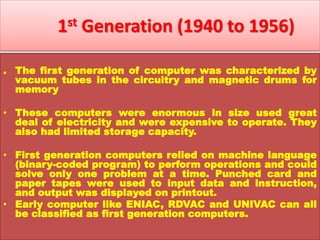
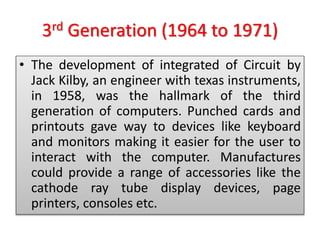
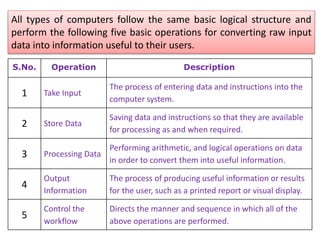
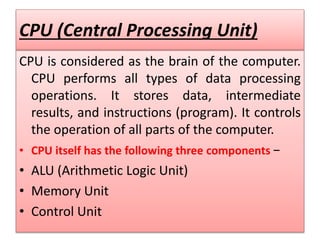
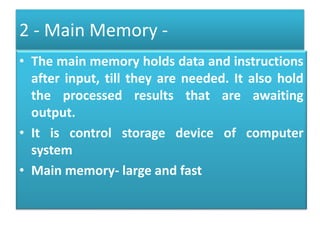
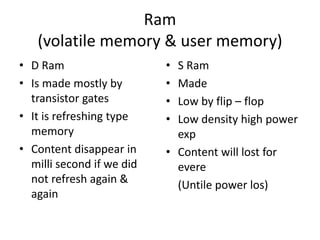
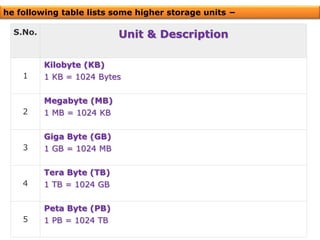
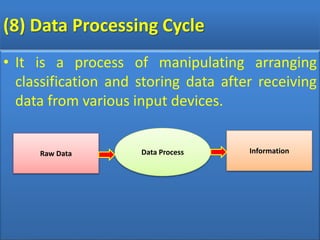
The document discusses the different generations of computers from the 1st to 5th generation. It provides details about the characteristics of each generation including the technologies used and some examples of computers from each generation. The 1st generation used vacuum tubes and magnetic drums. The 2nd generation saw the introduction of transistors replacing vacuum tubes. The 3rd generation brought integrated circuits and operating systems. Personal computers emerged in the 4th generation along with other advances. The 5th generation focuses on parallel processing and artificial intelligence.