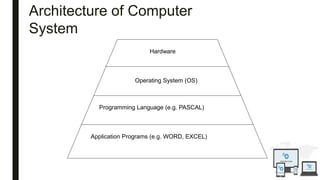
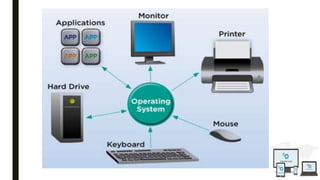
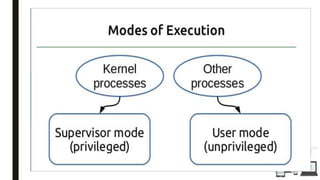
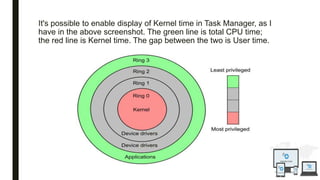
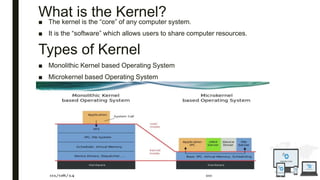
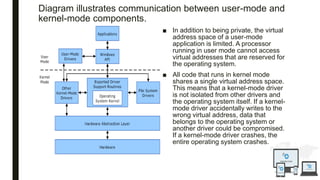
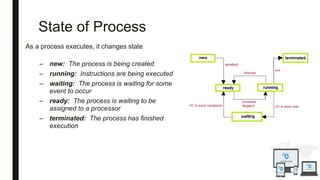
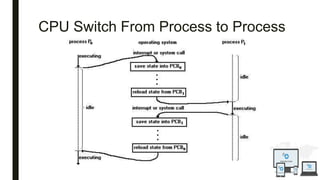
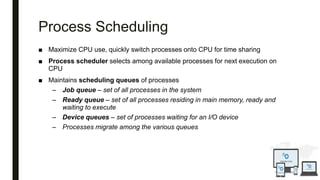
The document discusses an operating system topic presented by the Ethernet group consisting of three members. It defines an operating system as the set of programs that controls a computer and provides an interface between the user and hardware. The functions of an operating system include process management, memory management, file management, and security management. It also discusses the differences between user mode and kernel mode in an operating system.