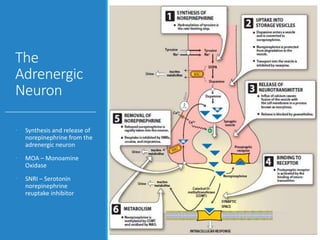
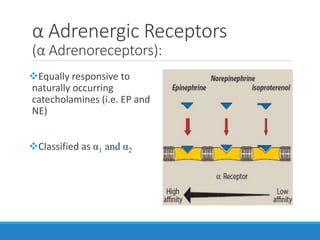
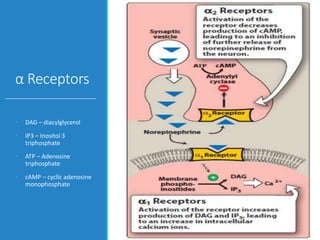
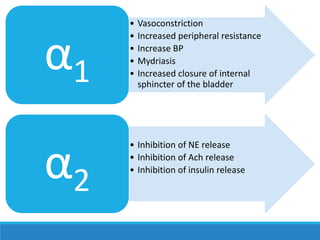
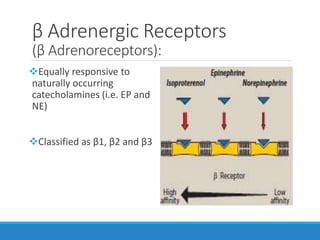
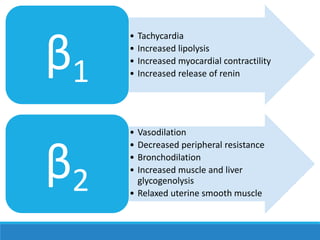
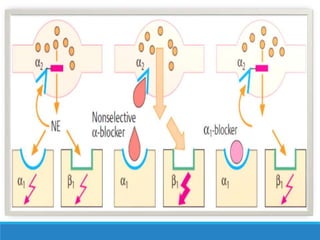
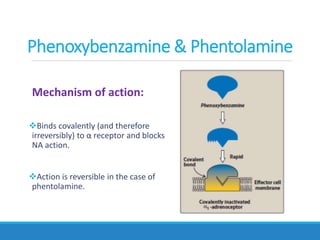
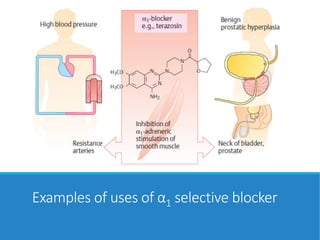
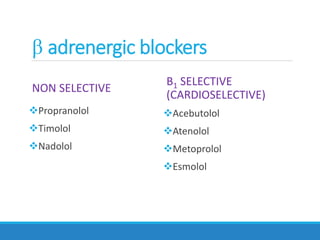
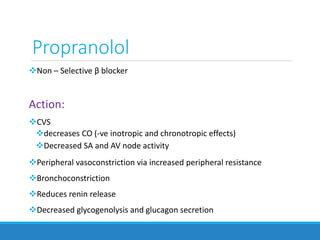
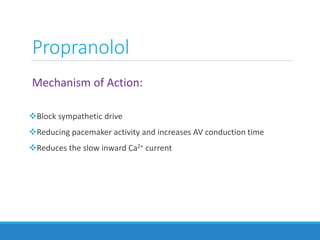
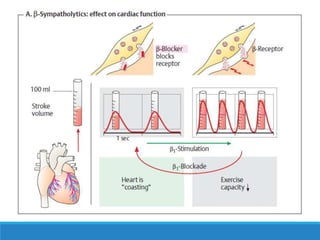
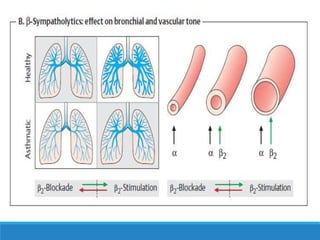
This document discusses antiadrenergic drugs, including their mechanisms of action and effects. It describes α and β adrenergic receptors, and different types of α and β receptor blockers. α blockers such as prazosin, terazosin, and doxazosin are selective for α1 receptors, causing vasodilation. Non-selective α blockers like phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine block both α1 and α2 receptors. β blockers include non-selective drugs like propranolol and timolol, as well as cardioselective drugs such as atenolol and metoprolol that mainly block β1 receptors. These drugs are used to treat hypertension, an