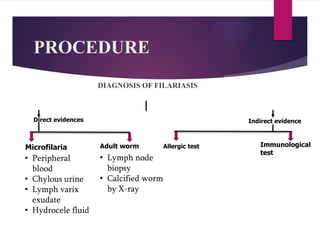
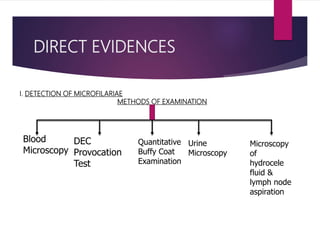
This document outlines the laboratory diagnosis of filariasis through direct and indirect evidence detection. Direct evidence methods include microscopy of peripheral blood, urine, lymph fluid and tissues to look for microfilariae. Concentration techniques like Knott's and membrane filtration increase detection sensitivity. The DEC provocation test induces microfilariae circulation. Indirect evidence involves immunological tests like ELISA and rapid diagnostic cards, as well as imaging and xenodiagnosis examining mosquito vectors. Treatment involves diethylcarbamazine or albendazole, with MDA programs used for prevention and control.




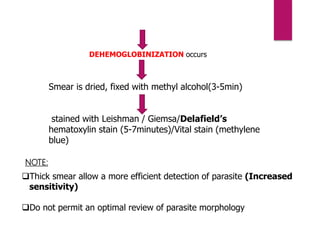


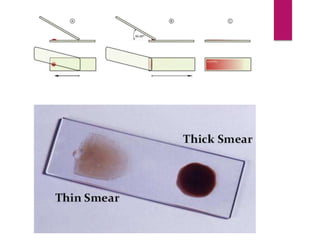
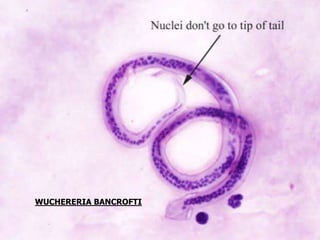
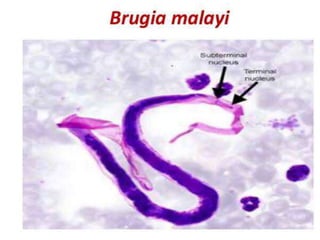

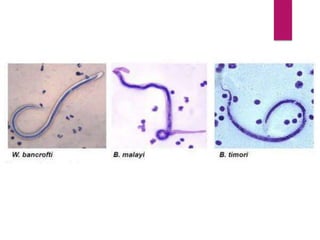
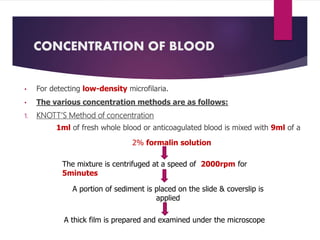

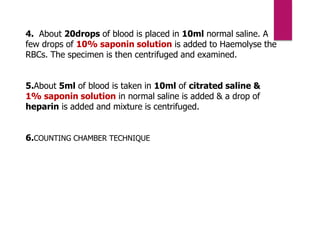


![PROCEDURE
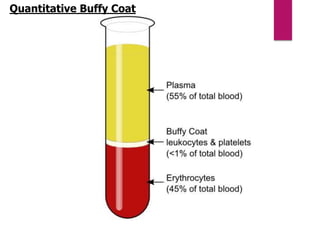
Blood is taken in a Microhaematocrit tube(QBC capillary tube)
[It is coated with acridine orange, EDTA & Heparin]
Centrifugation (5minutes)
Fluorescing parasites become concentrated in
the Buffy coat
The parasites can be visualized through the clear
glass wall of the tube
The acridine orange stains the DNA of the parasites.
The morphological characteristics, including the nuclear patterns
can be examined by ‘Flourescence microscopy’.
Very sensitive test.
NOTE:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filariasislaboratorydiagnosis-191104091254/85/Filariasis-laboratory-diagnosis-22-320.jpg)

![INDIRECT EVIDENCES
A. ALLERGIC TEST
Blood
examination
-Eosinophilia
Intradermal Test
• Immediate type of hypersensitivity
• Filarial antigen is injected on skin
B. IMMUNODIAGNOSIS
1. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay( ELISA)
2. Hemagglutination Test
3. Direct/Indirect Immunoflourescent antibody Test
4. Complement fixation Test
5. Immunoblotting
RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST: Immunochromatography filariasis card test
[93-100% sensitive]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filariasislaboratorydiagnosis-191104091254/85/Filariasis-laboratory-diagnosis-25-320.jpg)

![TREATMENT
• Drug of choice: Diethylcarbamazine [6mg/kg oral daily for 12 days]
• Albendazole [400mg twice daily orally for 21days
• Ivermectin [200mcg/kg]
• Doxycycline
PREVENTION AND CONTROL
i. Mass drug administration( MDA)
ii. DEC-Medicated salt
iii. Vector control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filariasislaboratorydiagnosis-191104091254/85/Filariasis-laboratory-diagnosis-27-320.jpg)
