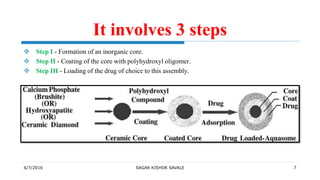
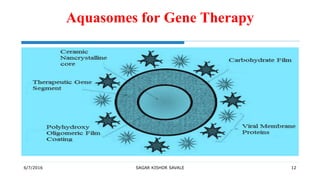
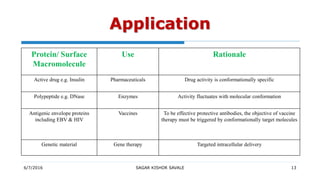
Aquasomes are three-layered self-assembled nanostructures, typically 60-300 nm in diameter, used for drug and antigen delivery, offering stability and protection to bio-active molecules. Their preparation involves forming a ceramic core, coating it with polyhydroxyl oligomers, and loading the desired drug, making them suitable for various applications including gene therapy, vaccine delivery, and as red blood cell substitutes. Characterization of aquasomes is conducted through methods like electron microscopy and x-ray powder diffractometry.
![6/7/2016 SAGAR KISHOR SAVALE 1
Aquasomes
Mr. Sagar Kishor Savale
[Department of Pharmaceutics]
avengersagar16@gmail.com
2015-2016
Department of Pharmacy (Pharmaceutics) | Sagar Savale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aquasomes-160607054701/85/Aquasomes-1-320.jpg)


![6/7/2016 SAGAR KISHOR SAVALE 4
Aquasomes are called as “ bodies of water ’’
1] Their water like properties.
2] Protect and preserve fragile biological molecules.
3] This property of maintaining conformational integrity as well as high degree of surface exposure
and in targeting of bio-active molecules like peptide and protein hormones, antigens and genes to
specific sites.
The carbohydrate stabilize nanoparticle of ceramic are known as “Aquasomes “](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aquasomes-160607054701/85/Aquasomes-4-320.jpg)
![6/7/2016 SAGAR KISHOR SAVALE 5
MECHANISM
1] Aquasomes protect bio-actives.
Carbohydrate coating prevents destructive denaturing interaction between drug and solid
carriers.
2] Aquasomes maintains molecular conformation and thus shows optimum pharmacological activity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aquasomes-160607054701/85/Aquasomes-5-320.jpg)