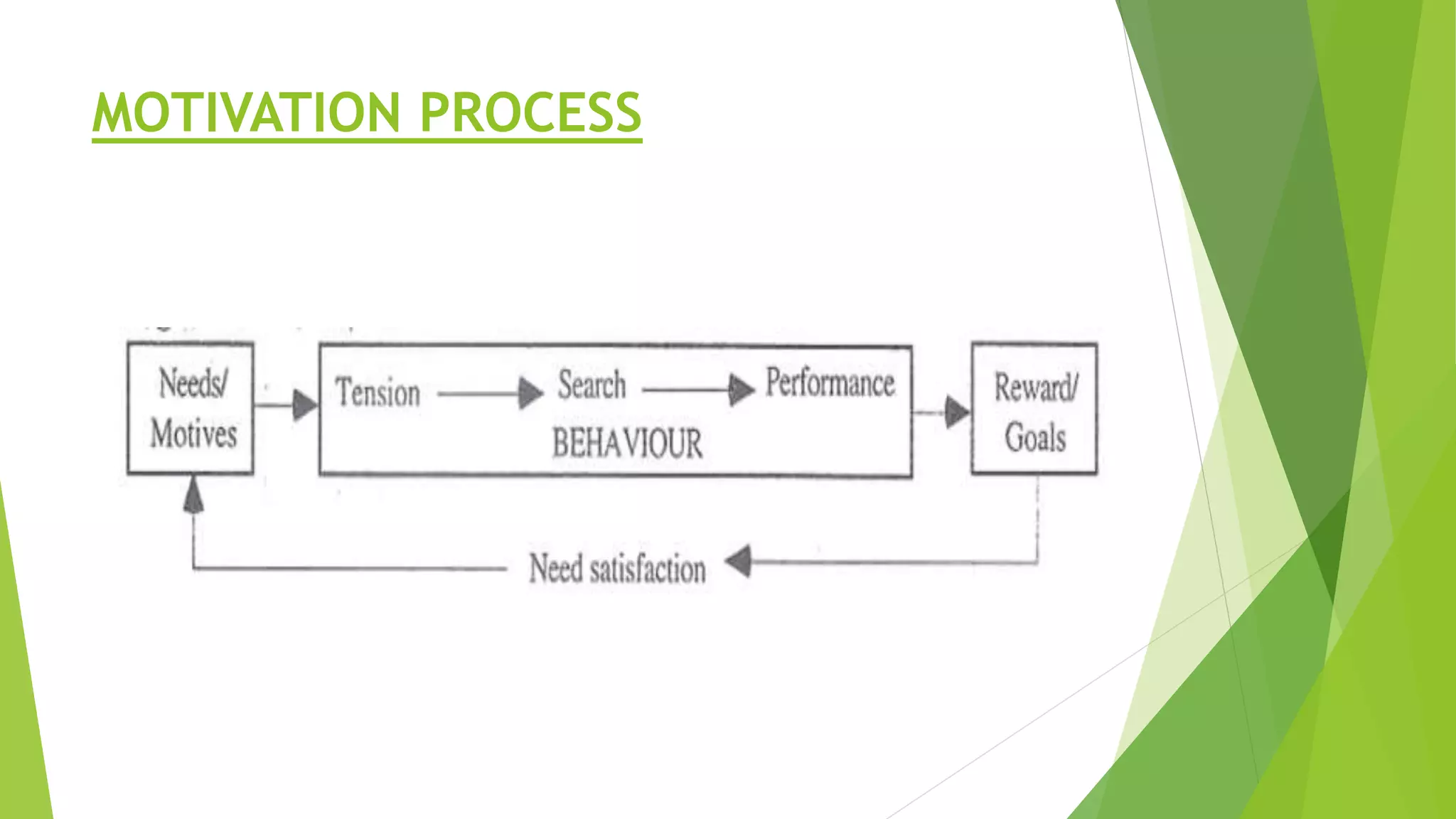
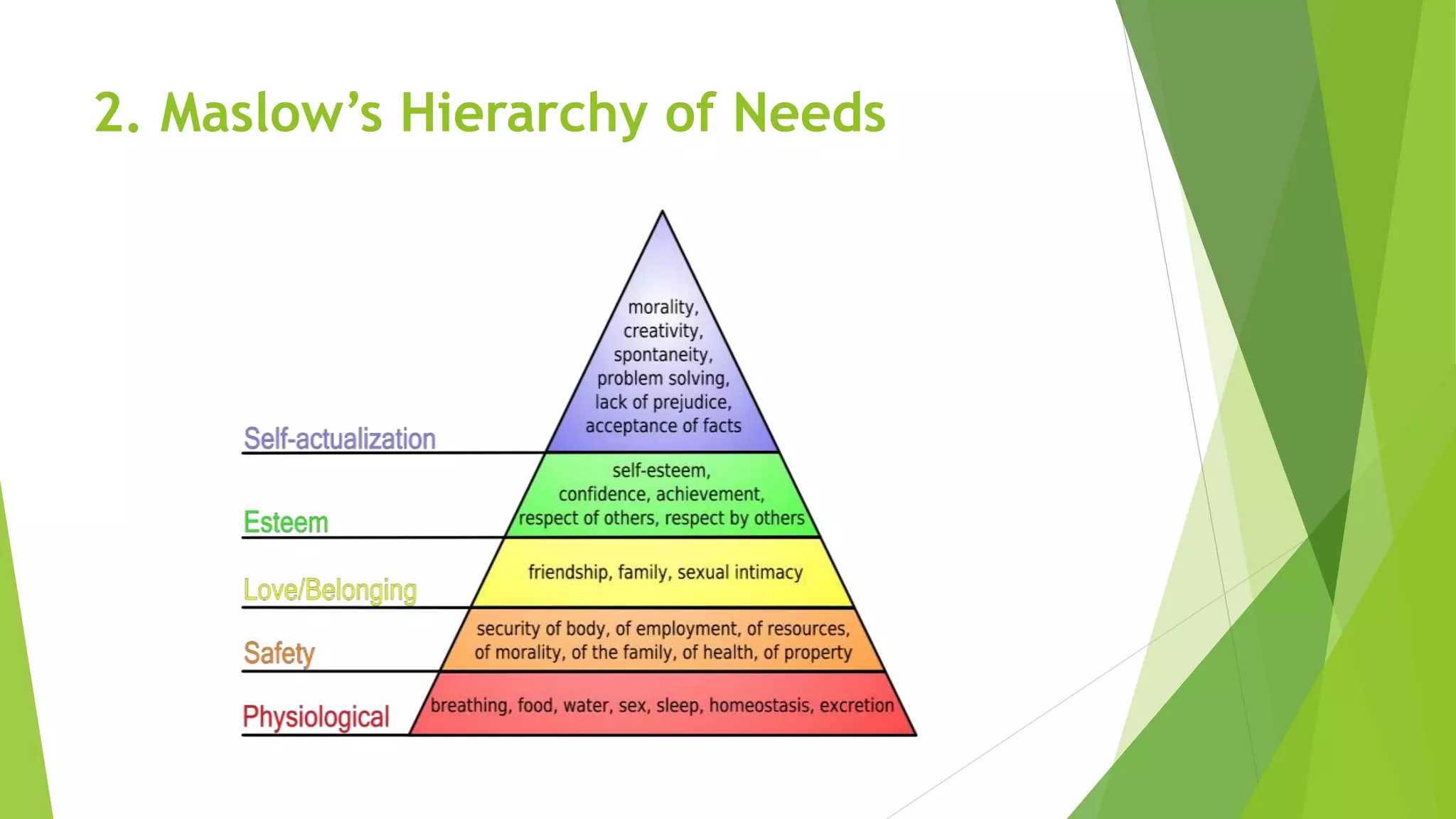
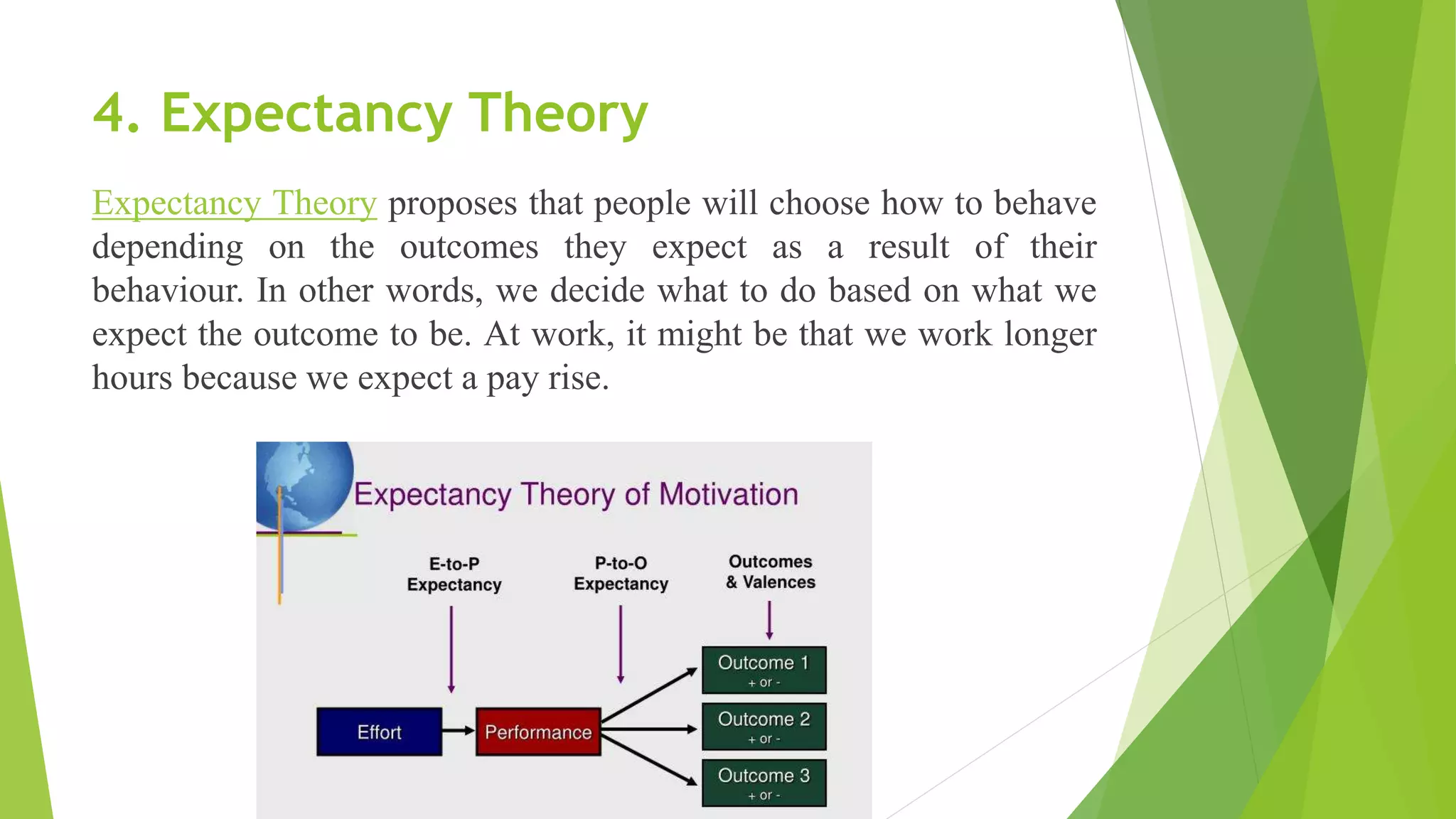
The document, presented by Mr. Abhay Rajpoot, outlines the definition, nature, and types of motivation, dividing them into intrinsic and extrinsic categories along with various minor forms. It reviews several motivation theories, including Herzberg's two-factor theory, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, the Hawthorne effect, and expectancy theory, emphasizing the importance of creating a motivating climate for employees. The benefits of motivation include job satisfaction, productivity, and personal growth, stressing the significance of recognizing individual needs among staff nurses and students.