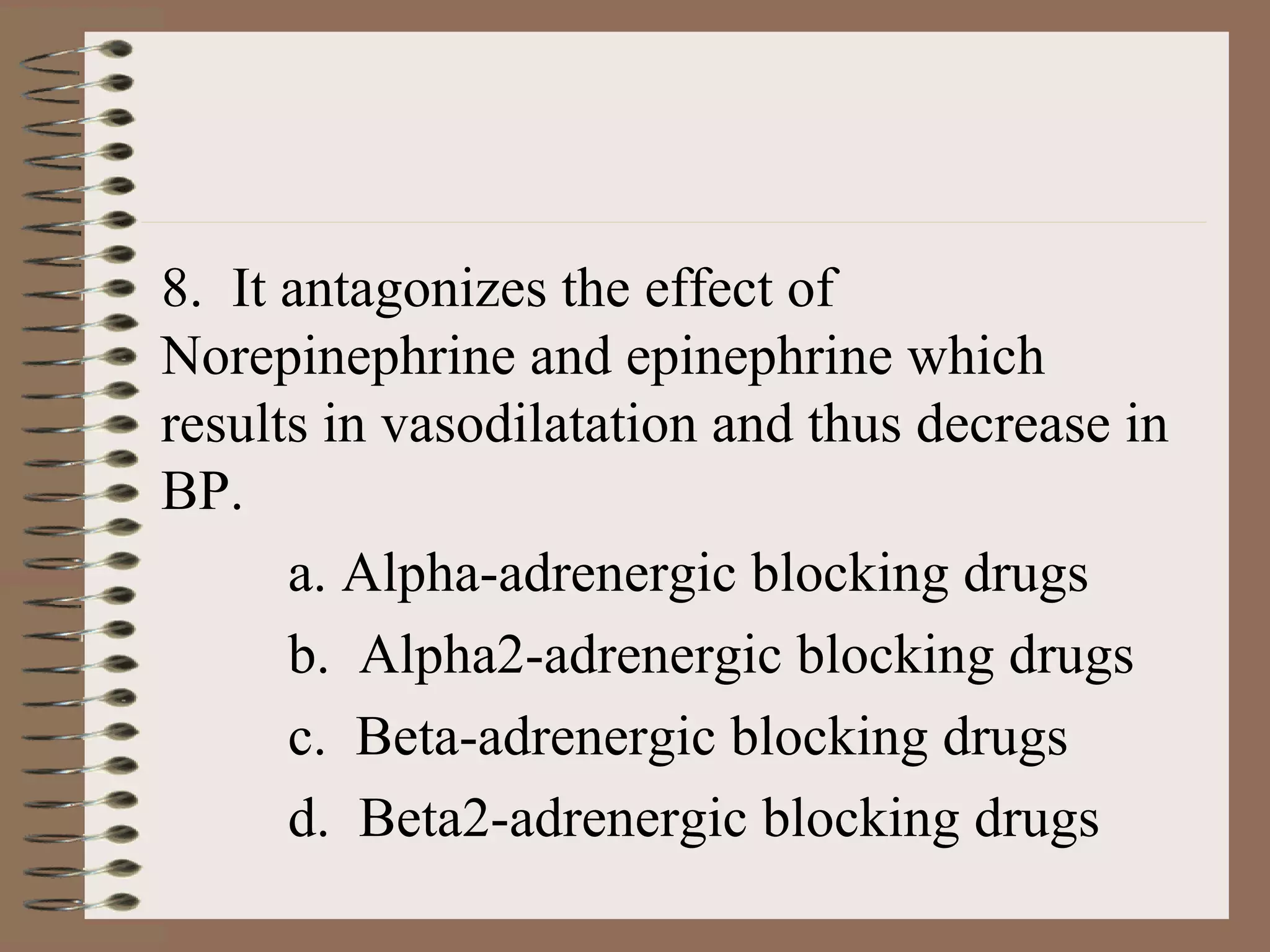
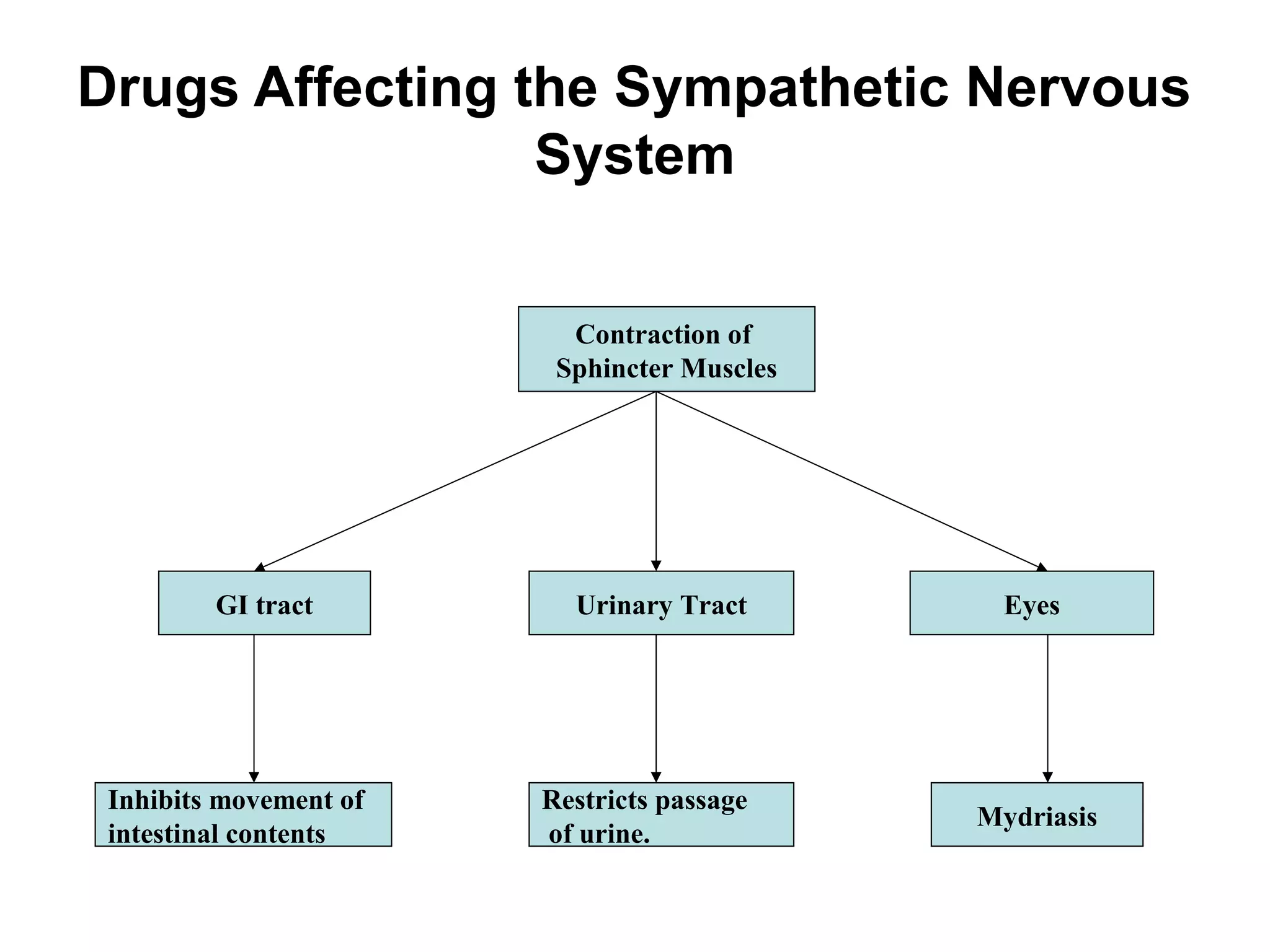
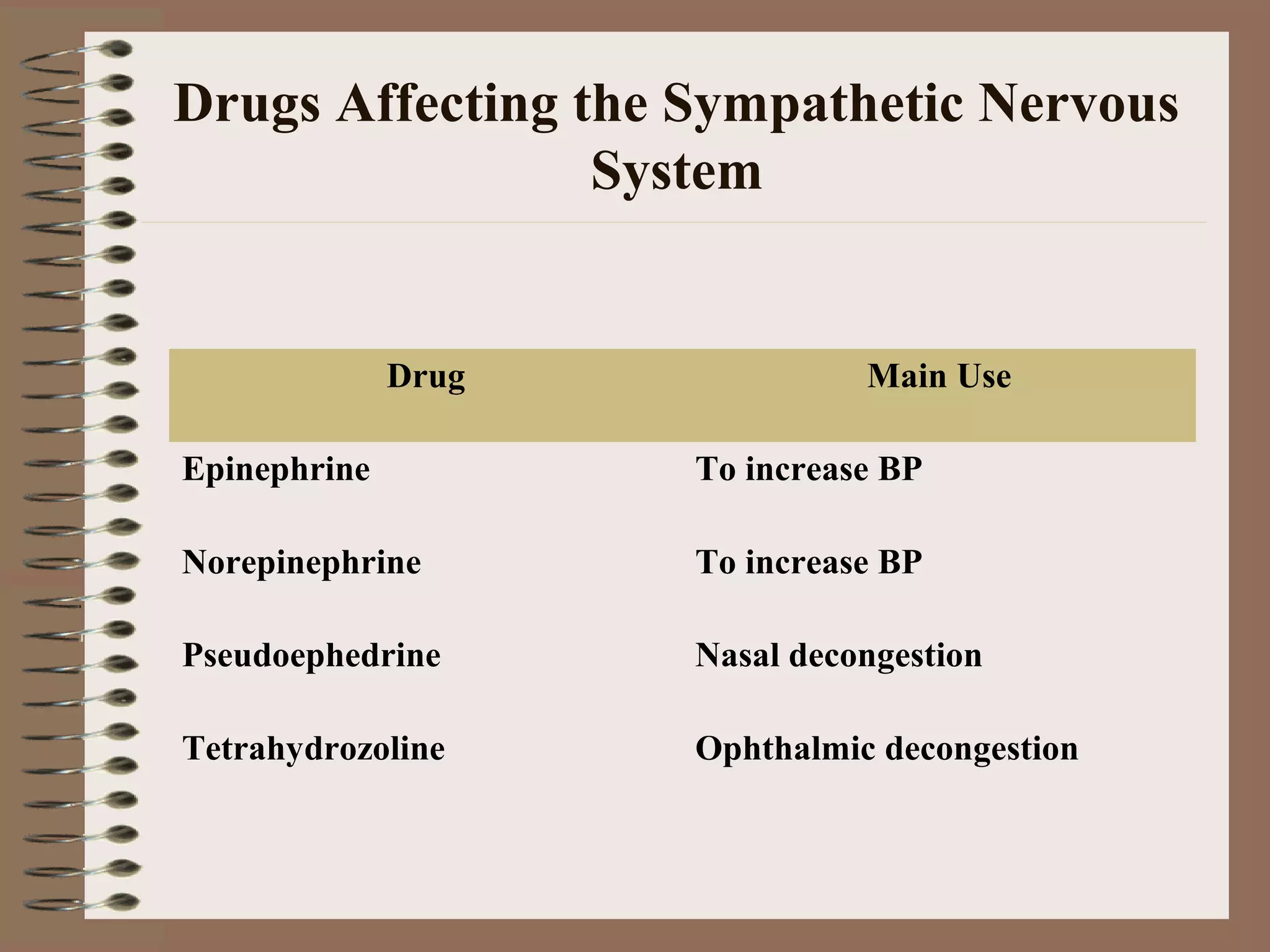
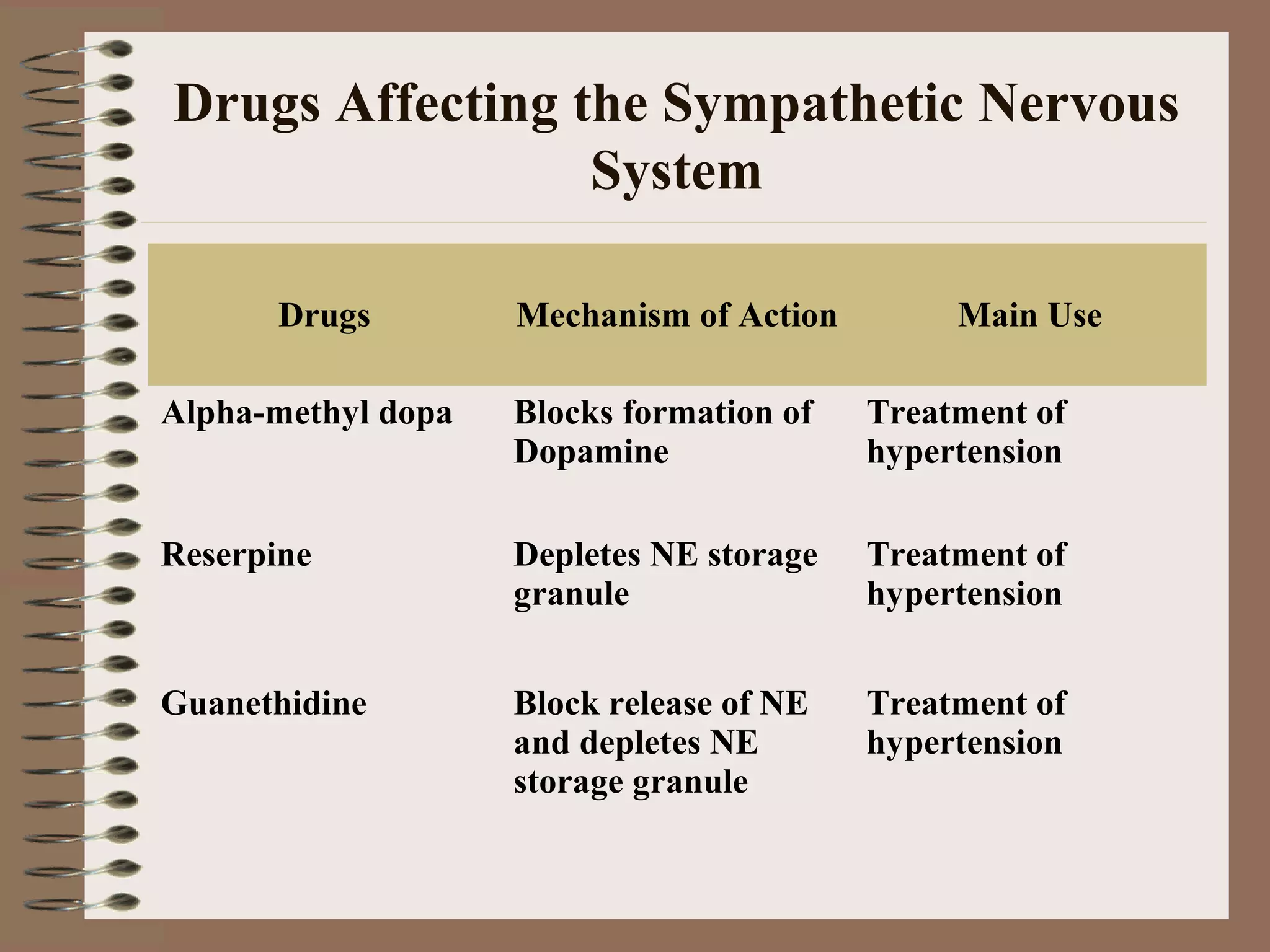
The document discusses drugs that affect the autonomic nervous system, specifically the sympathetic nervous system. It describes how drugs can stimulate or block receptors in the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathomimetic drugs like epinephrine stimulate receptors to increase heart rate, blood pressure, and bronchodilation. Sympatholytic drugs like alpha-adrenergic blockers antagonize norepinephrine and epinephrine, resulting in vasodilation and lower blood pressure. The document provides examples of drugs that target different receptors and their clinical uses for conditions like hypertension and asthma.