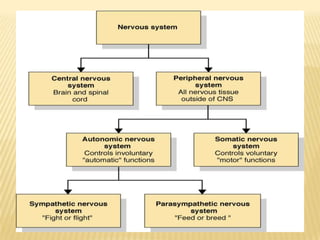
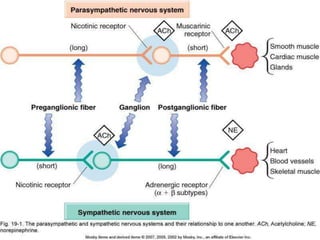
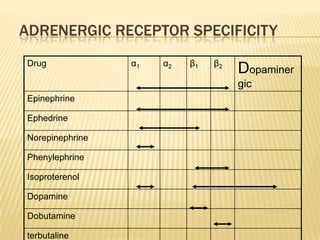
The document discusses drugs that act on the autonomic nervous system, including:
- Adrenergic drugs that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system by mimicking norepinephrine and epinephrine. This includes both catecholamines and non-catecholamines.
- Adrenergic blockers that block the actions of norepinephrine and epinephrine at adrenergic receptor sites. This includes both alpha-blockers and beta-blockers.
- Cholinergic drugs that stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system by mimicking acetylcholine, and anticholinergic drugs that block acetylcholine's actions. Cholinergic drugs can be direct-acting or indirect-