This document describes an automated waste segregator system that uses sensors and mechanical arms to sort household waste into three categories: metal waste, dry waste, and wet waste. An Arduino microcontroller is used to control the sensors and mechanical components. Infrared sensors detect the presence of waste, inductive proximity sensors identify metal waste, and moisture sensors distinguish wet waste. Small DC motors and servo motors move the waste into the appropriate collection bins. The system was tested and achieved high accuracy in sorting metal waste, with room for improvement in sorting dry and wet waste. The automated waste sorting system provides an efficient solution for household waste management.


![ISSN (Print): 2456-6411 | ISSN (Online): 2456-6403 47 JREAS, Vol. 06, Issue 01, Jan 2021
Figure 3. Types of waste
4. Conclusion
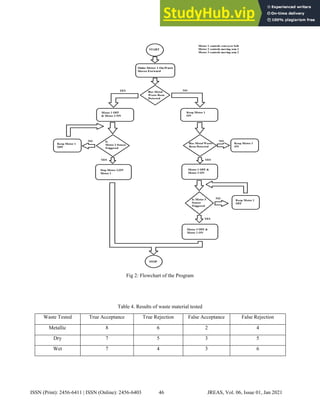
In this paper, the development of a low-
cost automated waste separator powered by Arduino
micro-controller is presented to effectively sort waste
according to its base at the household or small society
level. During the development process, the waste
separator prototype control system and sensing
mechanism are integrated using an Arduino Uno micro-
controller. The sensing part is built to distinguish
among three types of waste: 1) metallic waste, 2) dry
waste and 3) wet waste. The metallic waste utilized the
inductive proximity sensor in relation to the magnetic
field concept. However dry and wet waste used
moisture sensors to verify electrical conductivity. The
prototype of the waste separator possessed high
sensitivity on metallic waste in comparison to other
waste. This means that dry and wet waste sensitivity
needs to be improved for effective sorting. The
proposed concept and developed prototype have the
potential to be utilized in reducing the cost of solid
waste disposal in the future.
References
[1] M. K. Pushpa, Aayushi Gupta, Shariq Mohammed
Shaikh, Stuti Jha,Suchitra.V, “Microcontroller
Based Automatic Waste Segregator”,International
journal of innovative research in Electrical,
Electronics, Instrumentation and Control
Engineering Vol. 3, issue 5, May 2015.
[2] Amrutha Chandramohan, Joyal Mendonca, Nikhil
Ravi Shankar, Nikhil U Baheti, Nitin Kumar
Krishnan, Suma M S, Rashtreeya Vidyalaya
College of Engineering (R.V.C.E.) “Automated
Waste Segregator
[3] Abhay Bharadwaj, Rainer Rego, Anirban
Chowdhary, “IOT based solid waste management
system”, IEEE Annual India Conference
(INDICON), 2016.
[4] P. Ash, Bist, A., and Chandran.S, S., “Moving
towards Zero-Waste: A
Case-Study from Kerala, India”, IEEE Global
Humanitarian Technology,Conference,SouthAsia
Satellite Conference, Trivandrum, India, 2013.
[5] Subhasini Dwivedi, Michael Fernandes, Rohit
Dsouza, A Review on PLC based Automatic Waste
Segregator, International Journal of Advanced Re-
search in Computer Engineering and Technology
(IJARCET) Volume 5 Issue 2, February 2016
[6] Fachmin Folianto, Yong Low, Wai Yeow,
"Smartbin smart waste management system", IEEE
International Conference on Intelligent Sensors
Sensors Network and Information Processing
(ISSNIP), 2015J.
[7] Clerk Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and
Magnetism, 3rd ed., vol. 2. Oxford: Clarendon,
1892, pp.68–73.
[8] S. Sakai, S. Sawell, A. Chandler, "World Trend in
Municipal Solid Waste Management" in
Environmental Preservation Center, Japan, vol. 16,
pp. 341, 1996.
[9] "Smart Garbage Monitoring and Clearance System
using Internet of Things", 2017 IEEE International
Conference on Smart Technologies and
Management for Computing Communication
Controls Energy and Materials (ICSTM), 2 – 4
August 2017.
[10] Mahmudul Hasan Russel, Mehdi Hasan
Chowdhury, Md. Shekh Nairn Uddin, Ashif
Newaz, Md. Mehdi Masud Talukder,
"Development of Automatic Smart Waste Sorter
Machine", International Conference on Mechanical
Industrial and Materials Engineering 2013
(ICMIME2013), 1–3 November, 2013.
METALLIC WASTE
True Accepatnce
True Rejection
False Acceptance
False Rejection
DRY WASTE
True Acceptance
True Rejection
False Acceptance
False Rejection
WET WASTE
True Acceptance
True Rejection
False Acceptance
False Rejection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/automatedwastesegregator-230806144012-8ea47e29/85/AUTOMATED-WASTE-SEGREGATOR-5-320.jpg)