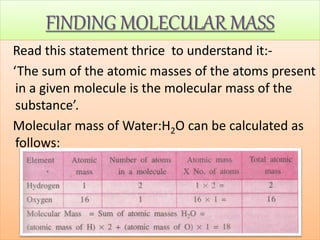
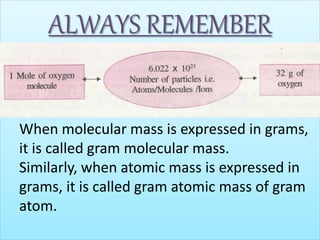
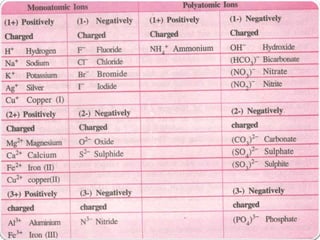
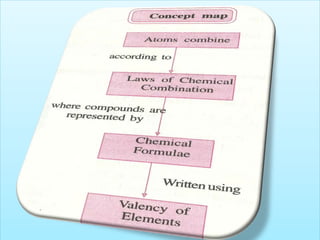
The document discusses several key concepts in chemistry including:
- Laws of chemical combination and conservation of matter discovered by scientists like Lavoisier and Proust through quantitative experiments.
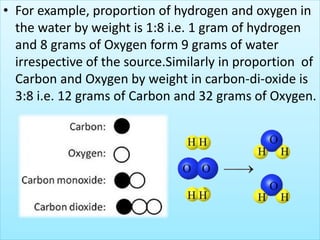
- Proust's law of constant proportions which states that elements are always present in a definite proportion by weight in a compound.
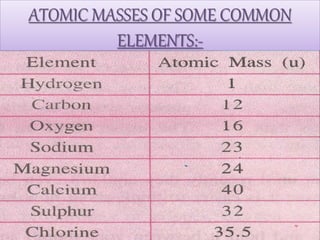
- Atoms being the fundamental units of matter and their structure including subatomic particles. Atoms are extremely small but their masses can be measured by comparison to hydrogen atoms.
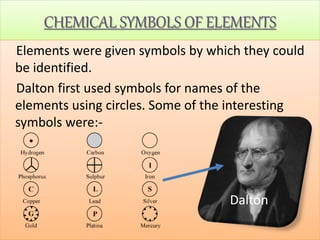
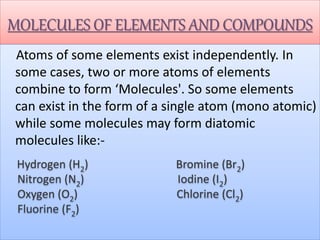
- Chemical symbols used to represent elements, including early systems and current IUPAC symbols. Molecules can be monoatomic or polyatomic.
- Concepts of mole, molar mass, and Avogadro