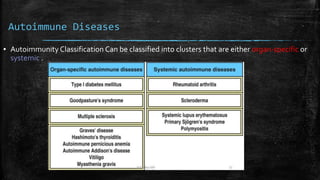
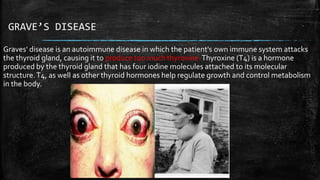
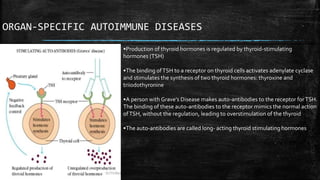
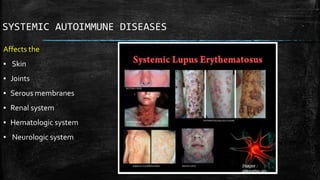
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages healthy body tissues. There are two main types - organ-specific diseases like Graves' disease which target a single organ, and systemic diseases like lupus that affect multiple body systems. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin rashes. While causes are unclear, genetics and environmental factors likely play a role. Treatment focuses on reducing immune system activity through medications like steroids, methotrexate, or targeted biologic therapies.