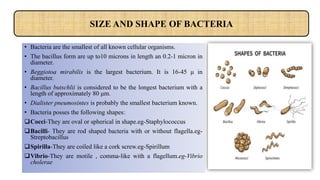
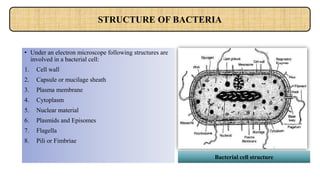
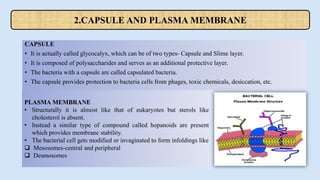
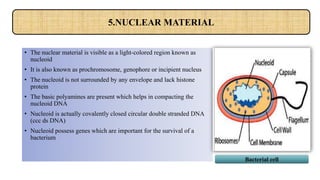
Bacterial cells have a simple structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They lack membrane-bound organelles and have no nucleus, instead containing a nucleoid of circular DNA. The cell structure includes a cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and sometimes a capsule. Bacteria can be rod-shaped, spherical, or spiral and range in size from 0.2 to 80 micrometers. They reproduce through binary fission and some can move using flagella or pili. Bacteria have many applications including in medicine, sewage treatment, energy production, and fermentation industries.