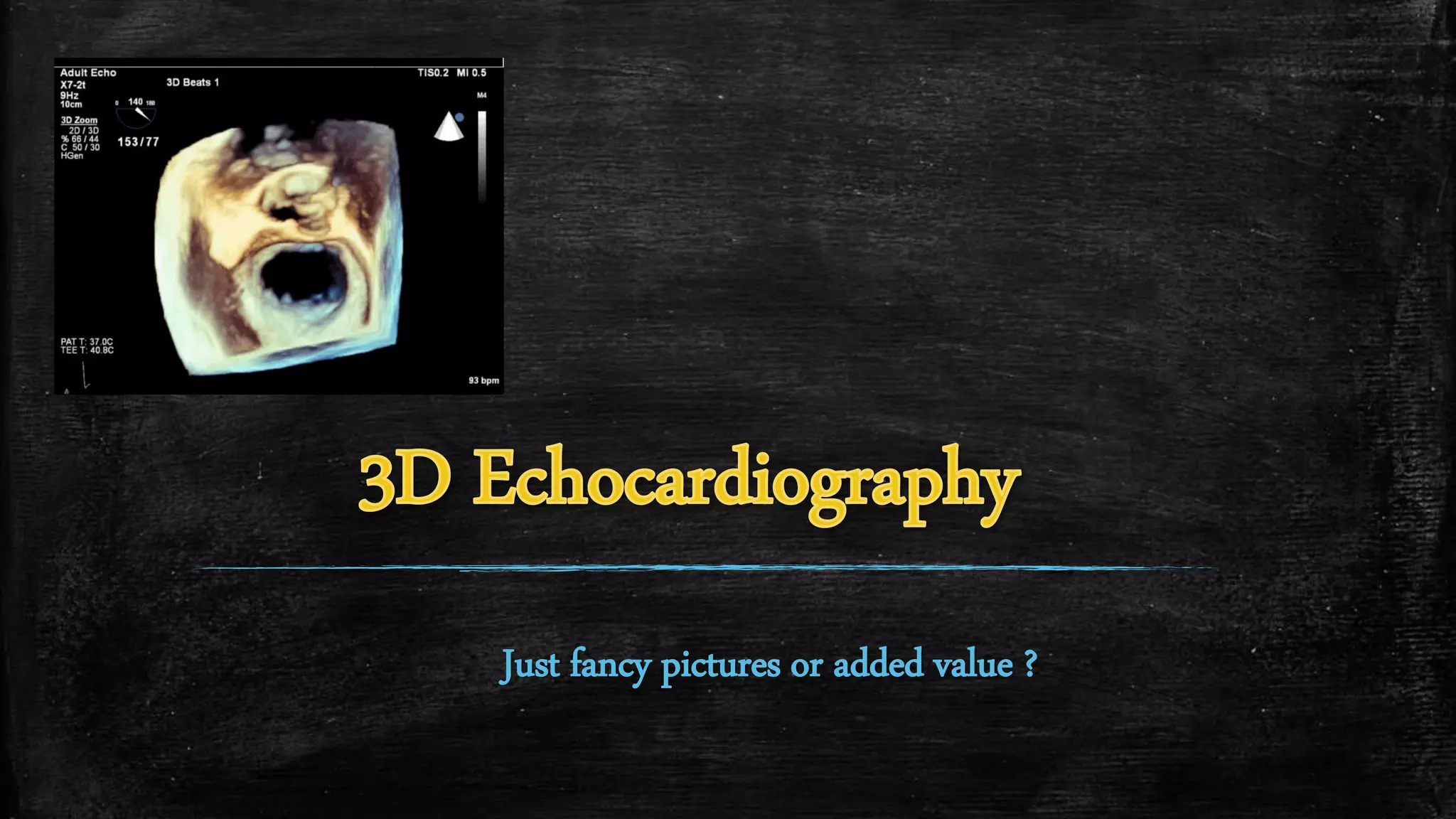
3D echocardiography provides several advantages over 2D echocardiography including showing the real-time 3D structure of the heart, easier demonstration of anatomy, and more accurate volumetric measurements without relying on geometric assumptions. Modern 3D transducers contain thousands of piezoelectric elements. Different acquisition modes such as live 3D, full volume, and 3D color Doppler allow visualization of cardiac structures from different angles in real-time or through offline analysis. While 3D echocardiography provides valuable clinical information, limitations include artifacts from arrhythmias and breathing, lower spatial and temporal resolution compared to 2D, and more complex data analysis.