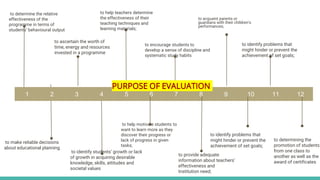
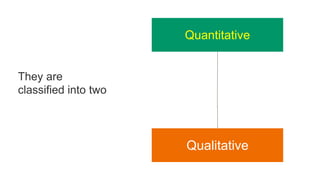
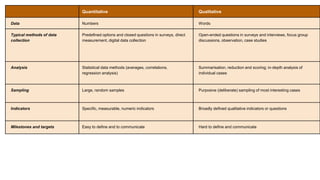
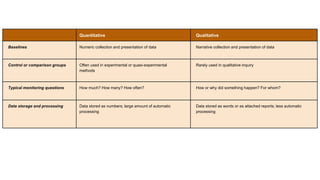
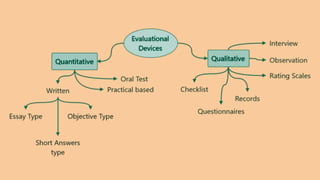
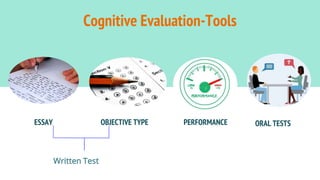
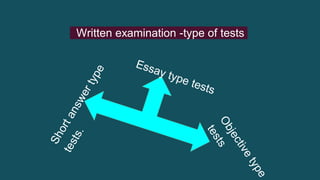
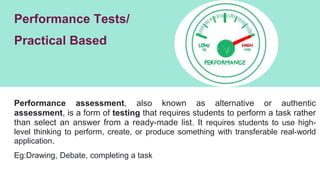
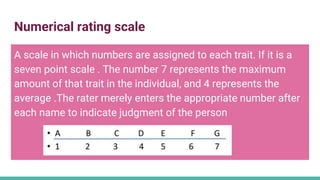
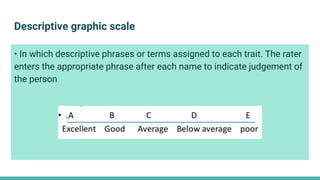
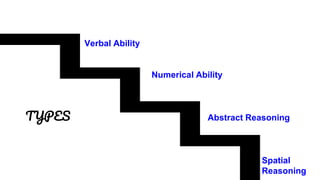
The document discusses various tools used for evaluation in education. It begins by defining evaluation and differentiating between quantitative and qualitative evaluation. It then describes different written, oral, and performance-based evaluation techniques. Specific tools covered include essays, objective tests like MCQs, observations, rating scales, aptitude tests, and methods for evaluating cognitive and non-cognitive learning outcomes. The document provides details on the purpose, types, advantages, and limitations of many of these evaluation tools.