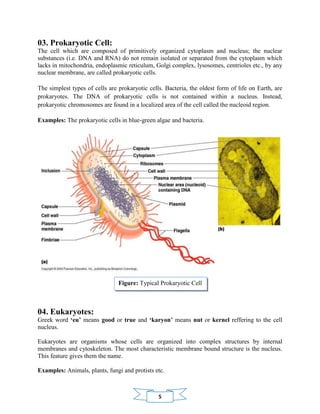
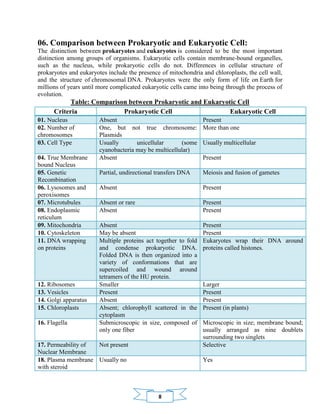
The document provides an overview of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including their definitions, structures, and key differences. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms without a nucleus, while eukaryotes are more complex and contain membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus. The text emphasizes the importance of understanding these cellular distinctions for studying genetics and microbiology.