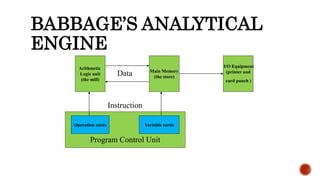
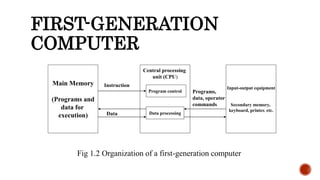
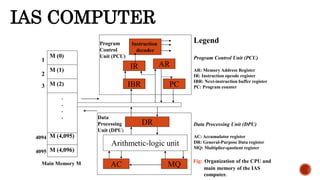
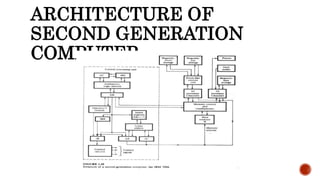
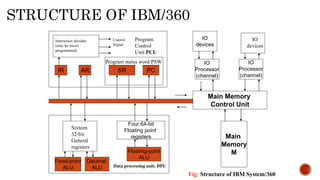
The document provides information about different generations of computers. It discusses Babbage's Analytical Engine as an early predecessor to modern computers. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, expensive machines. The second generation used transistors, making computers smaller, cheaper, and more reliable. The third generation used integrated circuits, making computers even smaller and faster. Later generations incorporated microprocessors, leading to the development of personal computers. The document also discusses some examples of specific early computers like the IAS and IBM 360.