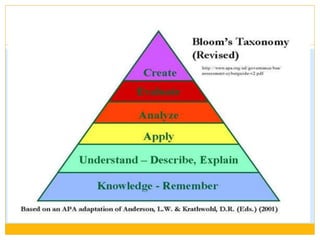
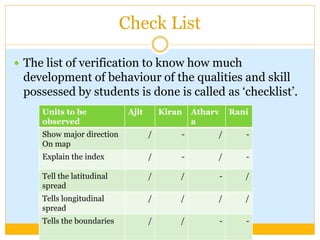
This document provides an overview of assessing and evaluating student learning. It defines assessment as gathering information on student learning and evaluation as analyzing and making judgments based on assessment data. The aims of student evaluation are outlined, including providing feedback and modifying instruction. The document discusses formative, summative, and diagnostic evaluation. It also covers various tools for evaluation, including observation, records, checklists, rating scales, and examinations. The qualities of good tests and advantages and disadvantages of different test types like oral exams, practical exams, essays, and multiple choice questions are summarized.