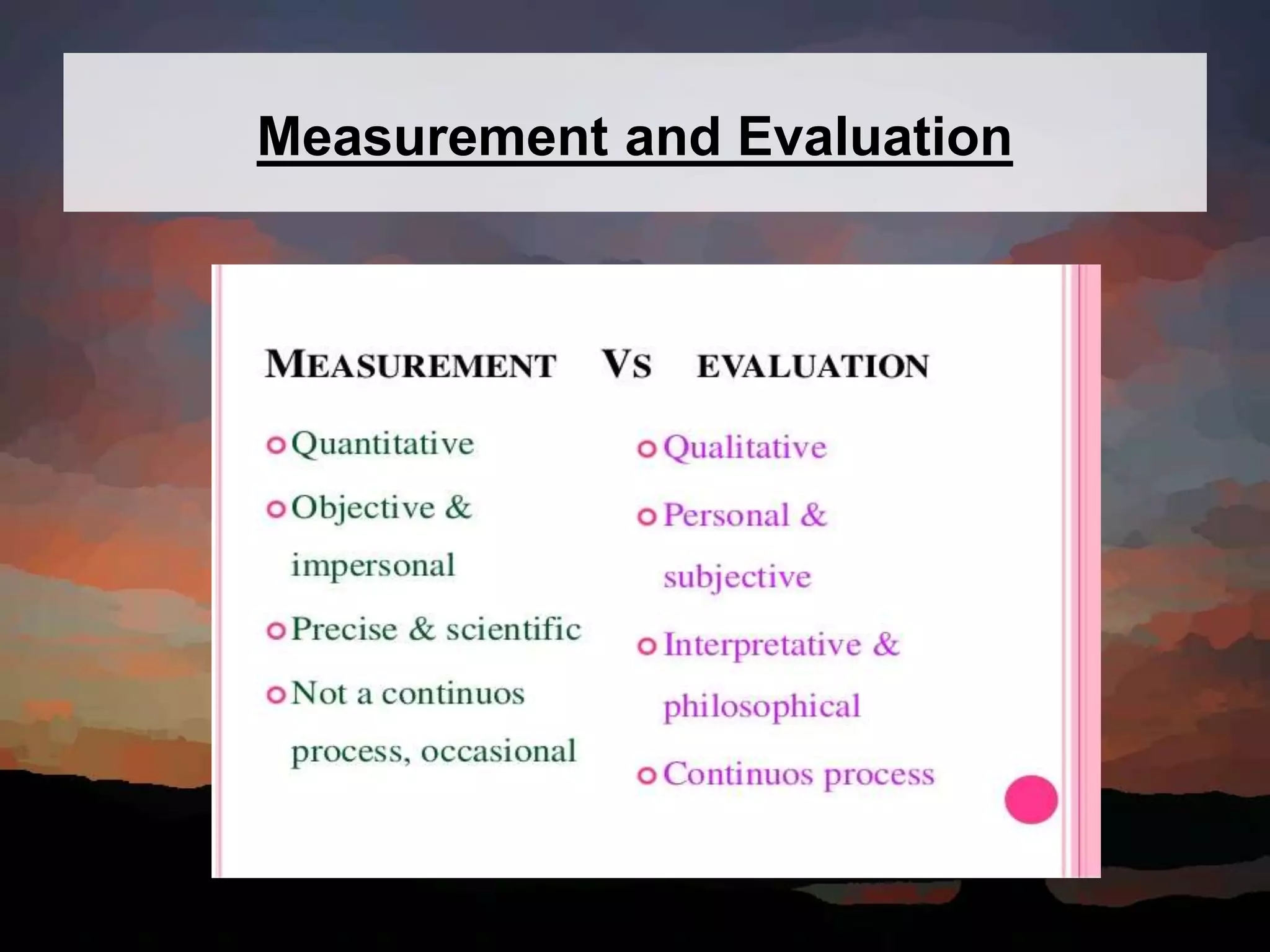
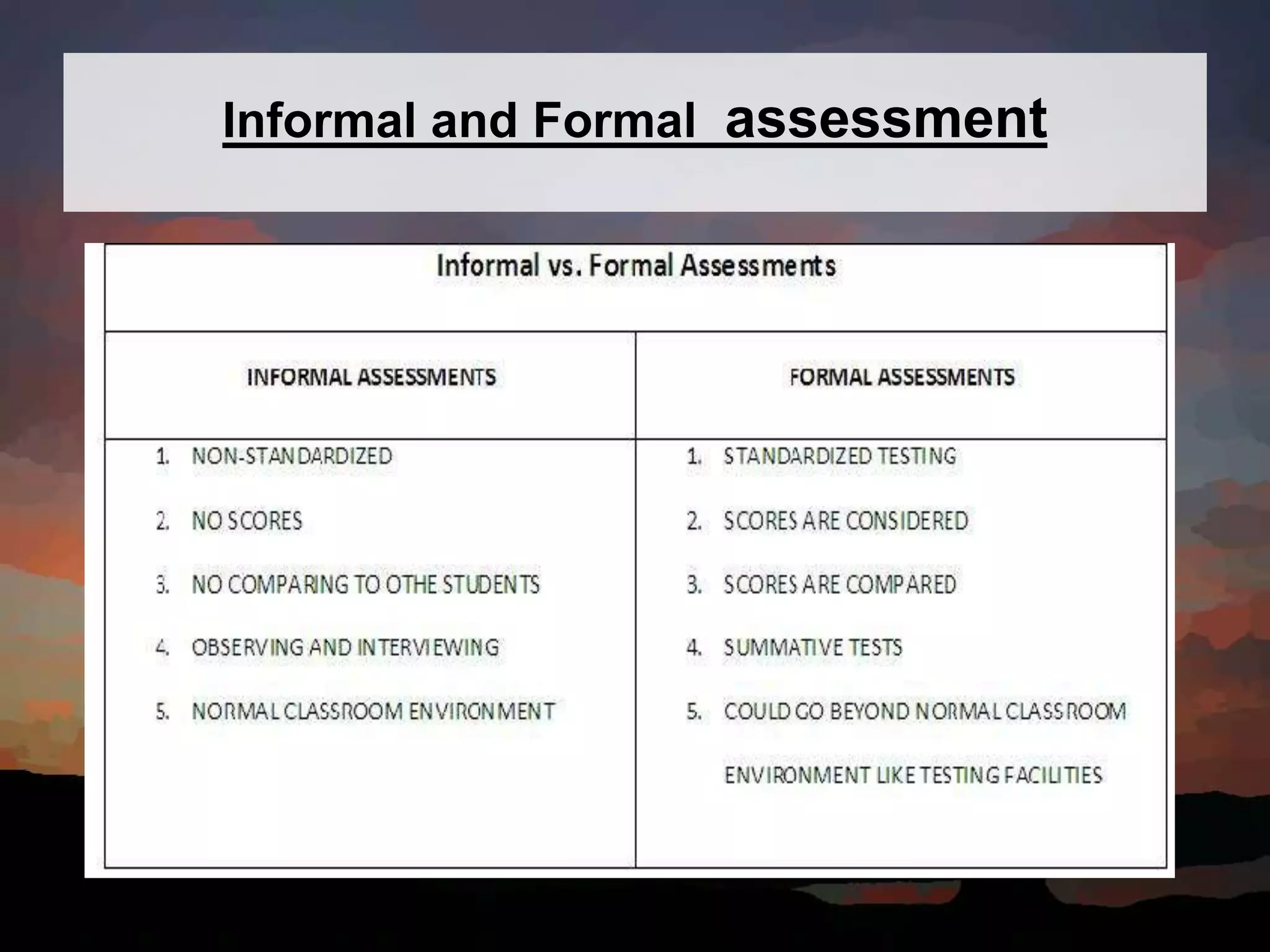
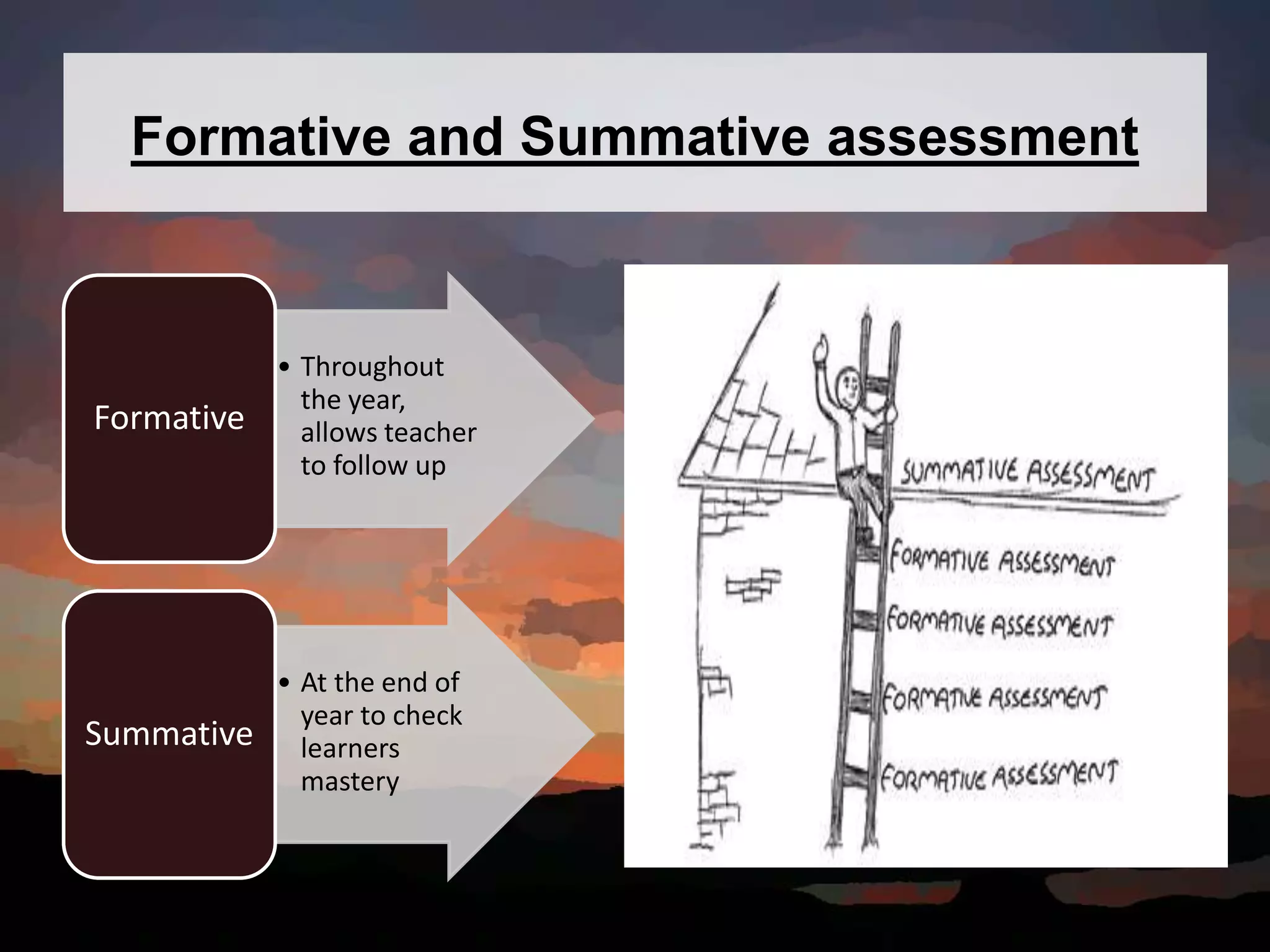
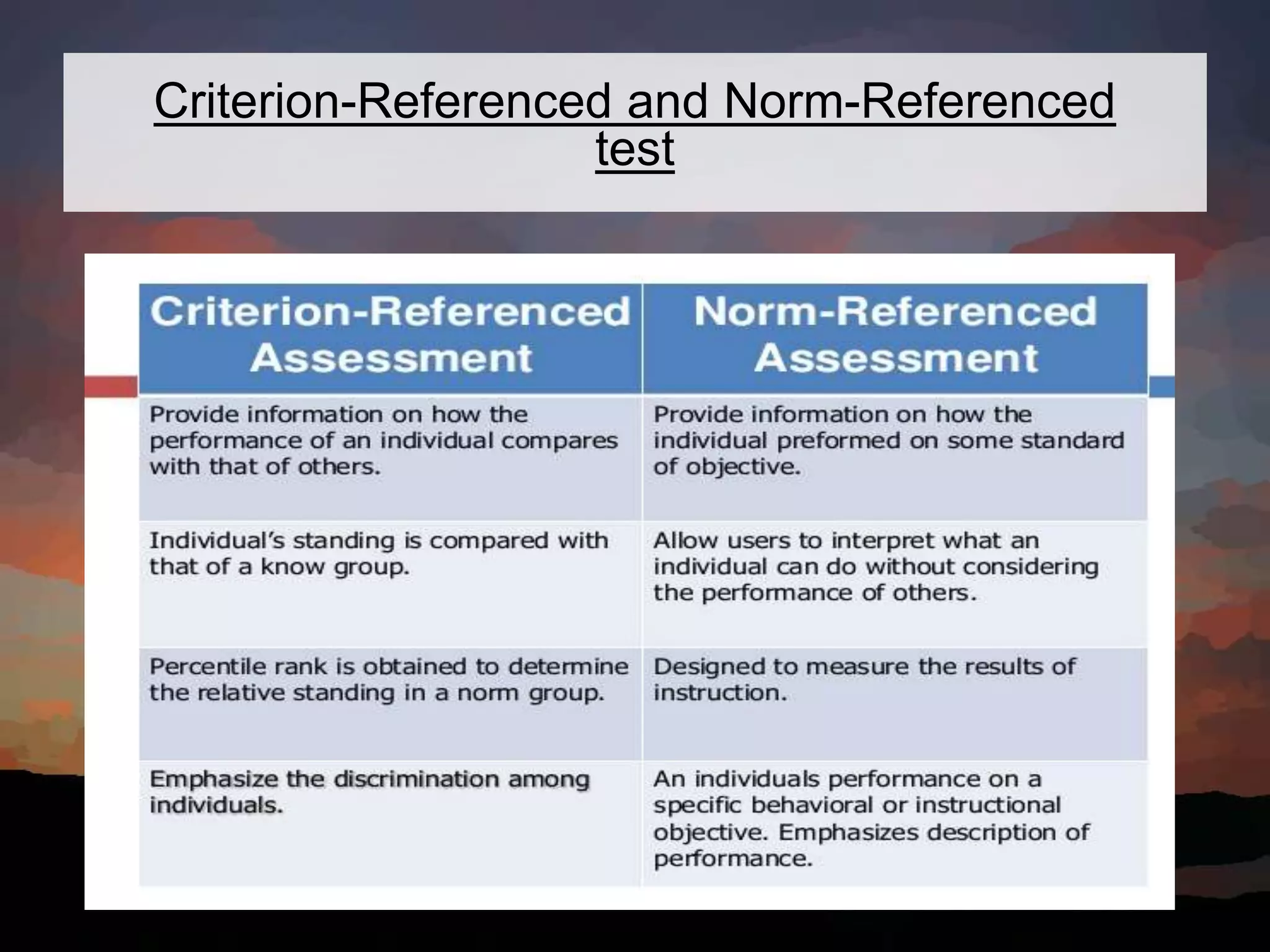
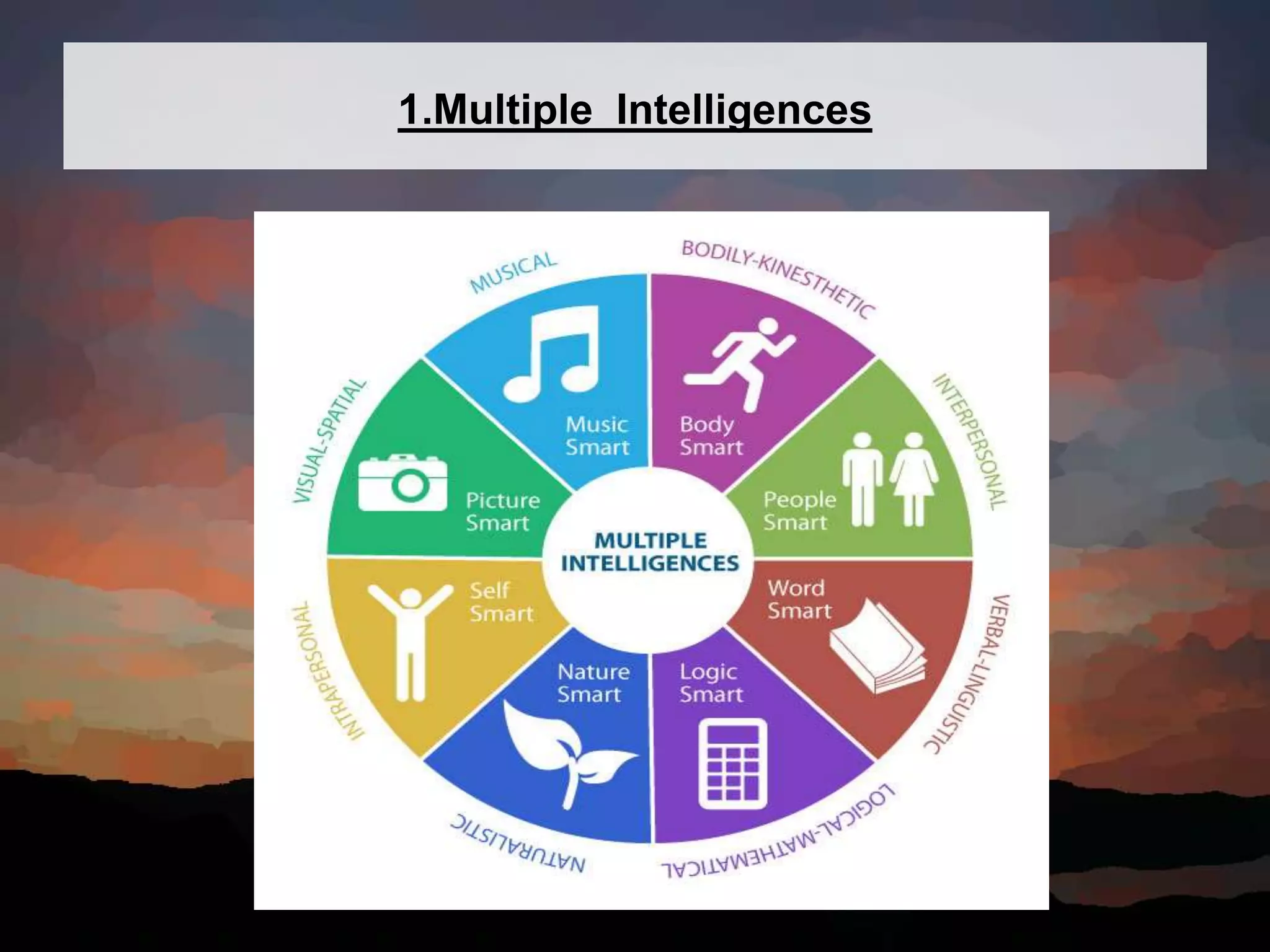
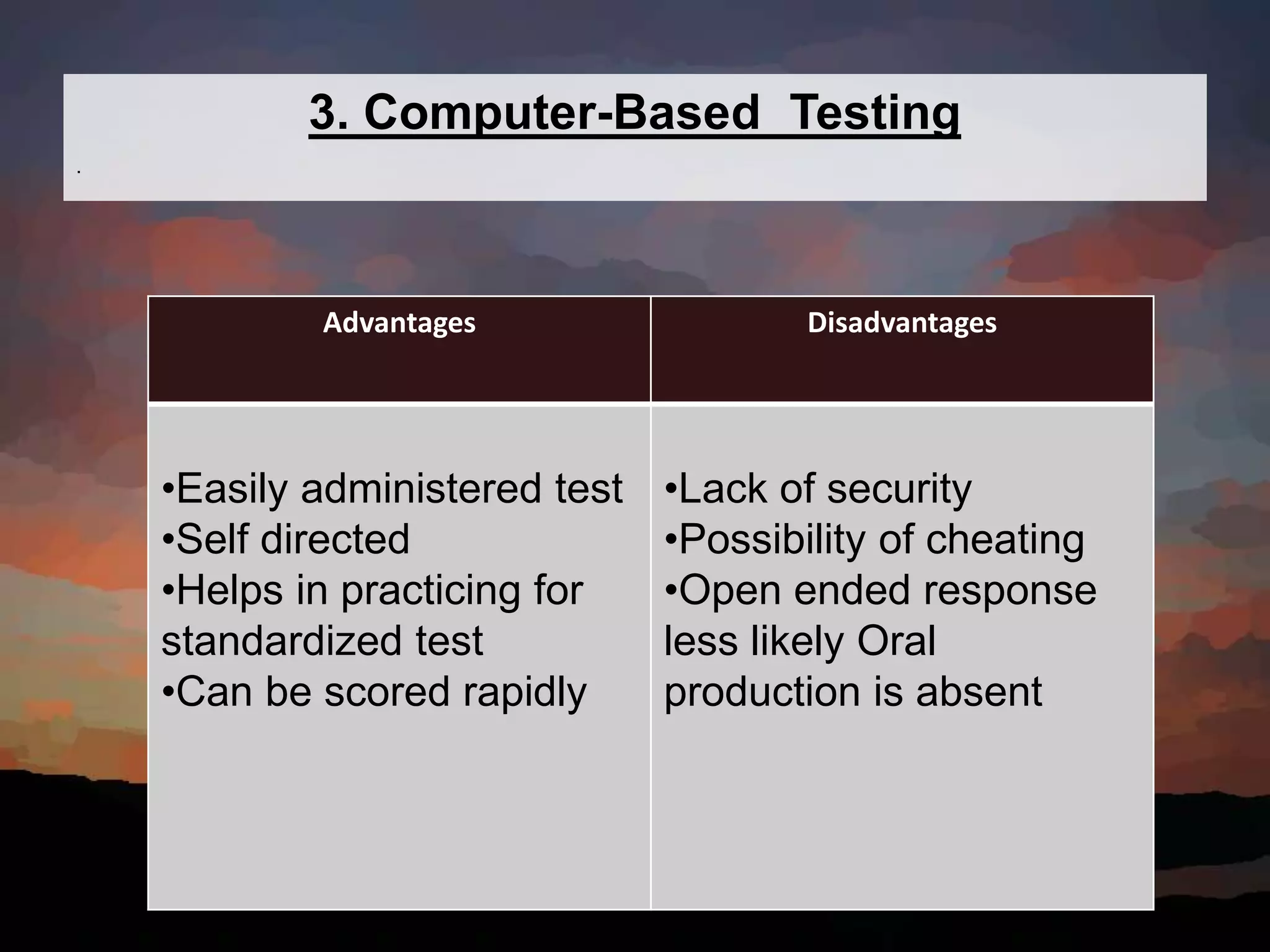
This document discusses key concepts in language assessment. It defines the differences between testing and assessment, and explains that measurement involves assigning numbers to performance while evaluation involves interpretation. Formative assessment occurs throughout learning to provide feedback, while summative assessment evaluates mastery at the end. Other topics covered include multiple intelligence theory, traditional versus alternative assessment, and ensuring tests are practical, reliable, valid, authentic, and promote beneficial preparation.