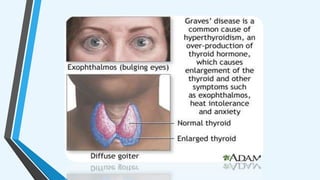
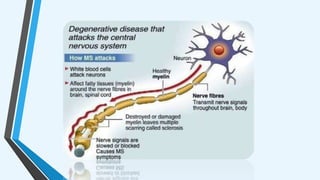
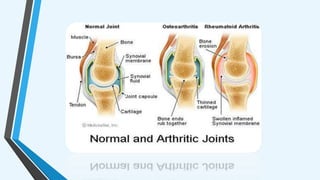
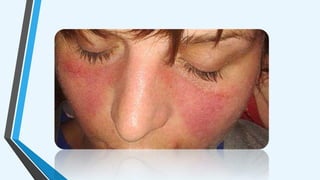
The document outlines various autoimmune diseases, including Addison's disease, Graves' disease, Hashimoto's disease, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, pernicious anemia, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Each condition is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own cells or tissues, leading to various symptoms and health complications. The document highlights the causes and specific immune responses associated with these diseases.