Embed presentation
Downloaded 55 times





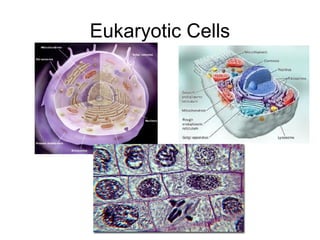


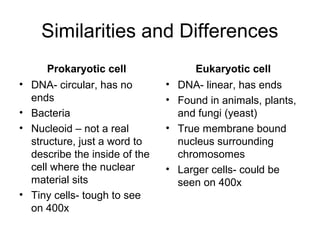


This document discusses the basic types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It provides definitions for the terms prokaryote and eukaryote based on their Greek roots and describes some key differences between the two types of cells. Specifically, it notes that prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus surrounded by a membrane and also contain membrane-bound organelles. The document encourages comparing and contrasting the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells using a double bubble map.









