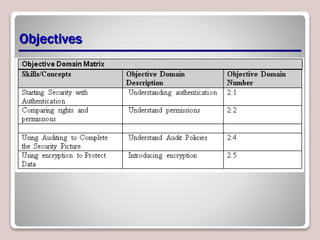
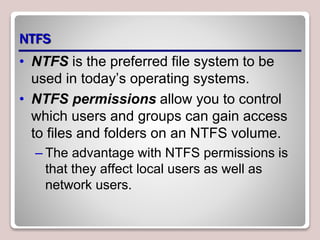
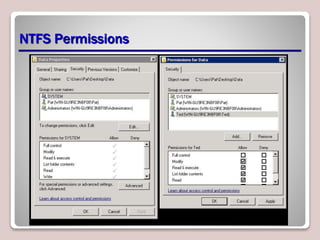
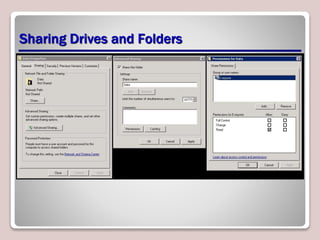
The document discusses authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) as a model for access control. Authentication verifies a user's identity, usually with a username and password. Authorization determines the resources and actions a user can access. Accounting tracks user activity for auditing purposes. Nonrepudiation prevents users from denying actions. Common authentication methods include passwords, smart cards, and biometrics. Technologies like Active Directory, RADIUS, and Kerberos are used to centrally manage AAA. Permissions and access control lists determine what access users have to files, folders, and other objects. Encryption and digital certificates enhance security.