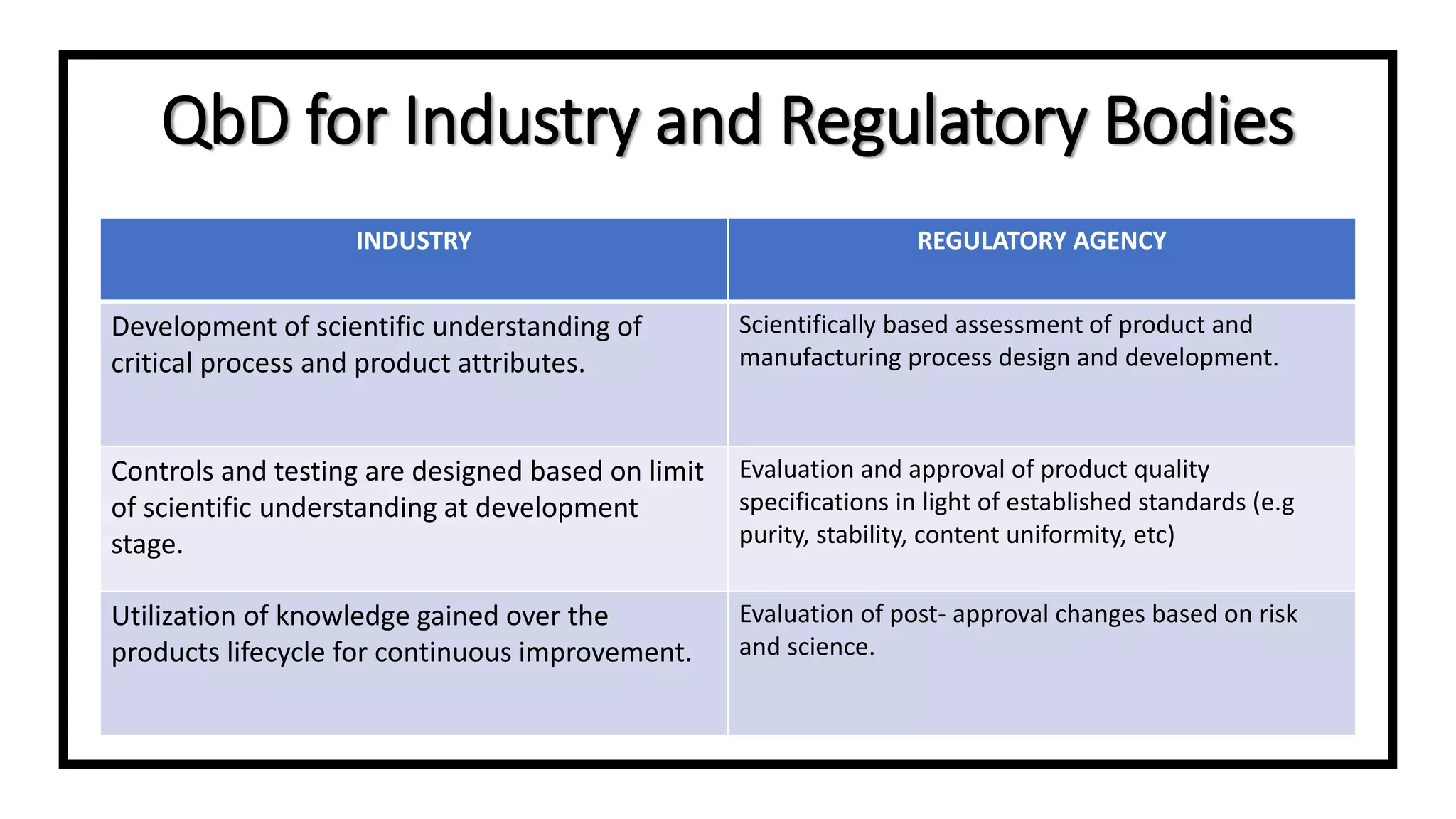
The document discusses the concept of Quality by Design (QbD), a systematic approach to pharmaceutical development adopted by the FDA and defined by ICH guidelines. QbD emphasizes meeting predefined objectives through a deep understanding of product and manufacturing processes, leading to cost savings and enhanced efficiency for both industry and regulators. The paper highlights regulatory and industry perspectives on QbD, including its benefits in improving product quality, innovation, and compliance.