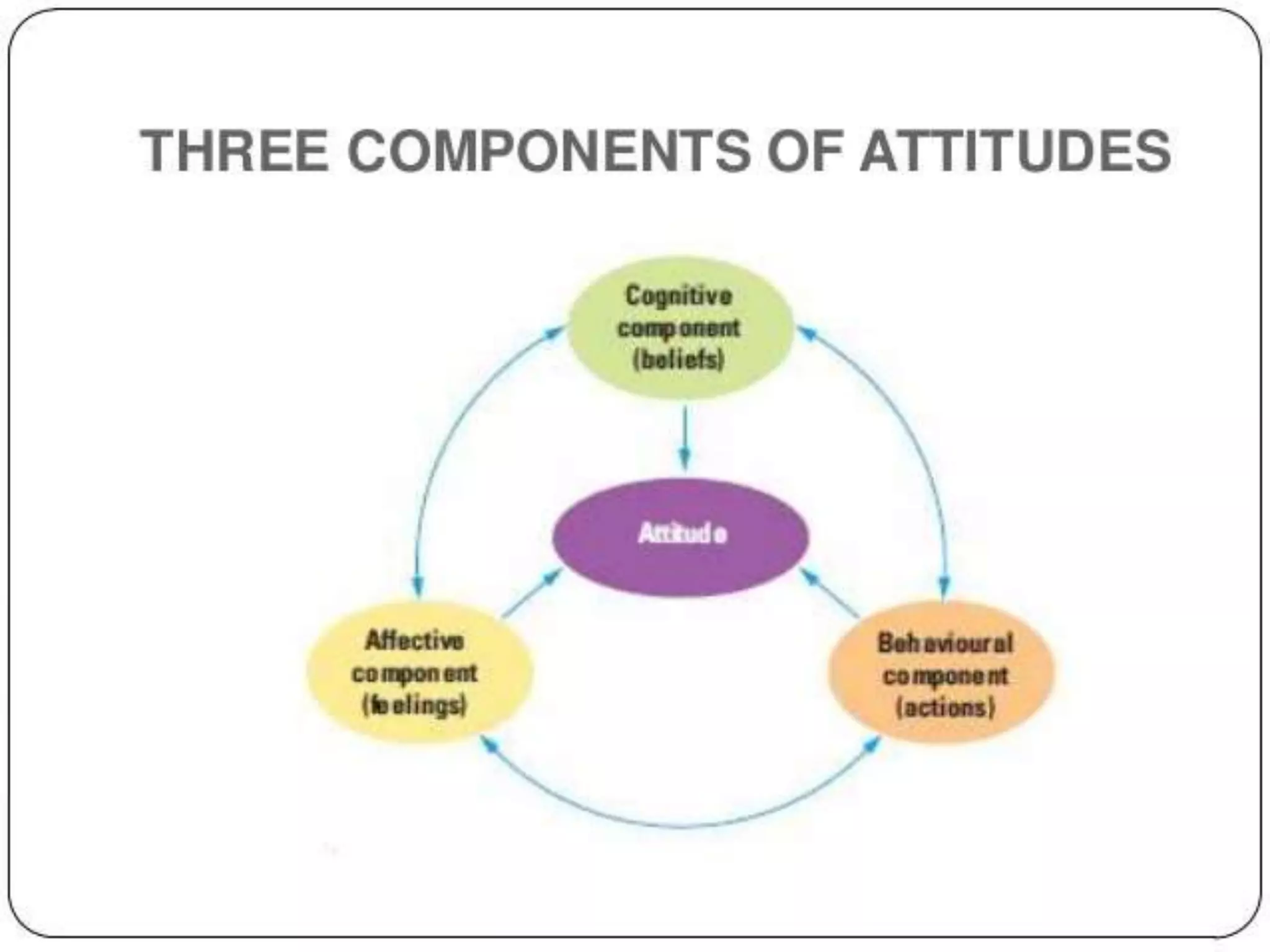
This document discusses attitudes and their components. It defines an attitude as having three components: affective (feelings about an object), behavioral (how the attitude influences behavior), and cognitive (beliefs about an object). It notes that attitudes strongly influence social thought by helping organize and evaluate stimuli, and that attitudes presumably have a strong effect on behavior by helping to predict behavior in different contexts. The document also discusses motivation, defining it as an inner drive to do something and persevere. It notes there are two types of motivation: intrinsic, coming from within, and extrinsic, coming from external rewards or punishments.