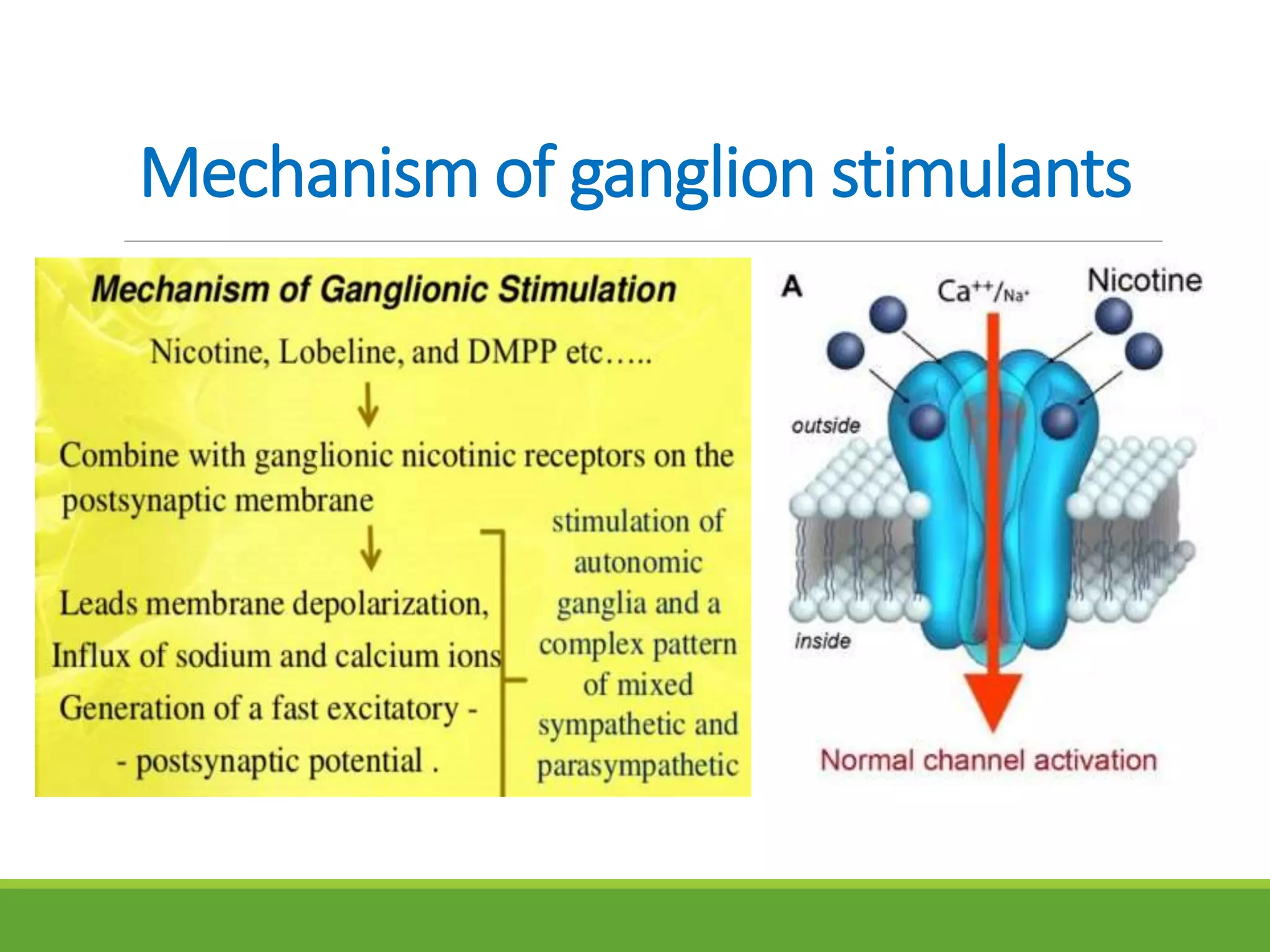
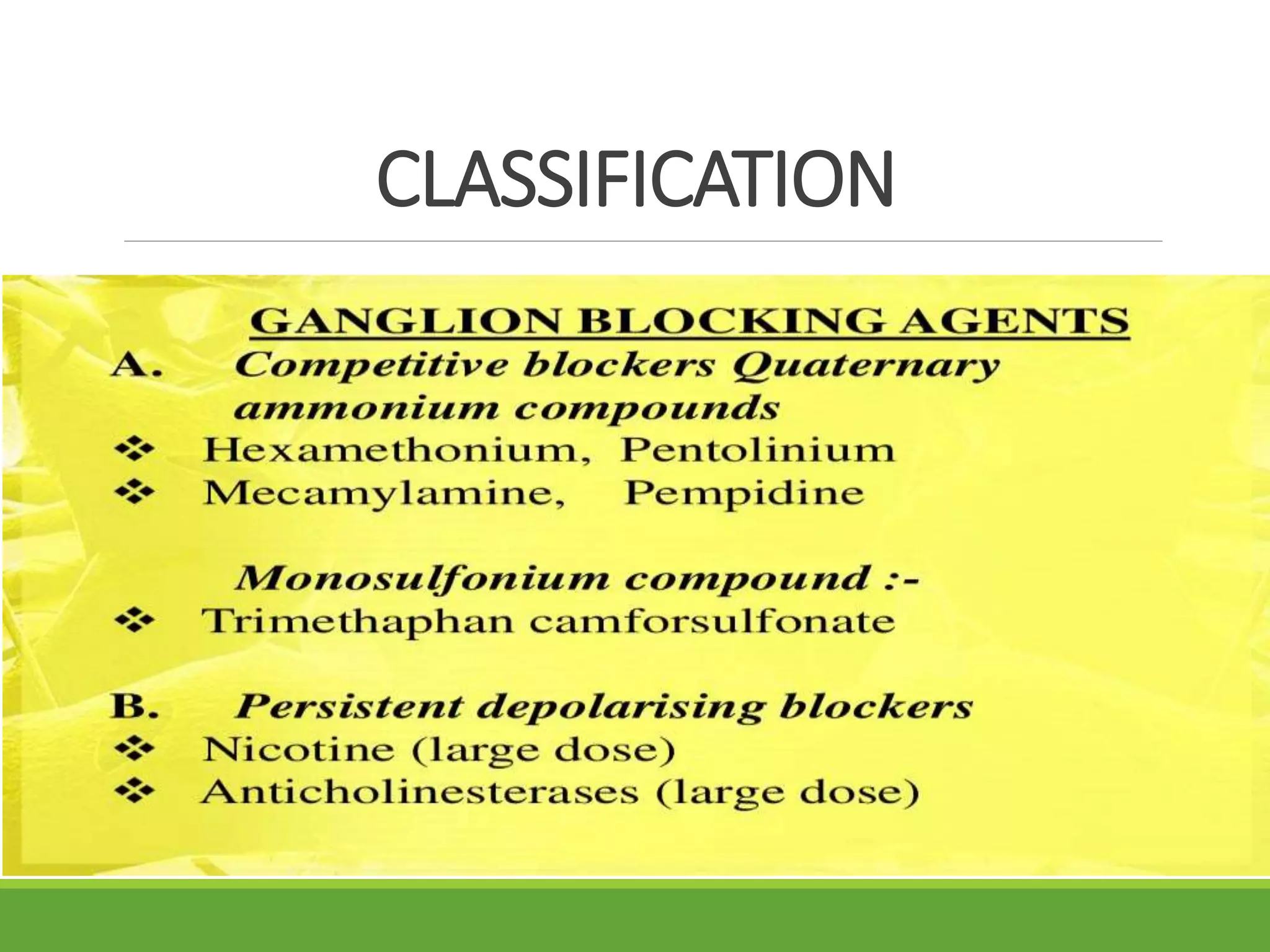
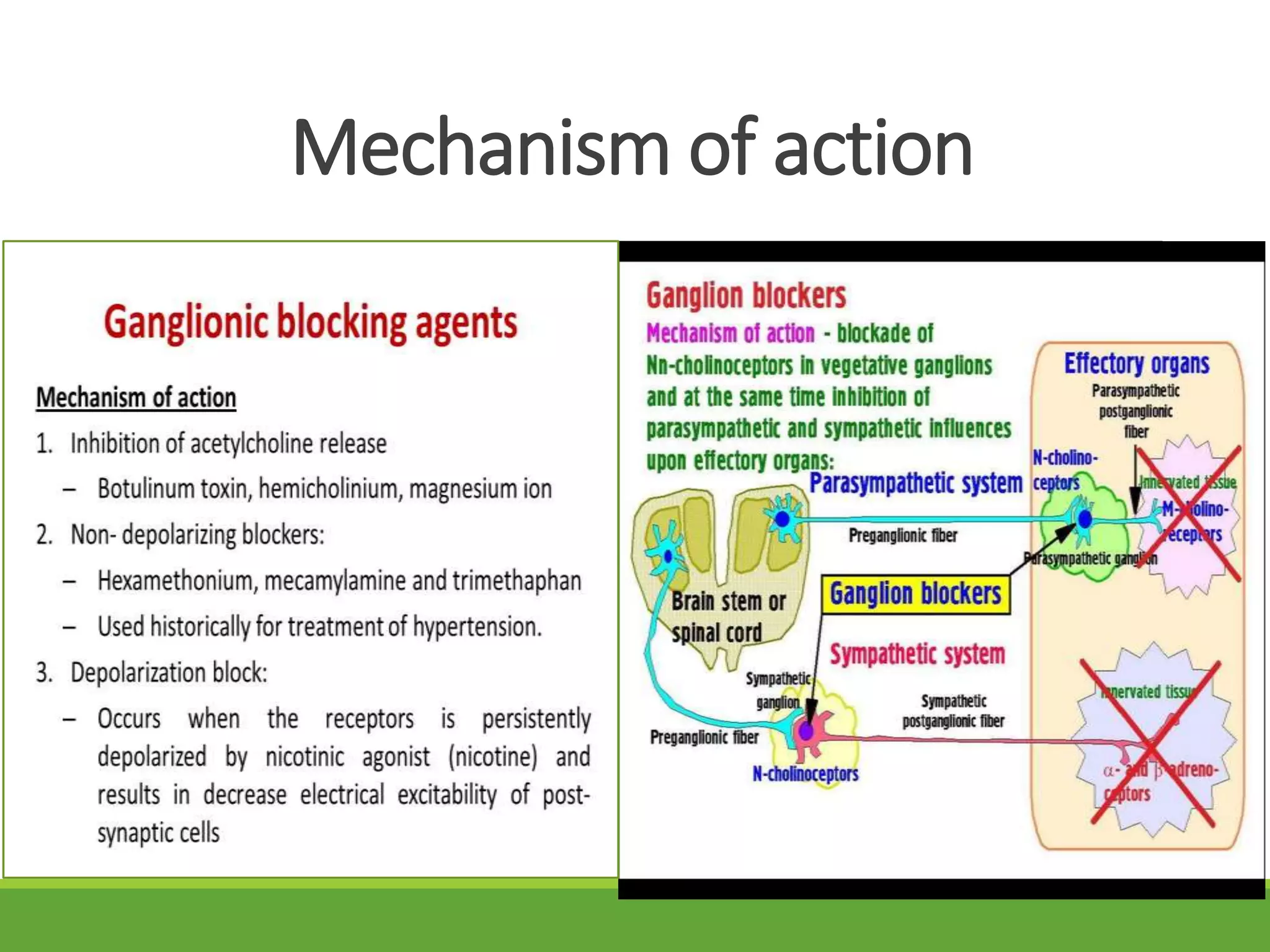
This document summarizes a presentation about ganglions and ganglion stimulants and blockers. It defines a ganglion as a cluster of nerve cell bodies in the autonomic nervous system. It describes how ganglion stimulants like nicotine activate nicotinic receptors on postganglionic neurons. These stimulants are used to help people quit smoking by reducing nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Ganglion blockers inhibit transmission between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons by antagonizing nicotinic receptors. They were previously used to treat hypertension but caused intolerable side effects. The document outlines the mechanisms, effects, uses and side effects of both ganglion stimulants and blockers