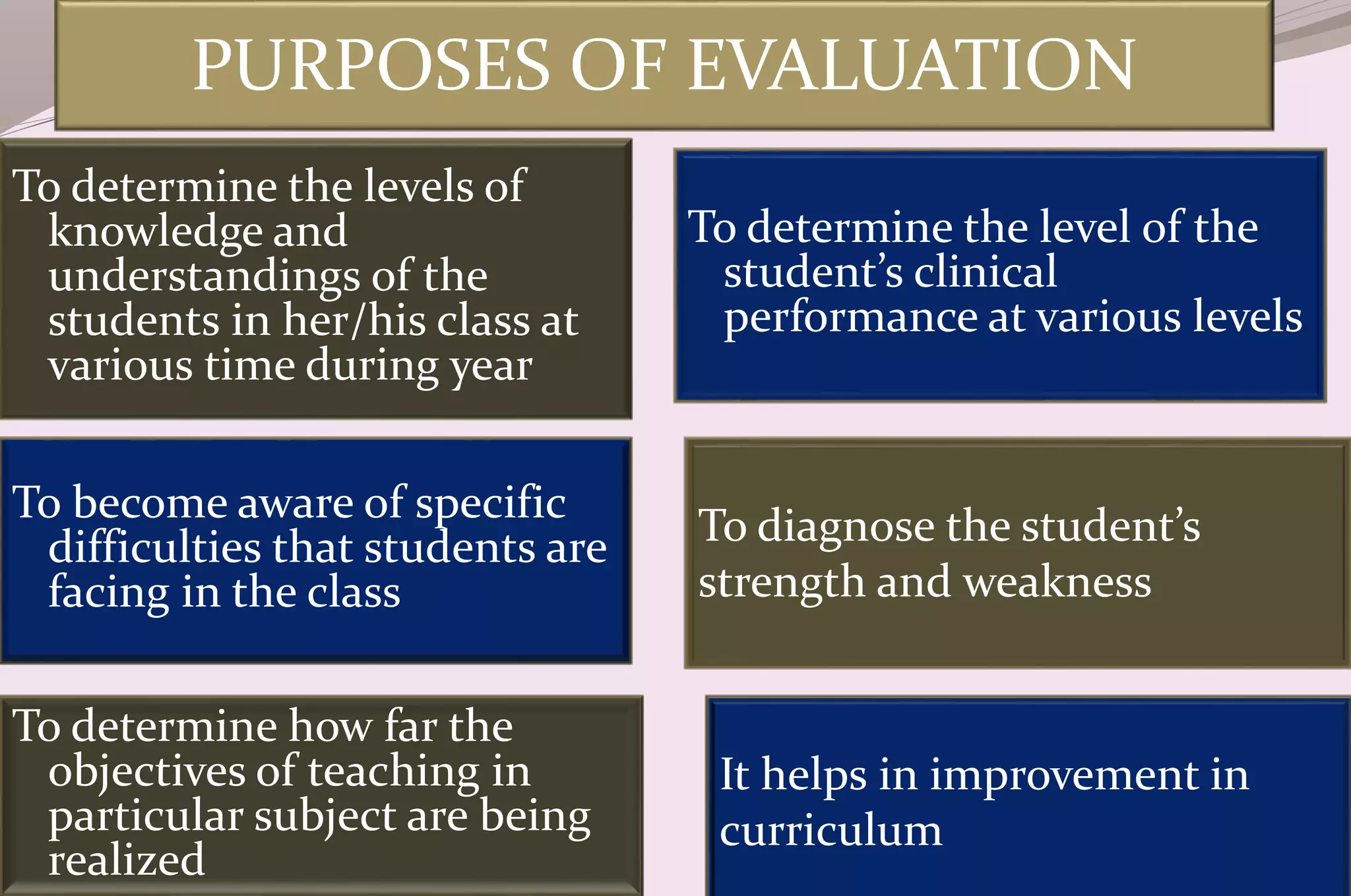
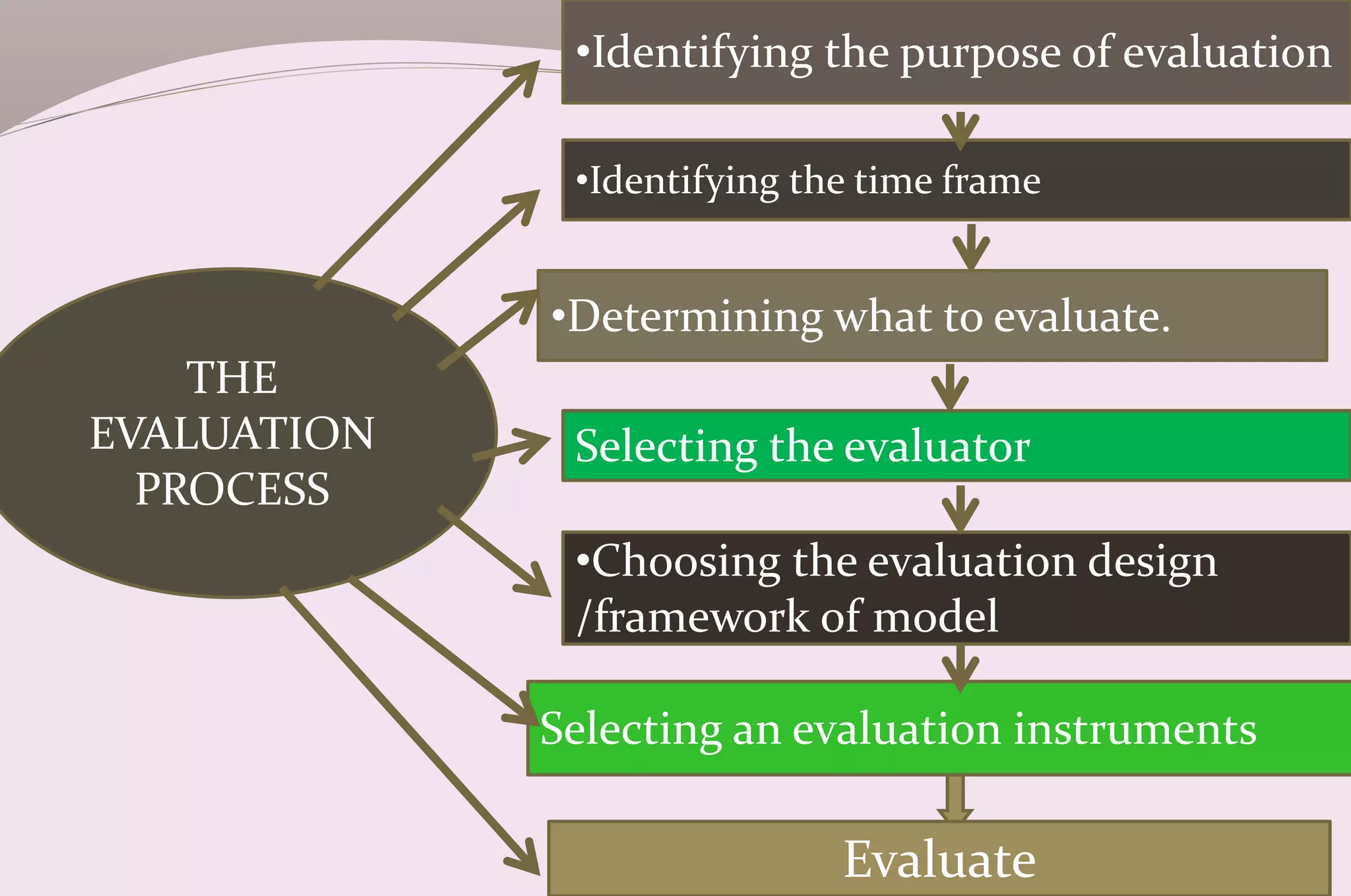
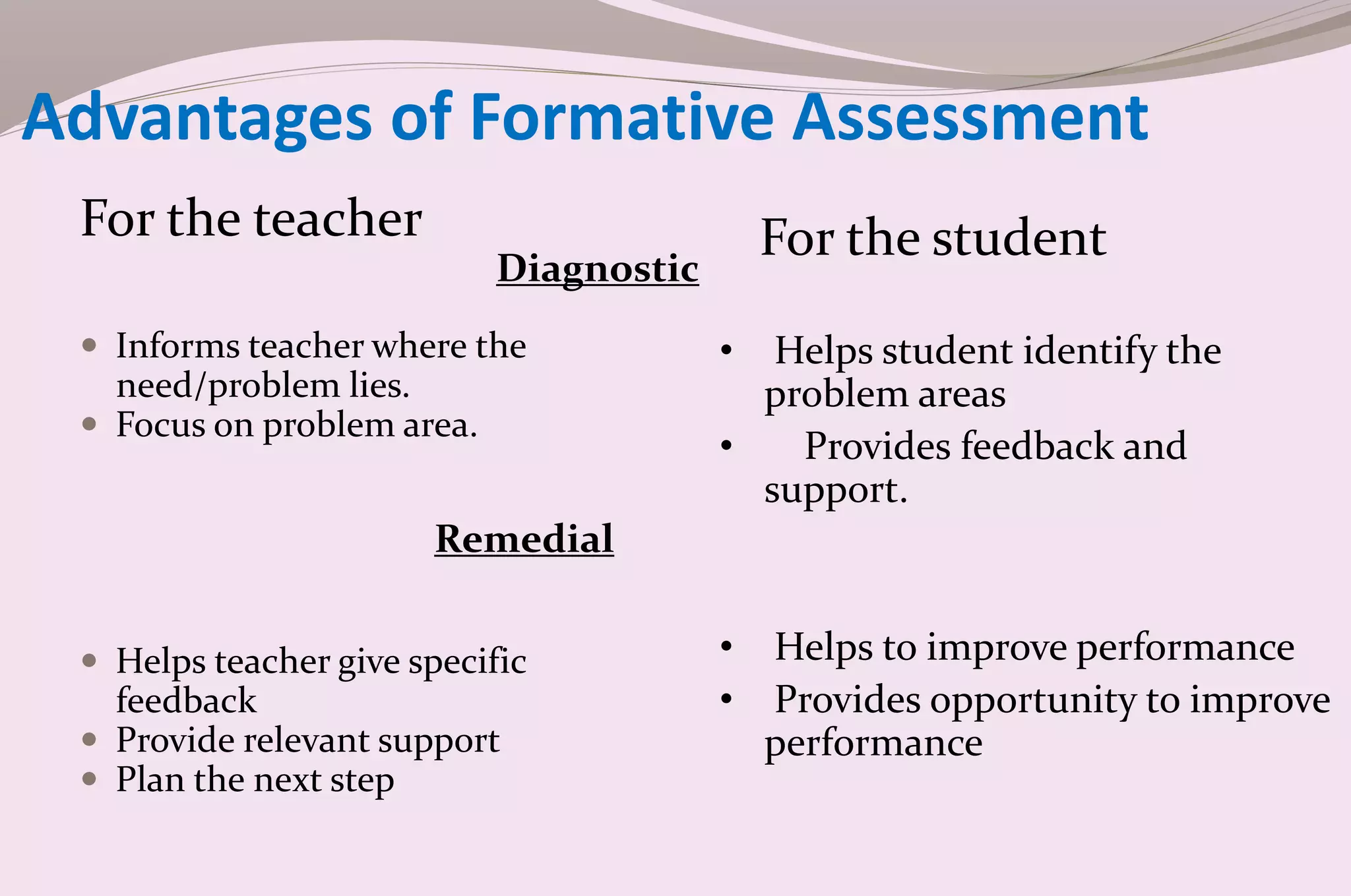
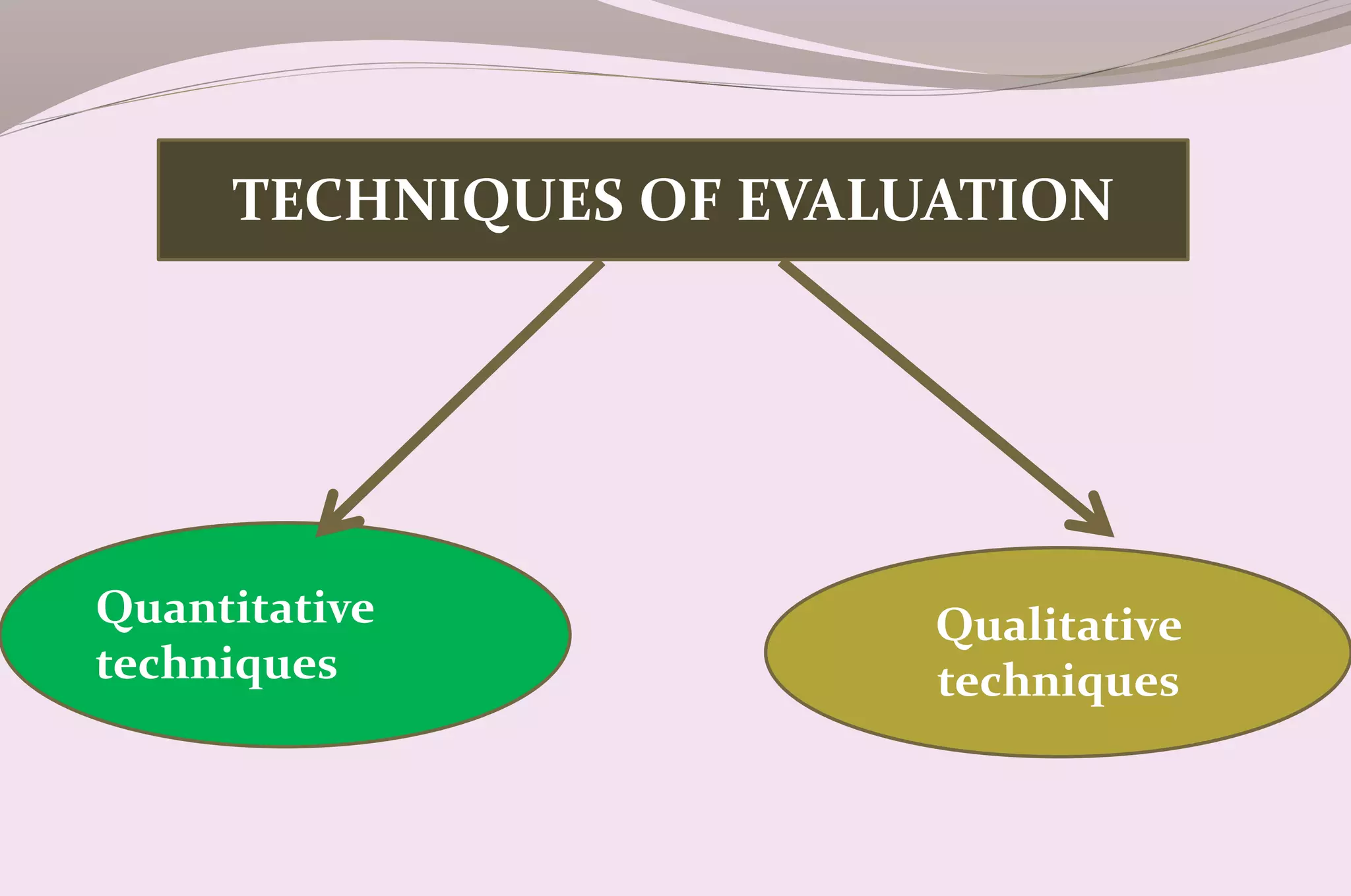
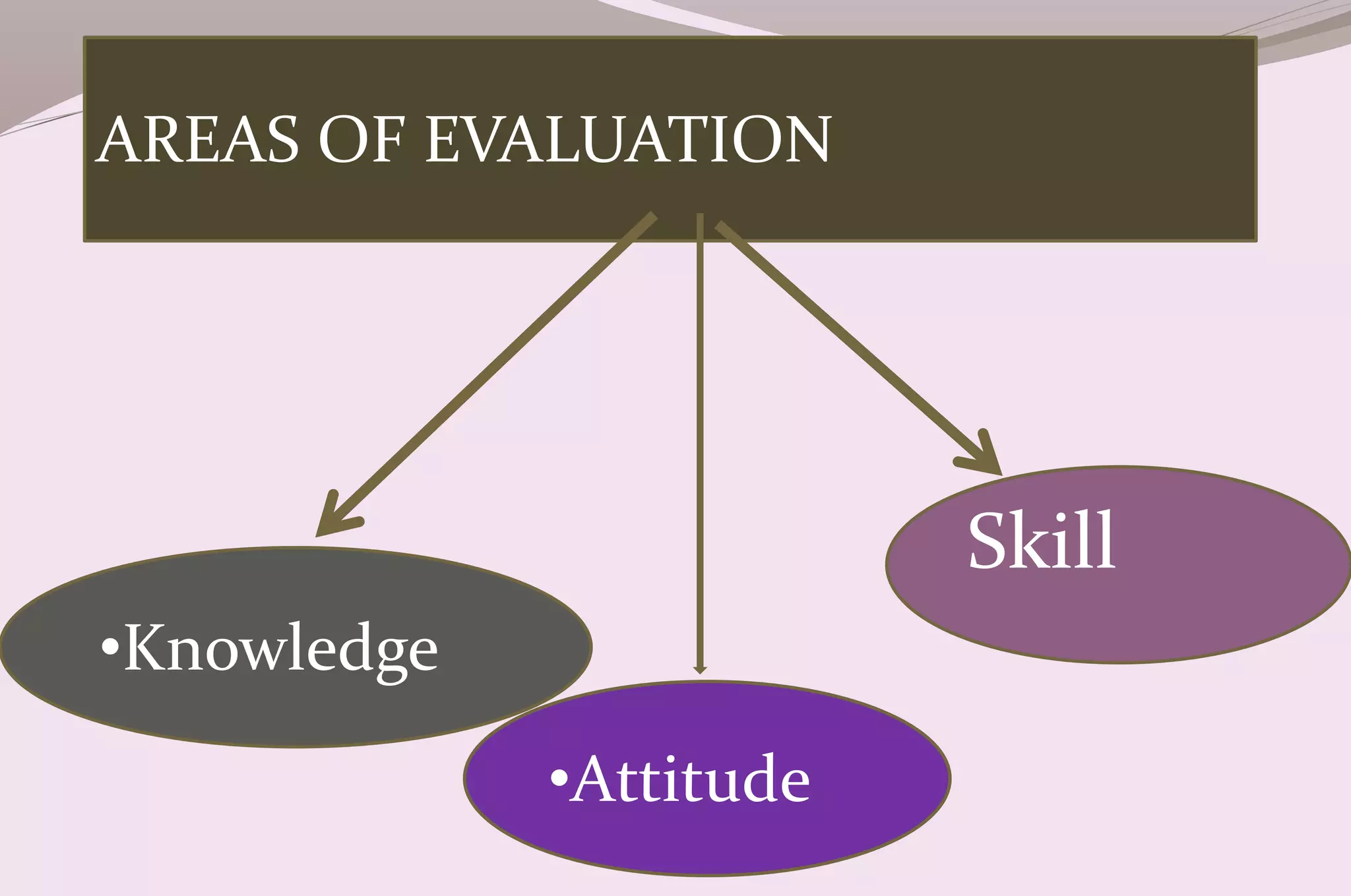
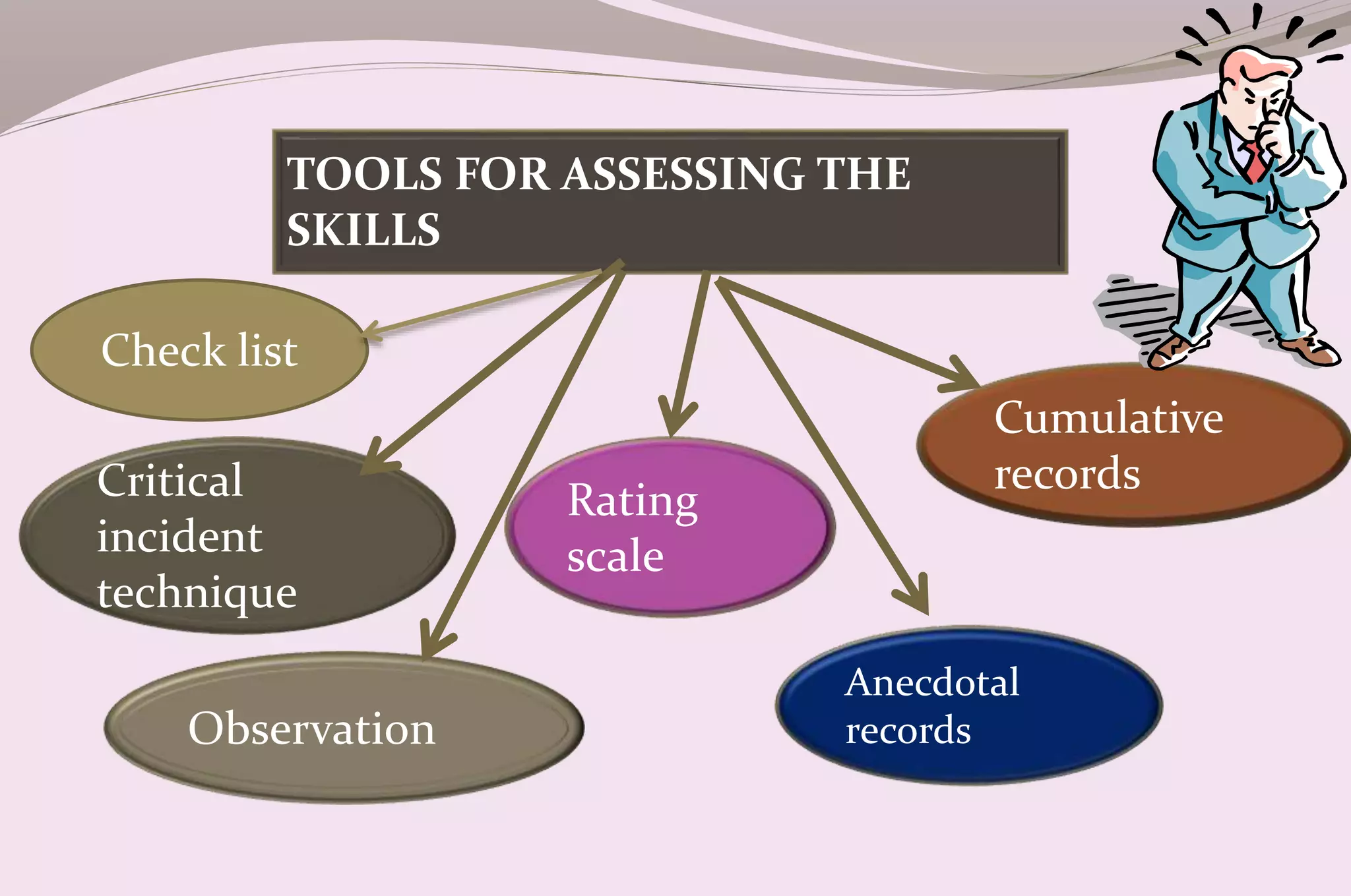
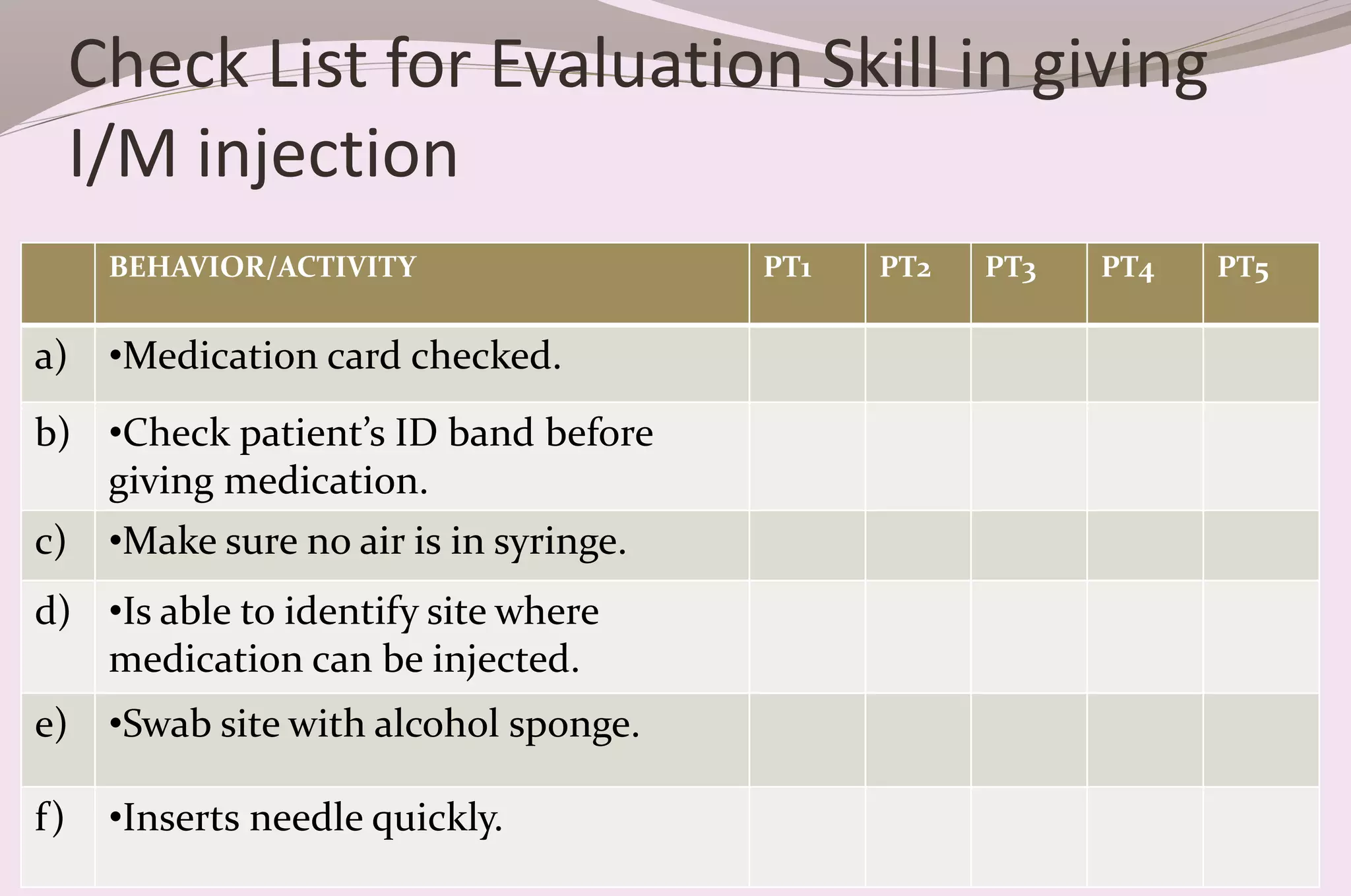
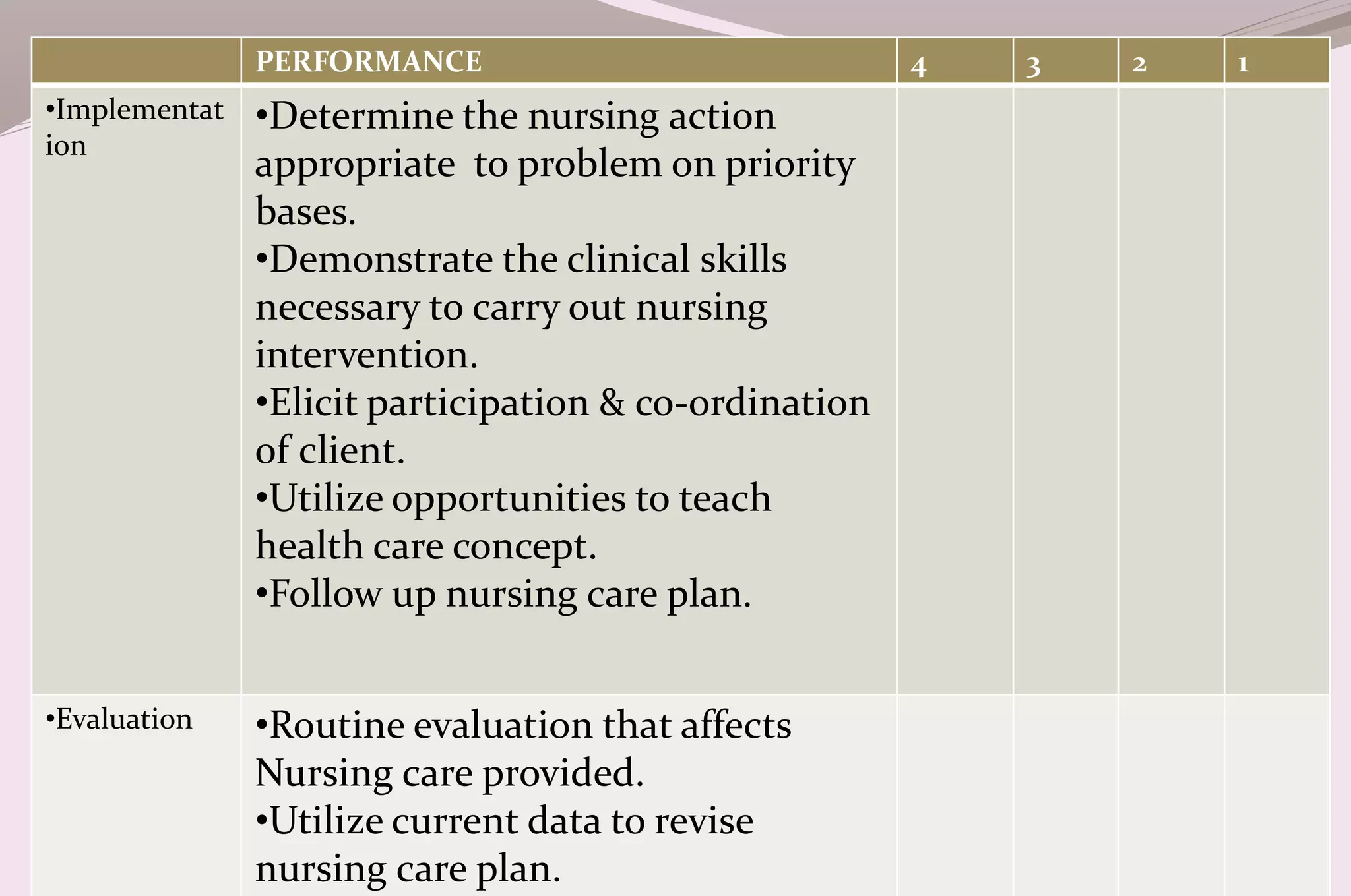
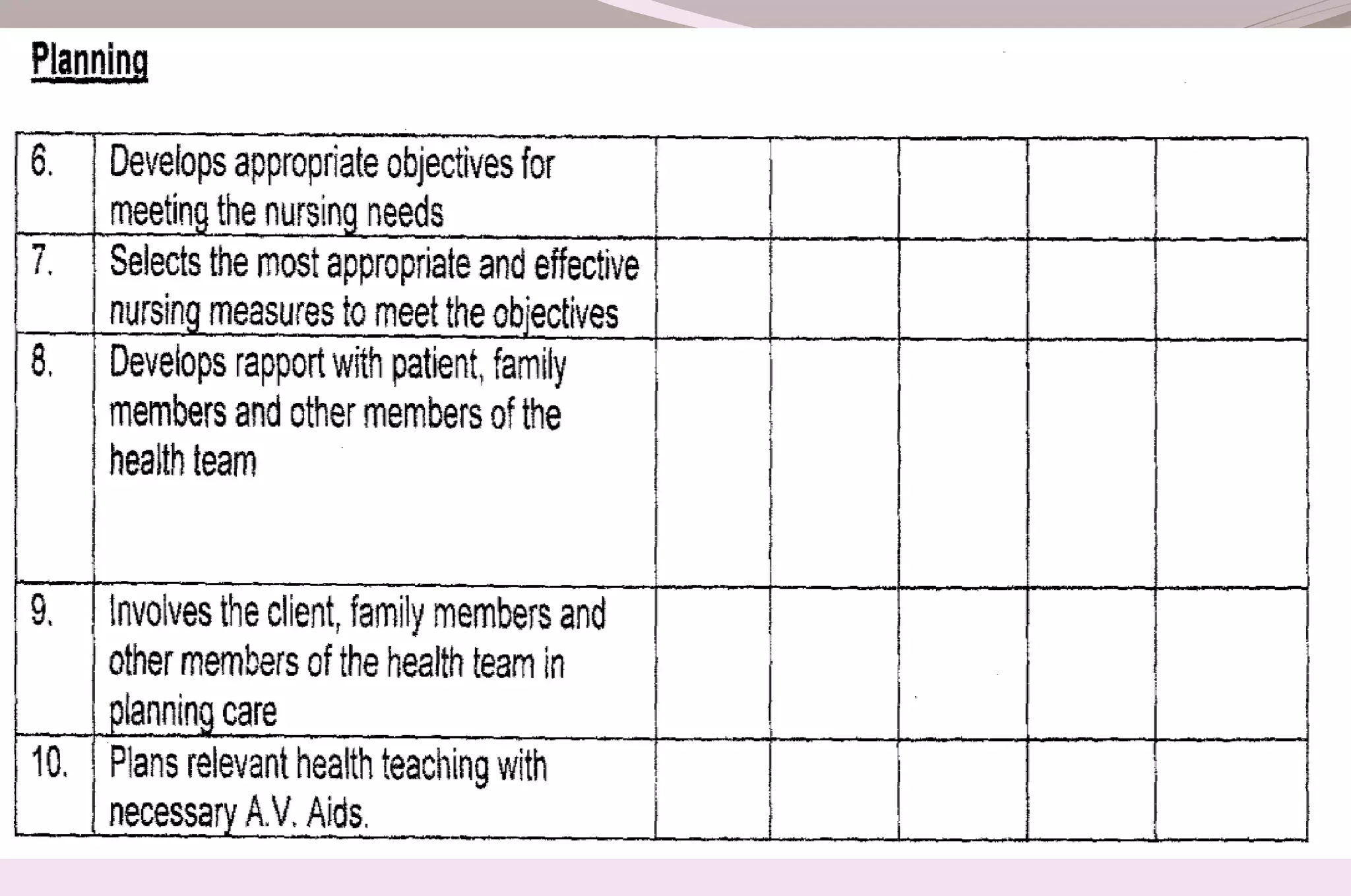
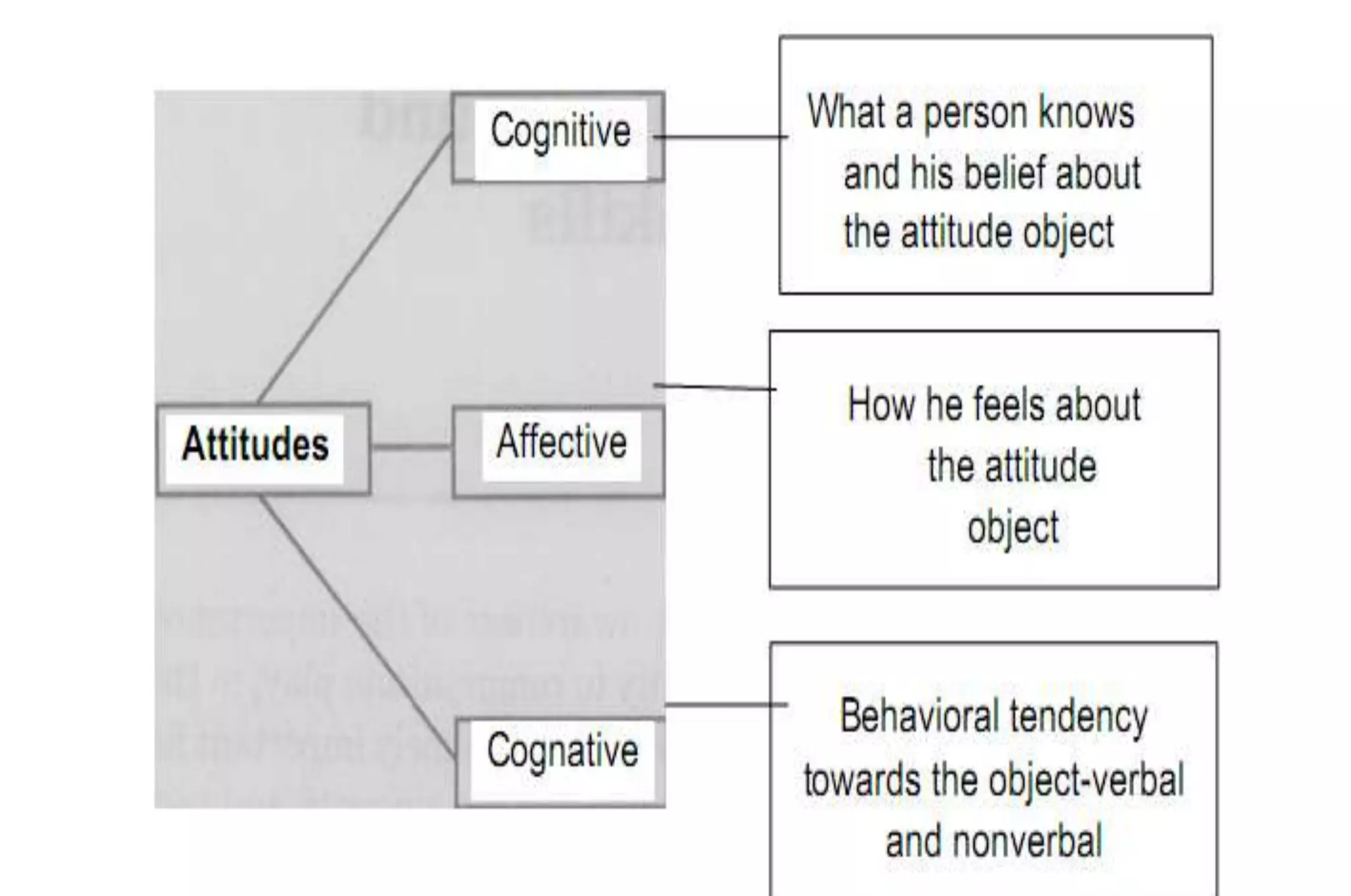
Evaluation is a process of judging the effectiveness of educational experiences. It involves collecting, recording, and interpreting information to determine the extent to which objectives are being attained and how effective teaching methods are. The document discusses the purposes, principles, characteristics, types (formative and summative), tools, areas (knowledge, skills, attitude) and methods of evaluation. Formative evaluation focuses on improving the learning process, while summative evaluation assesses learning outcomes using tools like tests, exams and projects. Both qualitative and quantitative techniques are used to evaluate students in a holistic manner.