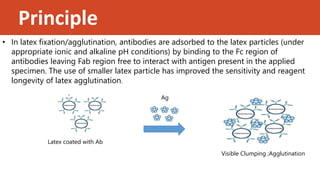
The latex fixation test, or latex agglutination test, is an antigen-antibody reaction used for diagnosing various diseases by detecting specific antigens or antibodies in patient specimens. It involves mixing patient samples with latex particles coated with antibodies, and positive results are indicated by visible clumping of the latex beads. Although it is simple, rapid, and widely used, the test has limitations such as potential false positives and the need for careful standardization of testing conditions.