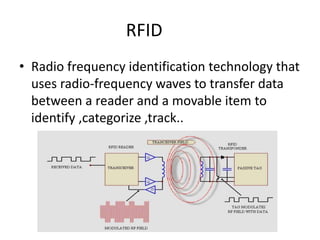
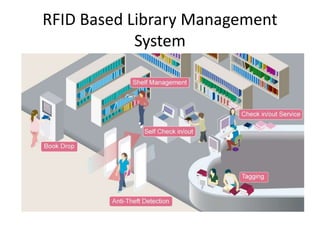
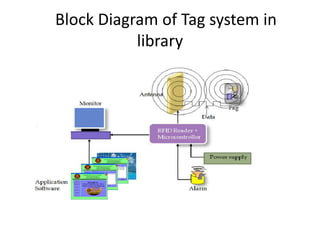
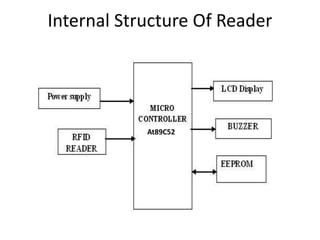
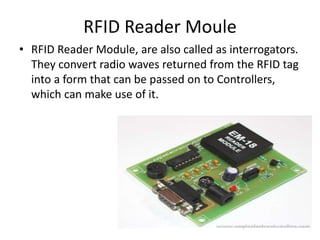
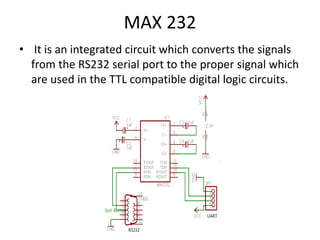
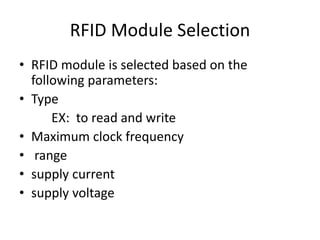
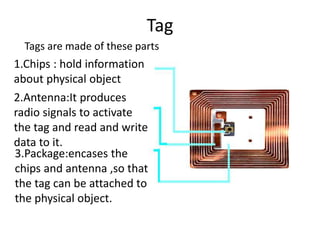
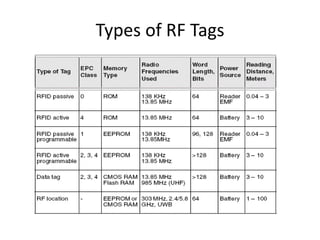
This document presents a project on an RFID-based library management system. It discusses using RFID technology to allow for fast and efficient book circulation, automatic check-in/out, and inventory tracking. The technical specifications and hardware components are described, including an RFID reader module, MAX232 chip, and At89c52 microcontroller. Different types of RFID tags are also outlined. The benefits of the system are improved services, security, and low cost automated operations. In conclusion, RFID technology is increasing in libraries and expected to improve efficiency and accuracy as prices decline.








![References:
• Karen coyle,”management of RFID in libraries”,preprint version
of article published in the journal of academic
librarianship.v.31.5.pp.486-489
• K.Finkenzeller, RFID handbook 3rd ed.,wiley 2010
• K.Fujisaki “the implementation of RFID technology in the
library and electromagnetic compatibility“ [in
japanese],monthly EMC,183,86-94.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid01lmsystem12-171020172032/85/RFID-Based-Library-Management-System-18-320.jpg)