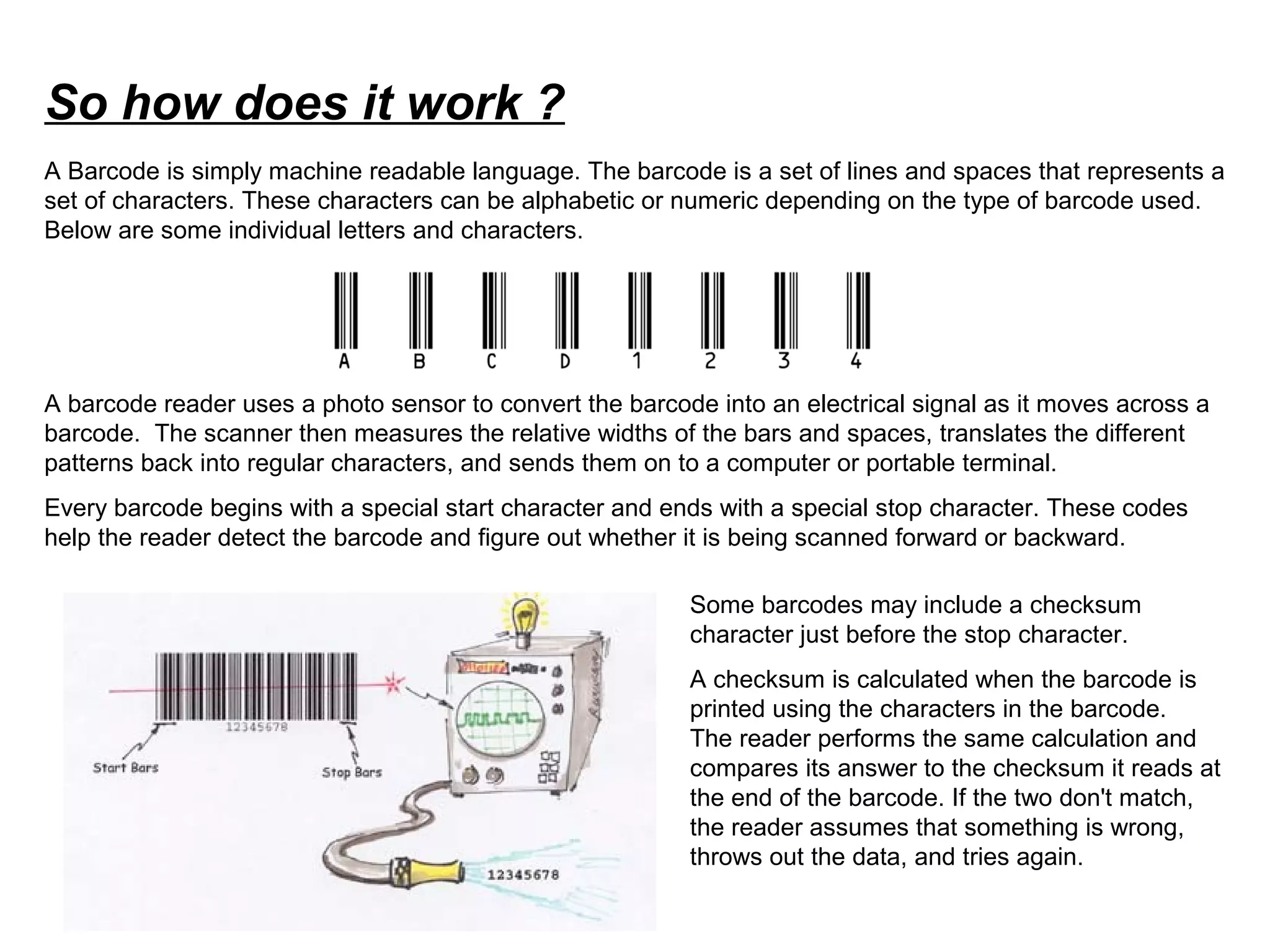
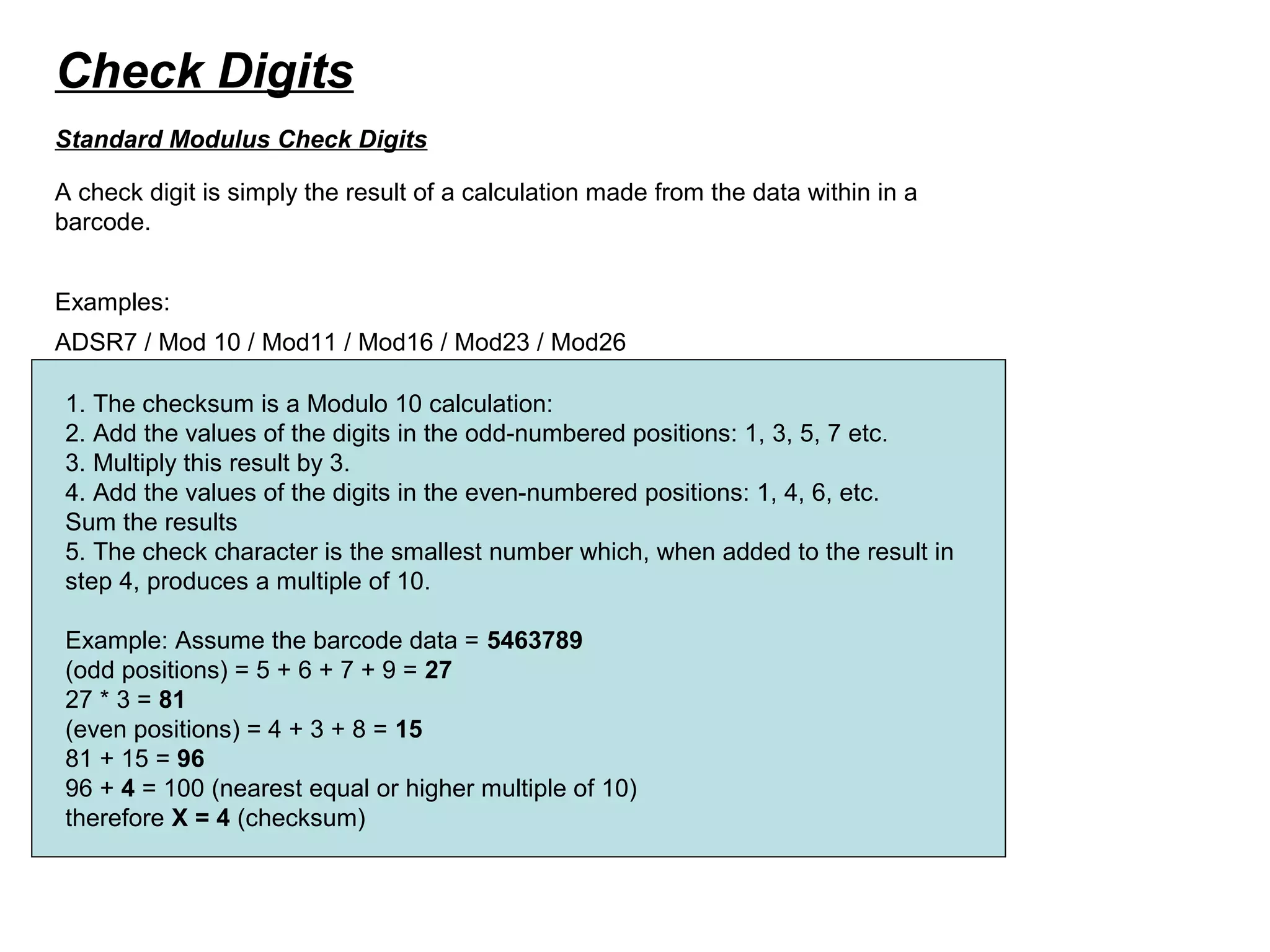
Mr. Woodland and Silver developed the barcode after being asked by a supermarket chain to find a better way to track inventory. Woodland drew lines of different thicknesses representing codes while visiting Miami in 1948, which led to the Universal Product Code barcode. A barcode uses a scanner to read patterns of bars and spaces that represent data about an object. It begins with a start character, ends with a stop character, and may include a checksum for error checking. Major barcode types include linear codes like UPC, Code 39, Code 128, and 2D codes like PDF417 and Data Matrix that can encode more data in less space.