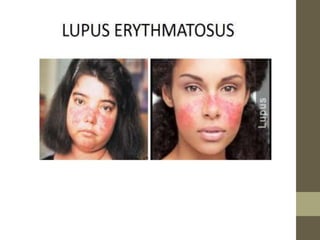
This document provides information on autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. It explains that autoimmunity occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own cells, causing diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis specifically causes joint inflammation and damage through autoantibodies attacking joint linings. Systemic lupus erythematosus more broadly attacks tissues, producing symptoms like rashes, fever, and kidney issues. Both have no cure but can be treated to reduce immune response and manage symptoms.