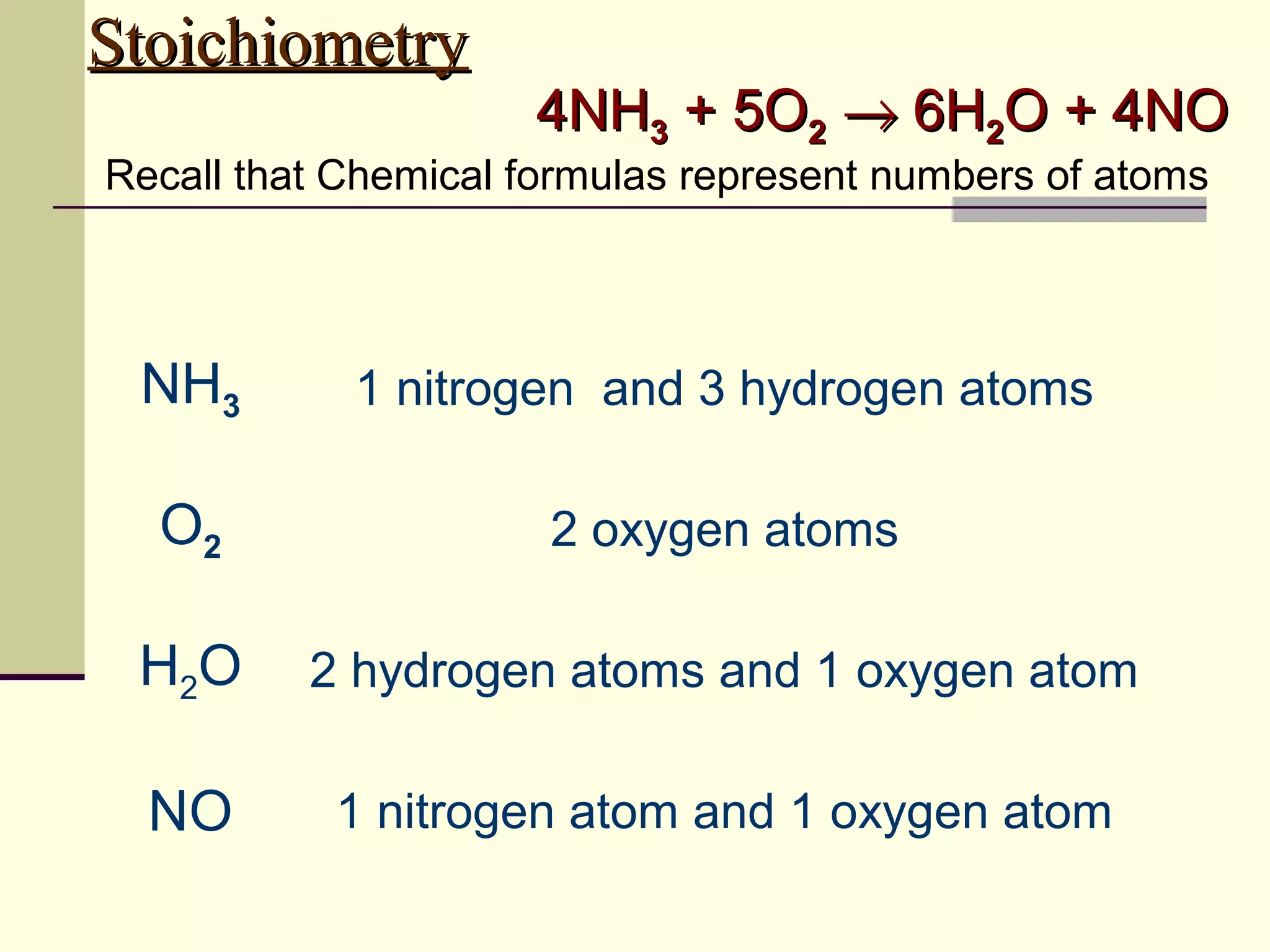
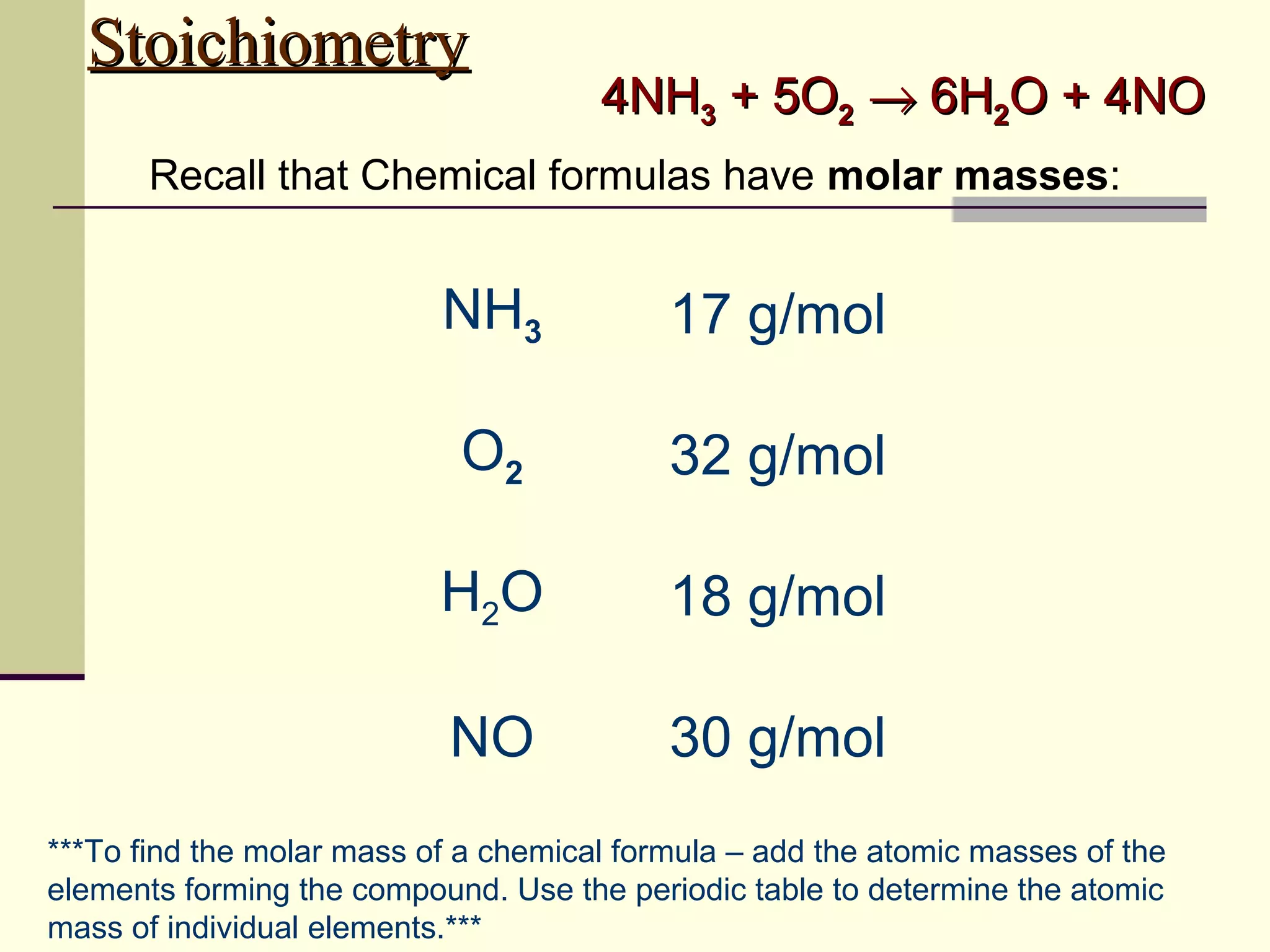
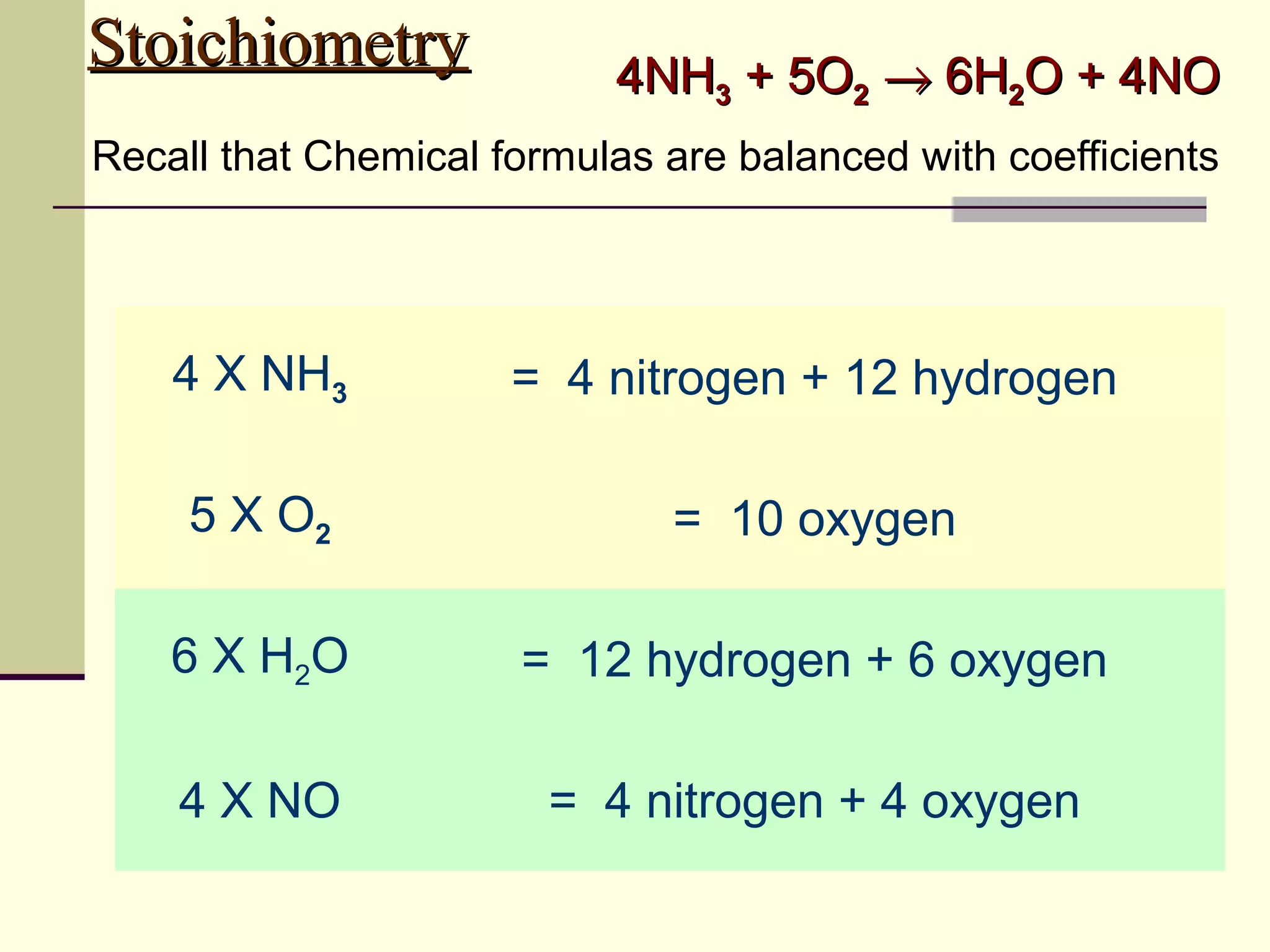
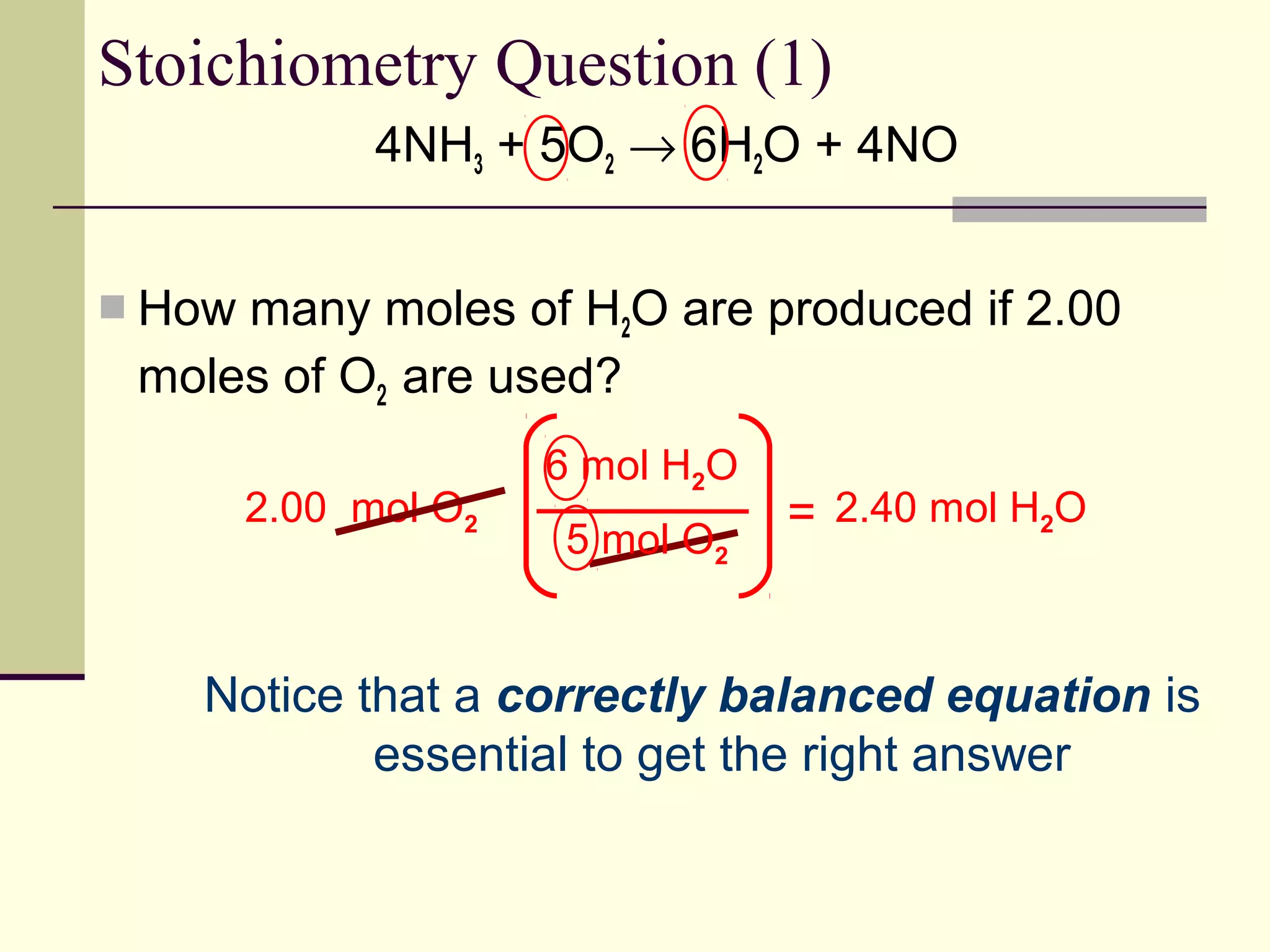
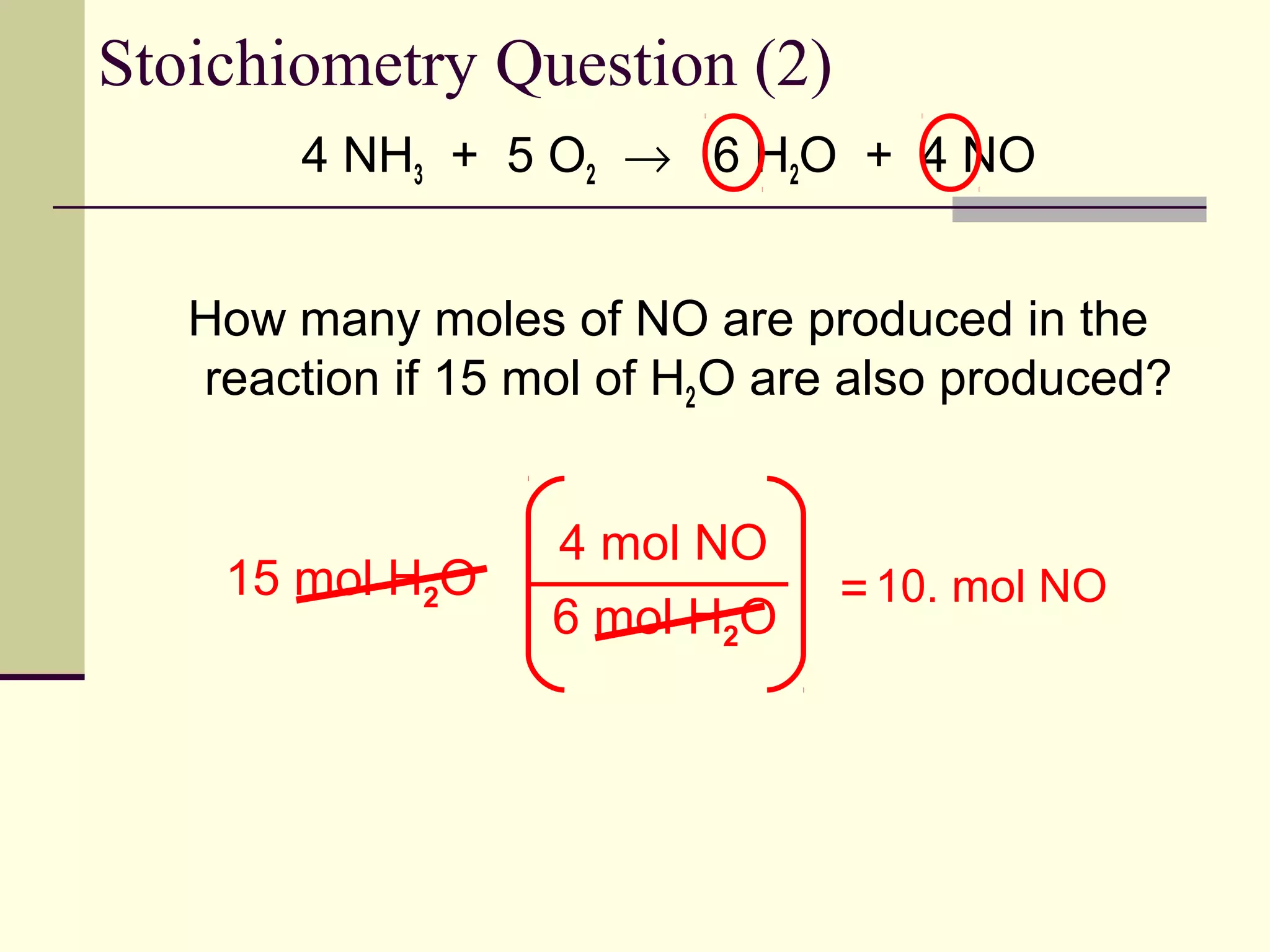
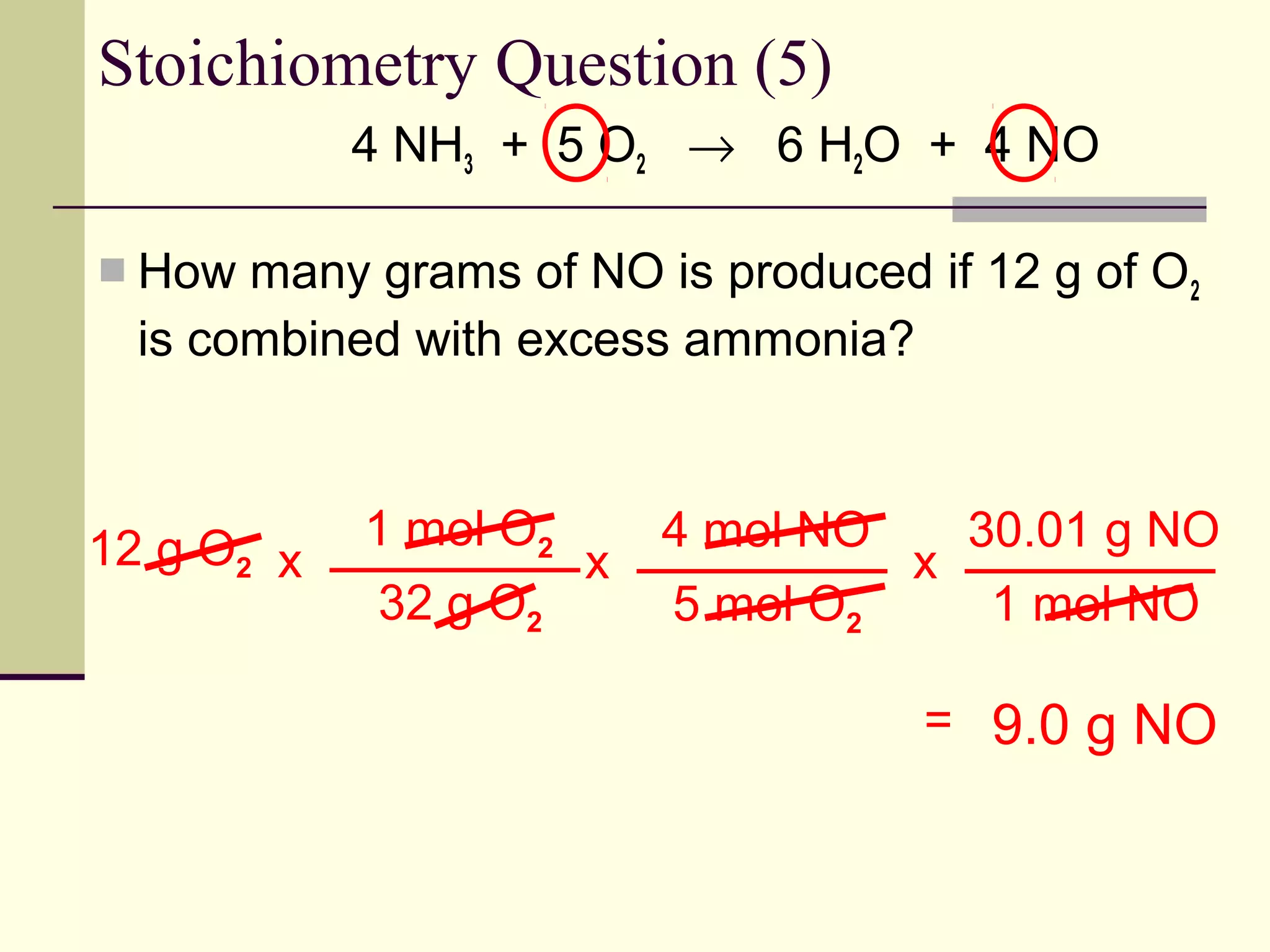
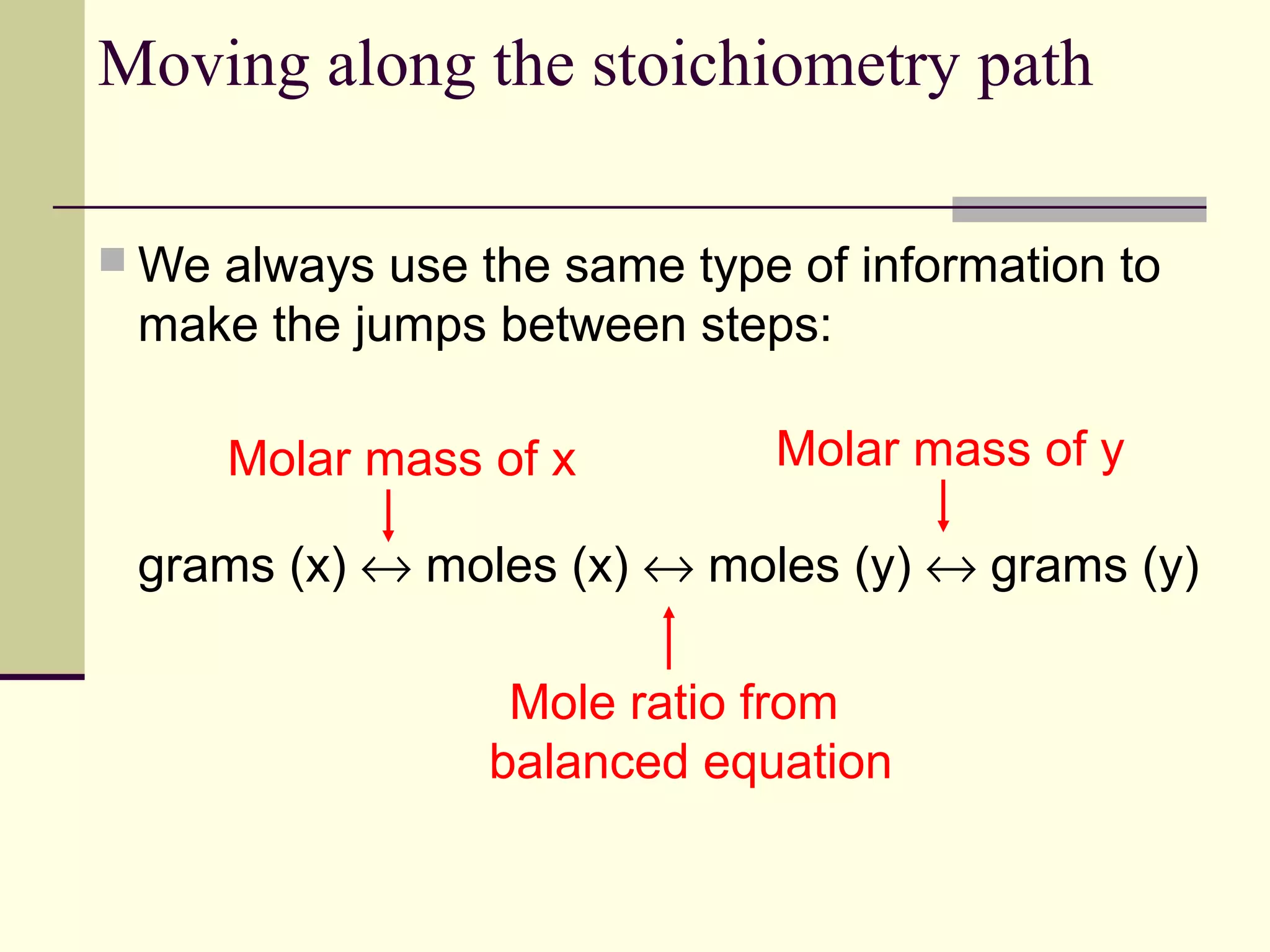
Stoichiometry is the measurement of elements and compounds involved in a chemical reaction. The document uses the example reaction of 4NH3 + 5O2 → 6H2O + 4NO to explain key stoichiometry concepts. These include: chemical formulas represent numbers of atoms and have molar masses; formulas are balanced with coefficients that represent mole ratios; and stoichiometry problems use mole ratios and molar masses to convert between grams and moles of reactants and products. Several stoichiometry practice problems are worked through as examples.