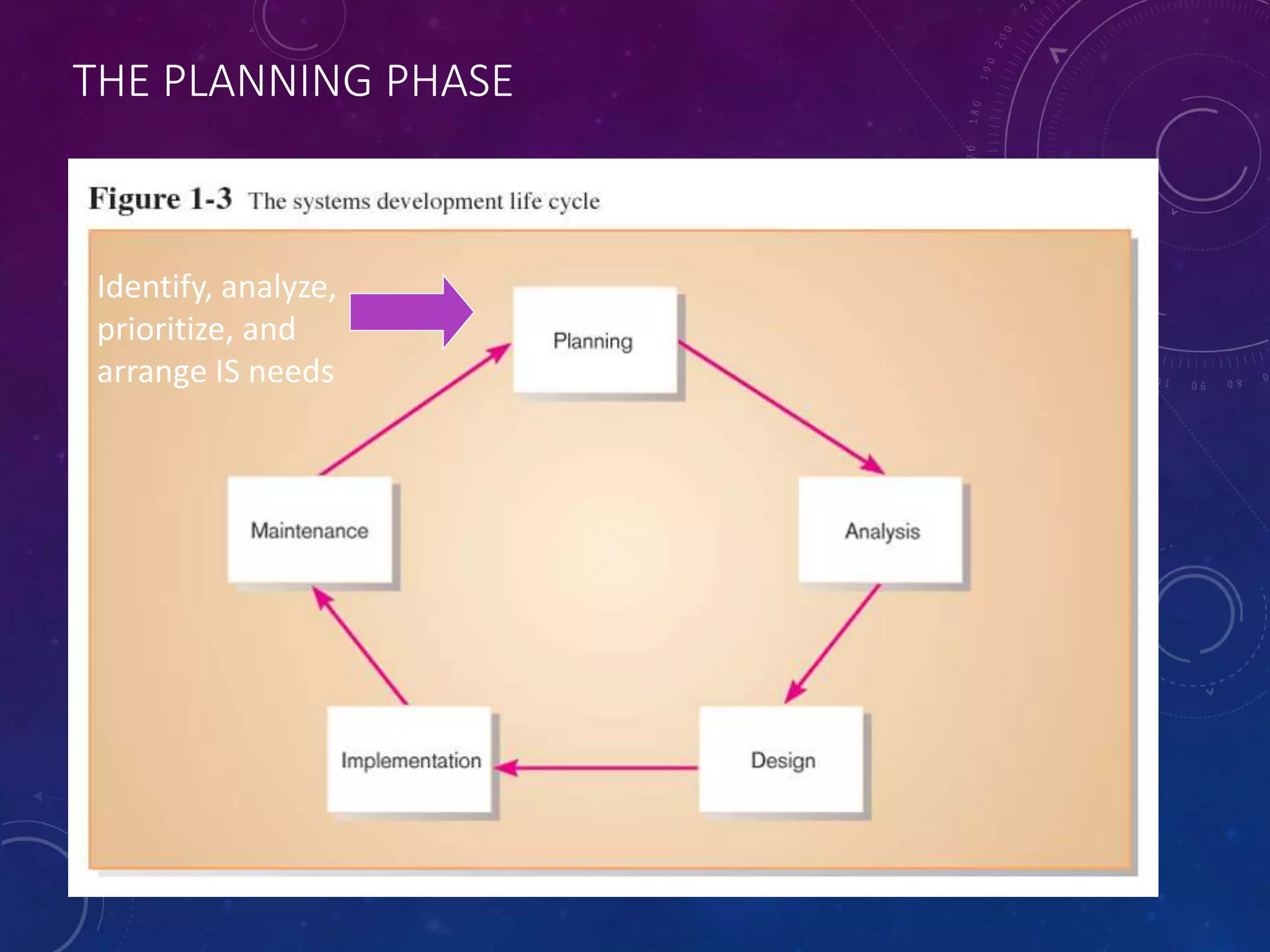
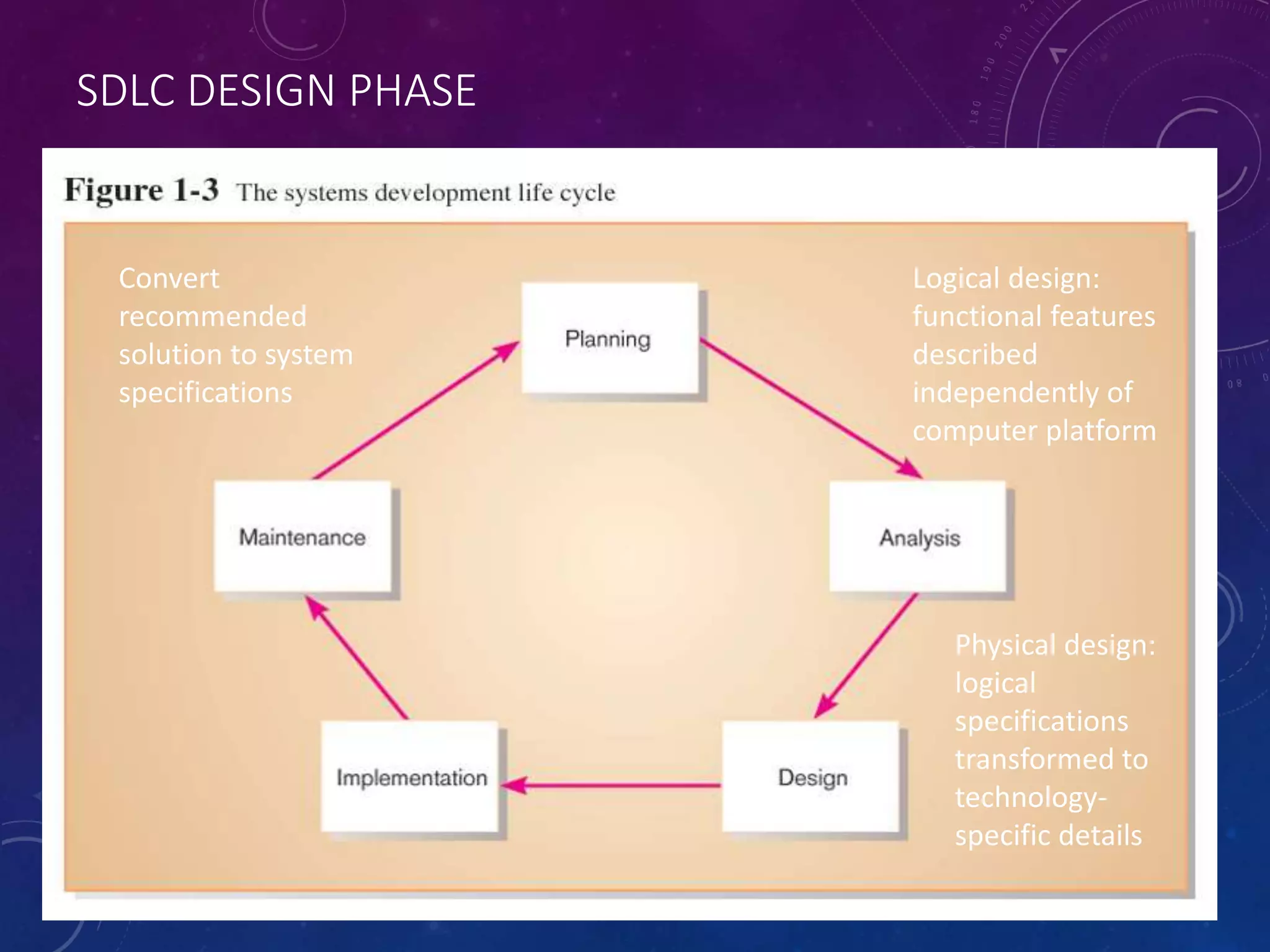
This document summarizes an analysis and design of an information system submitted by four students. It discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC) process, which includes planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance phases. In the analysis phase, key system functions are defined and the problem domain is understood. The design phase includes creating logical and physical designs using principles like abstraction, modularity, and refinement. Tools like data flow diagrams and data dictionaries are used to design the system.