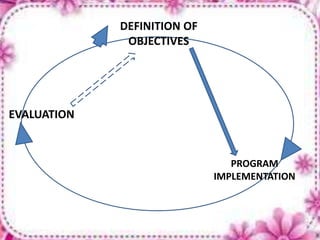
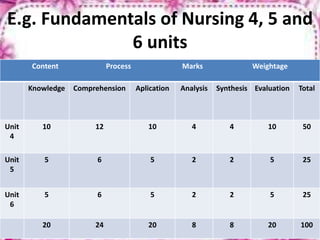
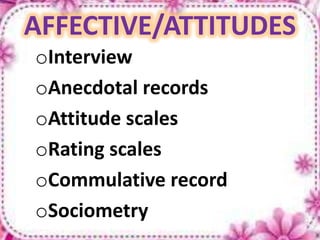
This document provides an overview of evaluation in education. It discusses the objectives, definition, purpose, process, tools and trends of evaluation. Evaluation is defined as a systematic process of determining the extent to which instructional objectives are achieved by learners. The key purposes of evaluation include diagnosis, prediction, grading, selection and guidance. The evaluation process involves identifying the purpose and time frame, selecting instruments, collecting and interpreting data. Common evaluation tools include subjective and objective tests, rating scales, observation and performance assessments. Trends in evaluation emphasize relating objectives to evaluation and using evaluation to improve instruction.