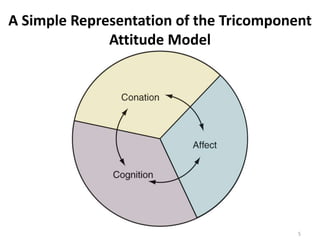
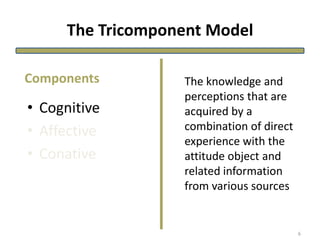
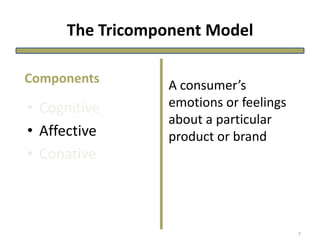
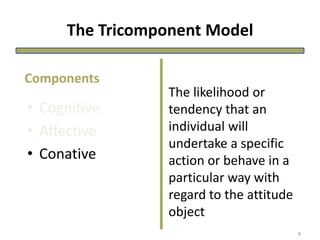
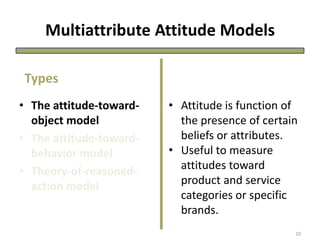
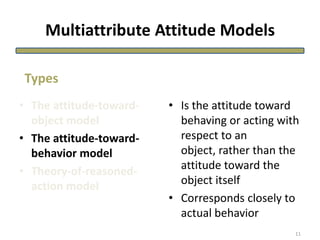
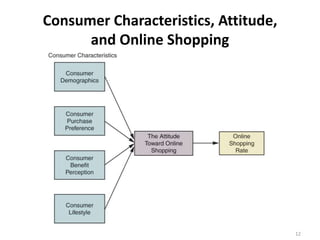
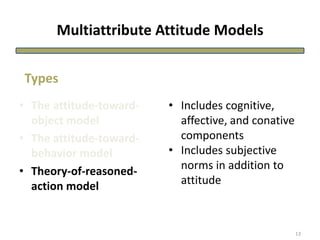
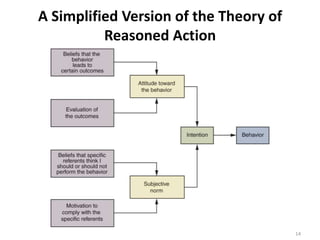
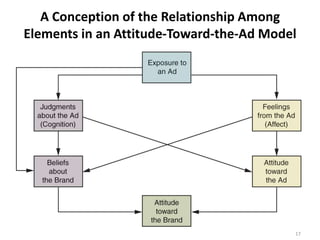
The document discusses theories of consumer attitude formation and change. It describes attitudes as learned predispositions to behave favorably or unfavorably towards an object. It presents models of attitude structure, including the tricomponent model dividing attitudes into cognitive, affective, and conative components. Multi-attribute models examine how attitudes are composed of beliefs about an object's attributes. The theory of reasoned action includes subjective norms. Strategies for changing attitudes include associating products with groups, resolving conflicts, and altering attribute beliefs. Attribution theory examines how people explain events and how that affects attitudes.