This document discusses attitudes, including what they are, their importance, characteristics, how they are formed and influenced. It provides several key points:
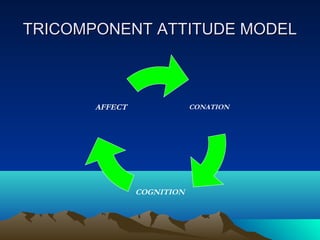
- Attitudes are predispositions to evaluate objects positively or negatively and have three components - beliefs, affect, and behavioral intentions.
- Attitudes are important because of their cognitive, affective, and connative functions.
- Characteristics of attitudes include favorability, accessibility, confidence, persistence, resistance, and ambivalence.
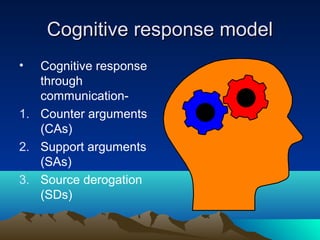
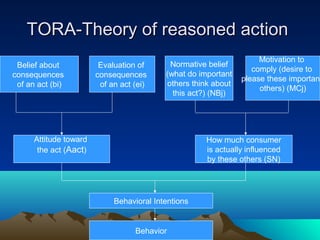
- Attitudes can be formed based on cognitions or emotions, and influenced cognitively or affectively. Common models for explaining attitude formation are the cognitive response model and the theory of reasoned action.