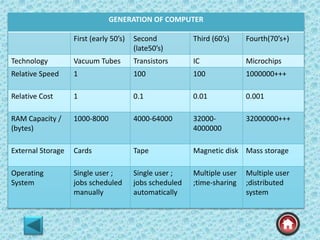
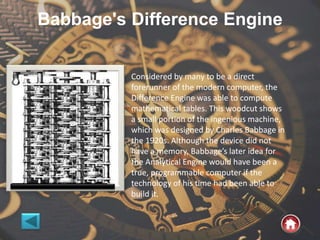
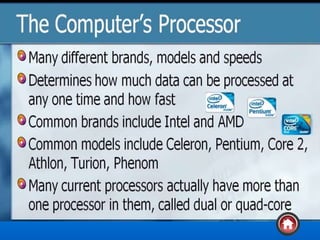
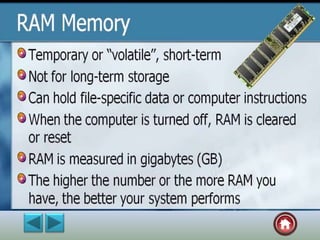
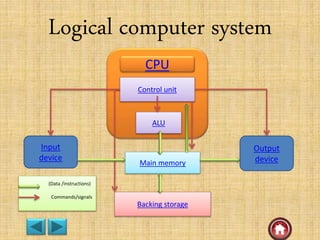
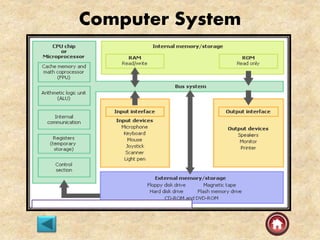
The document provides an overview of computer systems, detailing their history from the abacus to modern artificial intelligence. It describes the evolution of hardware, including the generations of computers, components like the CPU, RAM, and storage devices, and their respective functions. Additionally, it highlights the significance of input and output devices, as well as the introduction of new technologies such as microprocessors and integrated circuits.