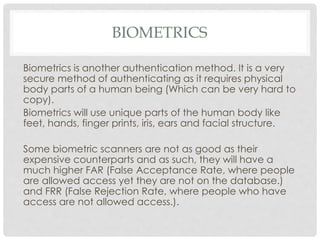
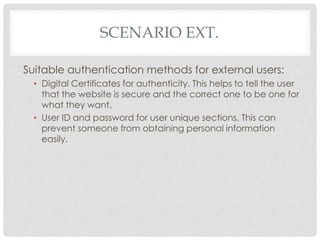
The document discusses various policies, procedures, and security measures that can be implemented to minimize security breaches in a network. It recommends establishing policies regarding data storage and access, backups, antivirus software, and user access privileges. It also stresses the importance of user training, physical security of network infrastructure, risk assessments, strong identification/authentication methods like two-factor authentication, and use of encryption and digital certificates. Authentication for internal users could include ID/password, physical access cards, and authentication devices, while external users benefit from digital certificates and unique ID/password combinations.