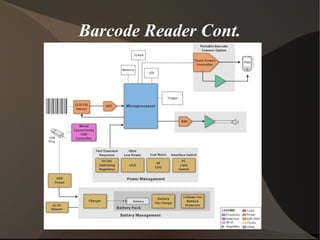
Barcodes represent alphanumeric information as patterns of black and white bars of varying widths. They were first used industrially in the 1960s and began appearing on grocery products in the 1970s. Barcodes automate processes like data entry by allowing information to be scanned rather than manually typed. There are two main types: linear barcodes like the UPC code and 2D barcodes. Barcodes are now widely used across industries like retail, warehousing, and healthcare to identify and track items.