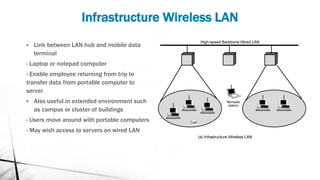
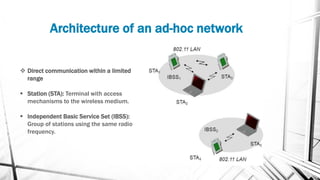
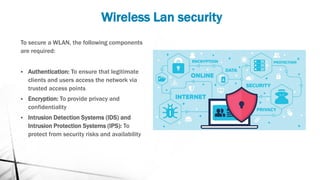
A Wireless LAN (WLAN) is a data transmission system that enables location-independent network access using radio waves instead of cables. Advantages include increased productivity, easy setup, flexibility, cost reduction, and scalability, making it suitable for various environments like enterprises, educational institutions, and temporary networks. Security measures for WLAN include authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard against unauthorized access and security risks.