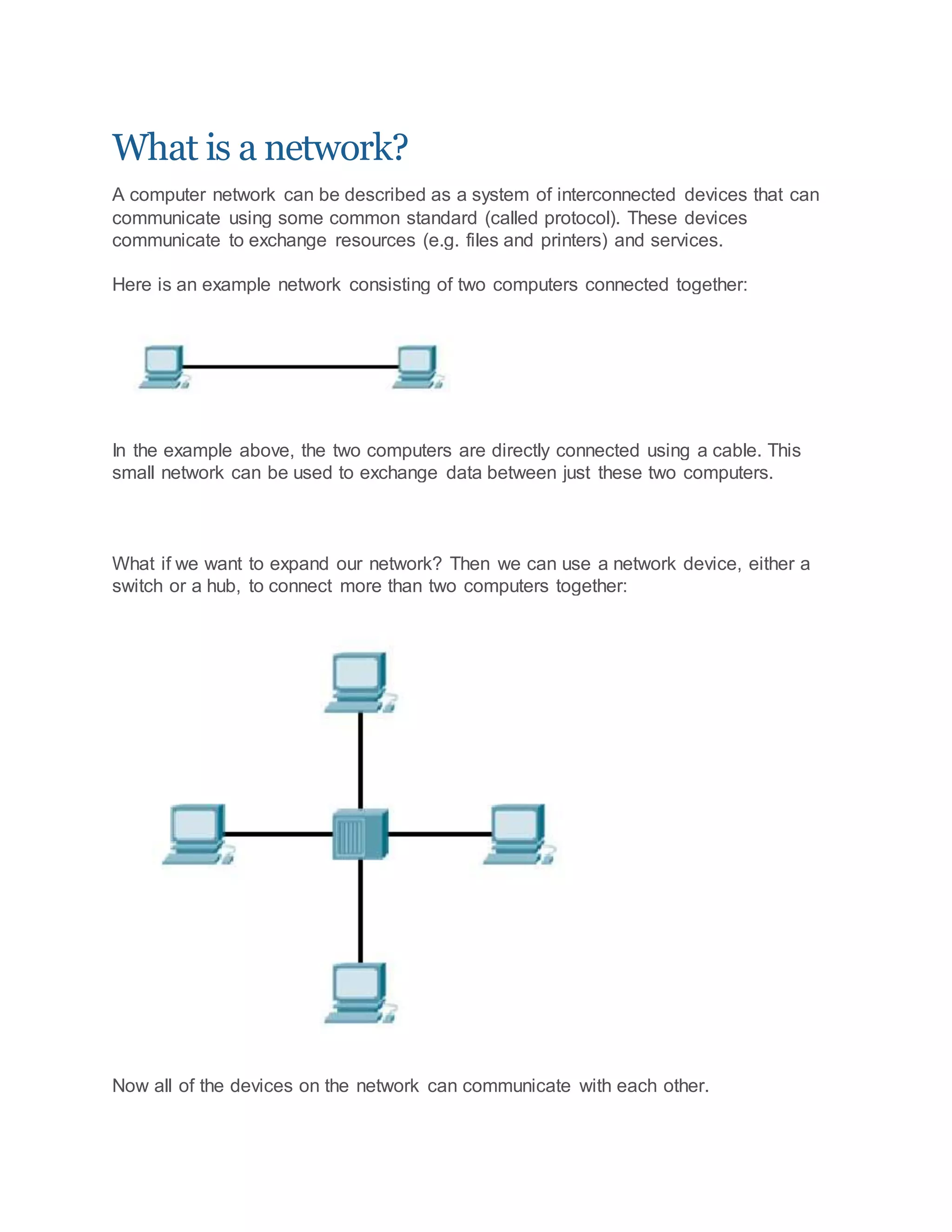
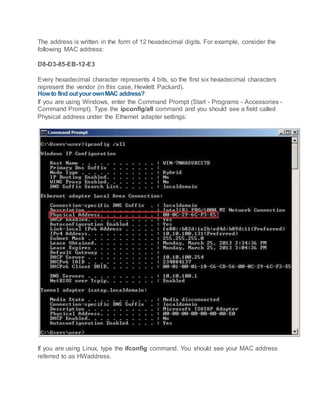
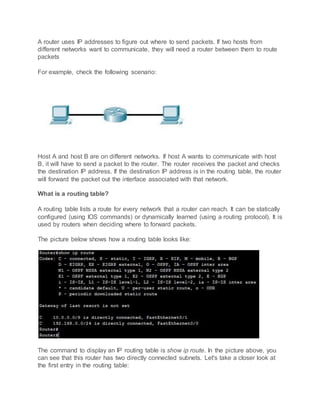
A computer network connects devices that can communicate using common standards. Devices exchange resources and services by communicating. Networks expand by connecting devices like switches or hubs, which serve as central points for computers to connect to. The OSI model describes network functions in 7 layers, while the TCP/IP model has 4 layers. Encapsulation is the process of adding headers and trailers to data as it passes through layers. Frames, packets, and segments refer to encapsulated data at different layers. Ethernet defines physical and data link standards, using MAC addresses to deliver frames. IP addresses identify devices, while private addresses are non-routable. Switches inspect traffic and make forwarding decisions for each port, unlike hubs which broadcast to all