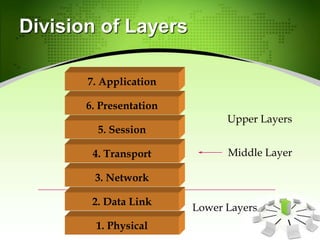
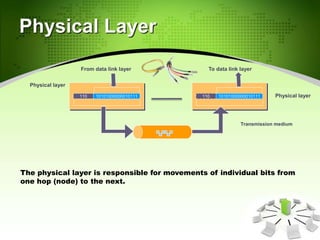
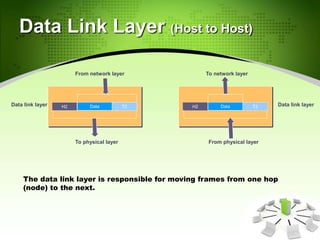
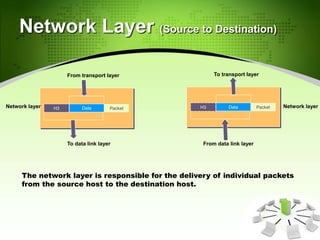
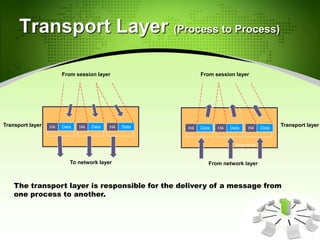
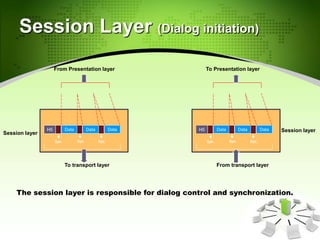
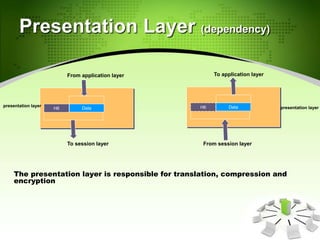
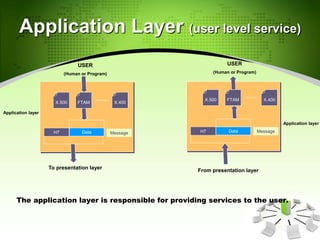
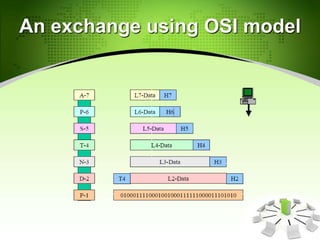
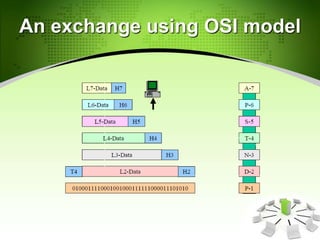
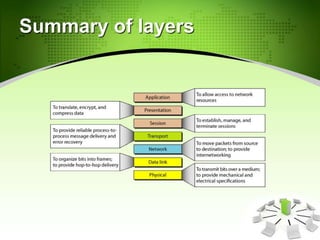
This document provides an introduction to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, which defines seven layers of network architecture: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. It describes each layer's responsibilities in moving data from one node or process to another. The Physical layer moves individual bits, the Data Link layer moves frames between nodes, the Network layer moves packets between hosts, the Transport layer moves segments between processes, and so on up to the Application layer which provides user-level services. An illustration is included showing how data is encapsulated and moves through each layer in an exchange between two systems.