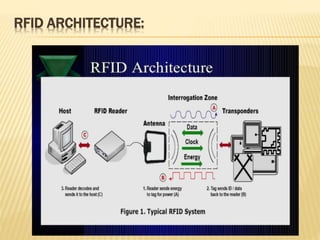
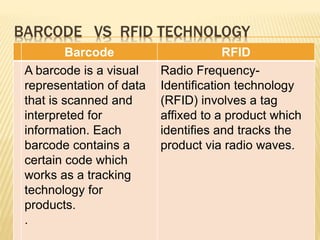
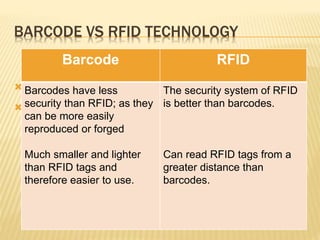
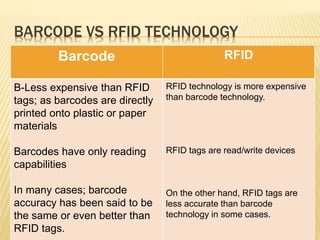
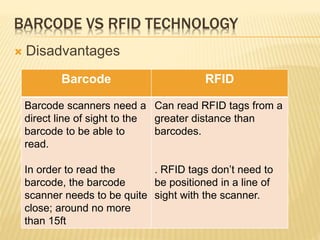
Barcode and RFID technology are identification tools. Barcodes use visual patterns that are scanned to represent data, while RFID uses radio waves to track tags attached to objects. RFID provides advantages like greater security, distance reading and updating capabilities compared to barcodes. However, RFID technology is generally more expensive than barcodes. Both technologies have various applications in areas like member identification, circulation, and stock verification in libraries.