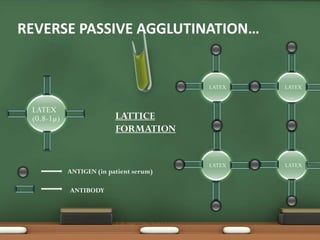
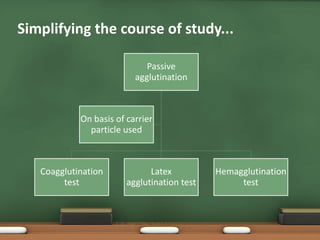
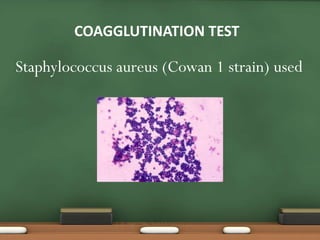
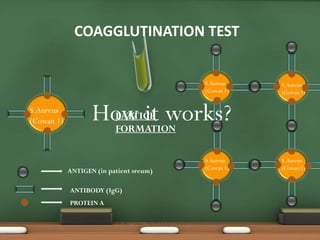
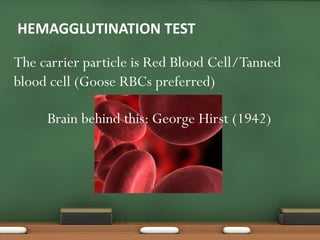
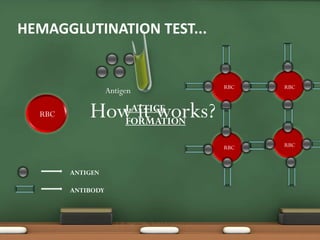
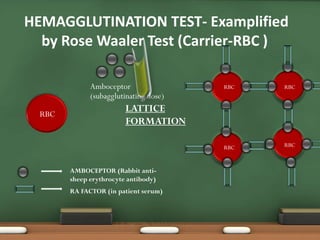
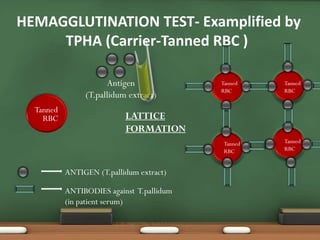
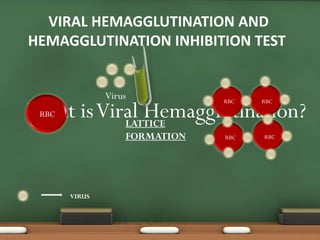
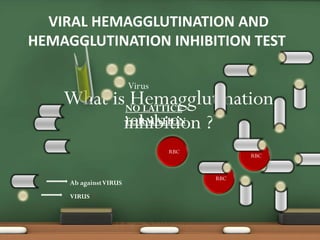
The document explains passive agglutination and its tests, describing it as a method that involves attaching soluble antigens to carrier particles for better detection of antibodies and antigens. It details various tests such as latex agglutination, hemagglutination, and their respective advantages and applications in laboratory settings. Recent advances in passive agglutination methods are also mentioned, emphasizing improved sensitivity and convenience over traditional precipitation tests.