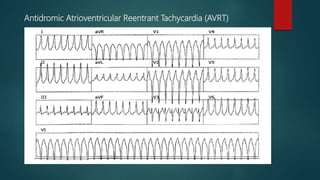
1) Antidromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) occurs in less than 10% of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and can be difficult to distinguish from ventricular tachycardia on ECG.
2) Electrophysiological testing is often required to make the distinction, looking at features such as the His-ventricular interval, the effect of atrial and ventricular pacing on the tachycardia, and the response to pharmacological interventions.
3) Diagnostic maneuvers like atrial extrastimulation that advances ventricular activation or termination of the tachycardia with ventricular pacing support the diagnosis of antidromic AVRT rather than ventricular tachycard

























![HIS BUNDLE–VENTRICULAR INTERVAL
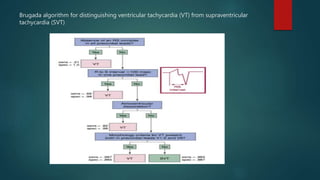
When the His bundle–ventricular (HV) interval is positive (i.e.,the His potential precedes the QRS
onset), an HV interval during the WCT shorter than that during NSR (HVWCT < HVNSR) indicates
VT or preexcited SVT. In contrast, an HVWCT equal to or longer than HVNSR indicates SVT with
aberrancy, BBR VT.
When the HV interval is negative (i.e., the His potential follows the QRS onset), BBR VT and SVT
with aberrancy are excluded. However, myocardial VTs and preexcited SVT generally have negative
HV intervals.
Prolongation of the VA (and VH) interval and tachycardia cycle length (CL) with transient RBBB
(caused by catheter- induced trauma or introduction of a ventricular extrastimulus [VES]) is
diagnostic of antidromic AVRT using a right-sided.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avrtvzvt-161103150658/85/Avrt-vz-vt-28-320.jpg)





