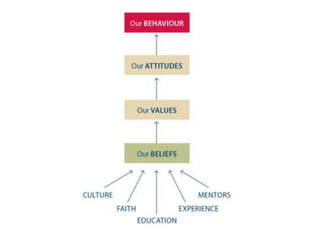
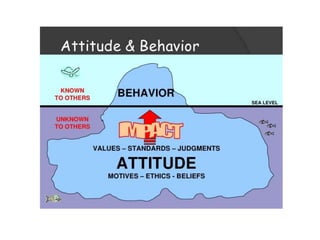
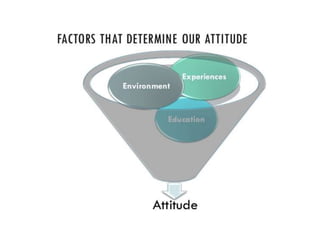
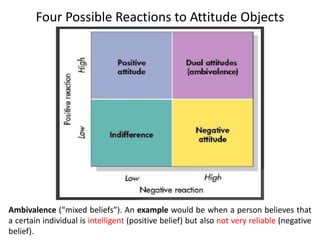
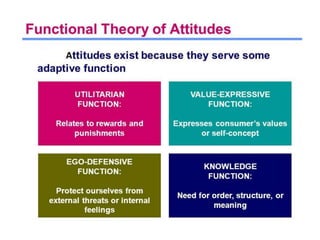
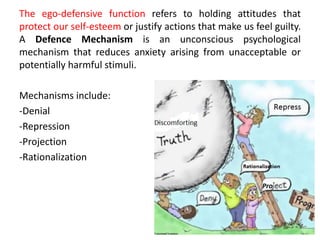
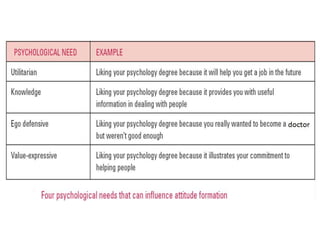
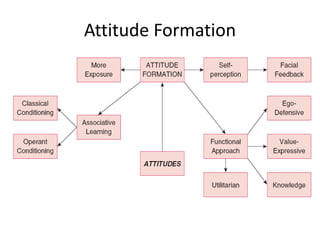
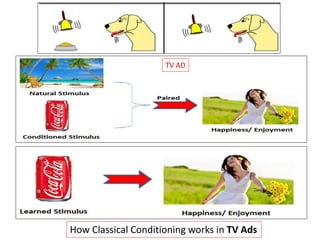
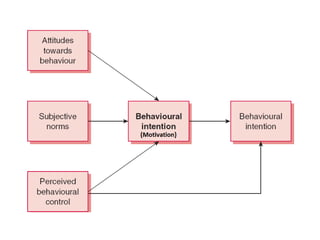
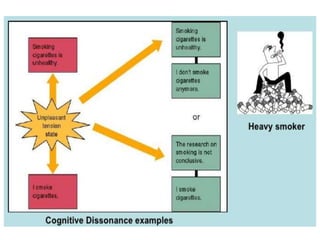
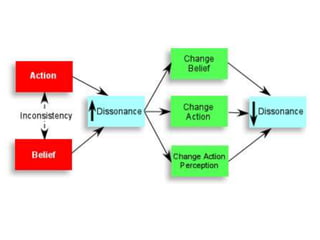
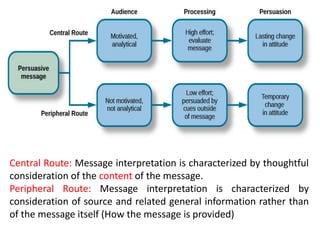
The document discusses various theories and mechanisms related to attitude formation and change. It describes four main ways attitudes can be formed: mere exposure, associative learning, self-perception, and functional reasons. Attitude change can occur through self-perception, learning theory, cognitive dissonance, and persuasion. The theory of planned behavior model proposes that attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control influence behavioral intentions and actual behaviors.