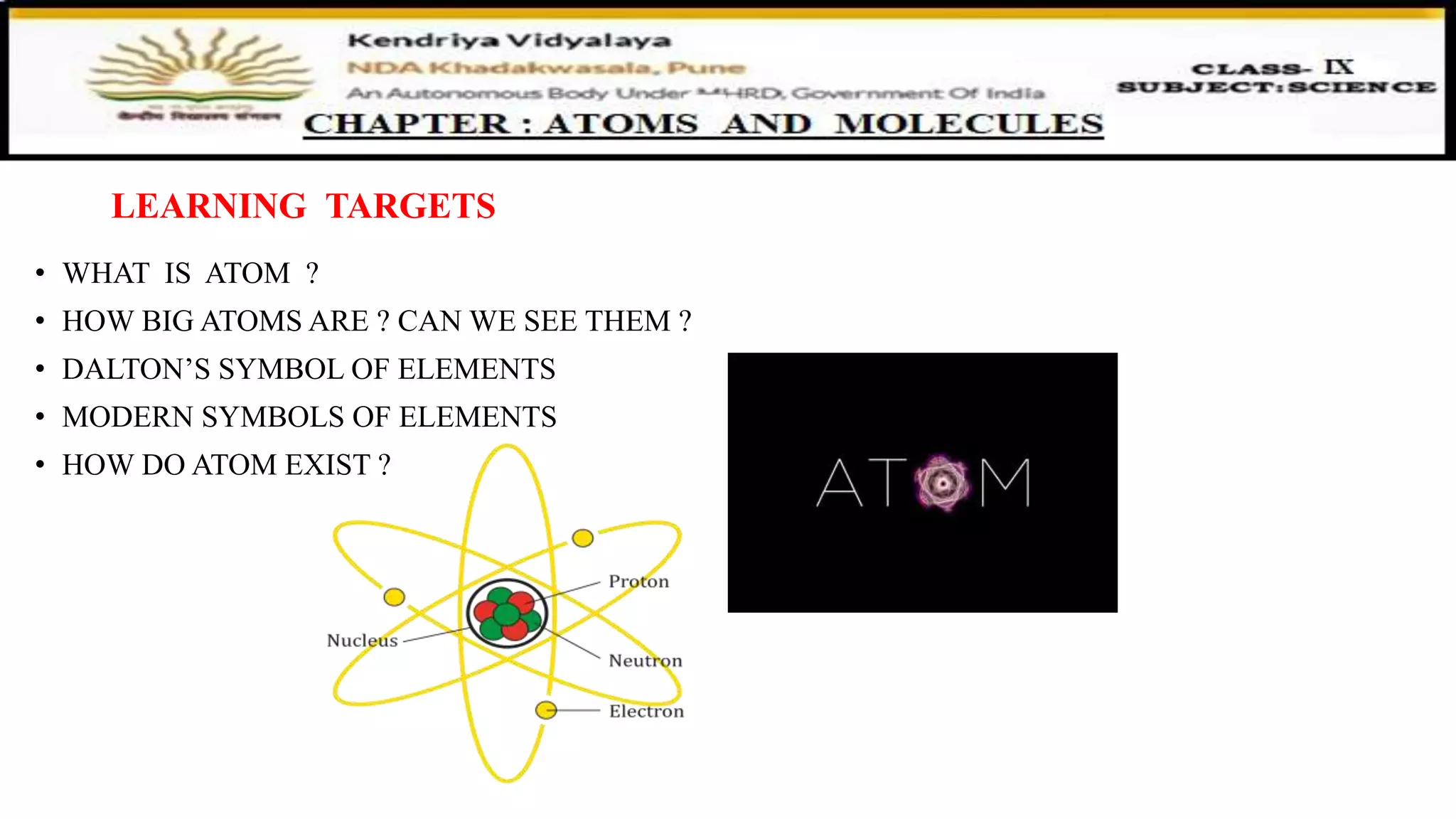
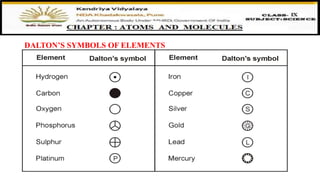
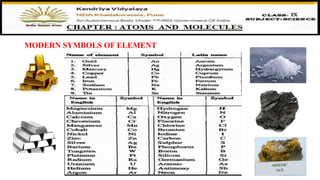
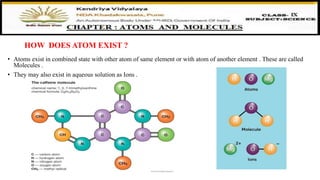
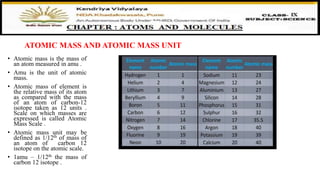
The document discusses atoms, their size, visibility, and existence, stating that atoms are the smallest particles of elements and may exist independently or in combined states as molecules. It explains atomic mass and units, detailing how atomic masses are measured relative to carbon-12 and providing examples with chlorine isotopes. Symbols for elements are also addressed, highlighting Dalton's original symbols and the modern representation based on the element's name.