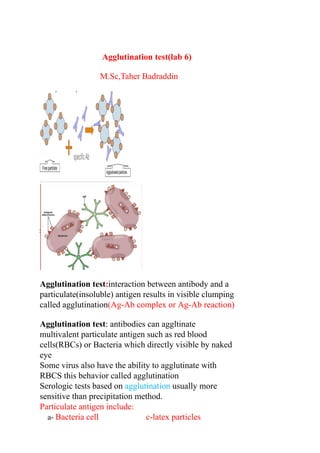
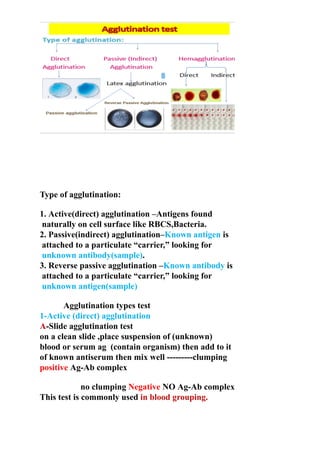
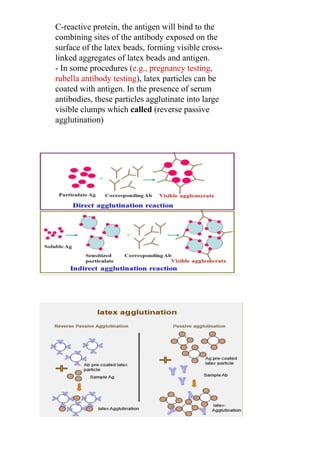
The document discusses agglutination tests, which detect antibodies or antigens by causing particulate substances like blood cells or bacteria to clump or agglutinate when combined. There are several types of agglutination tests, including direct/active tests where antigens are naturally present on cells/bacteria, indirect/passive tests where known antigens are attached to carriers to detect unknown antibodies, and reverse passive tests where known antibodies are attached to carriers to detect unknown antigens. Common applications of agglutination tests include blood typing, detecting infections like typhoid or brucellosis, and diagnosing conditions like pregnancy or rheumatoid factor.