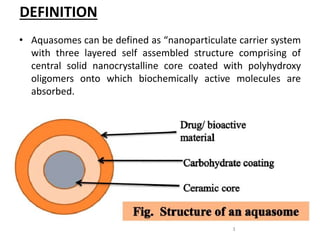
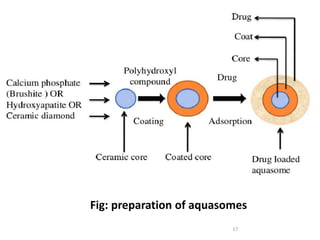
Aquasomes are a nanoparticulate carrier system composed of a central solid nanocrystalline core coated with polyhydroxy oligomers onto which biologically active molecules are absorbed. They are spherical structures between 60-300nm in size that protect and preserve fragile molecules. Aquasomes are prepared using a simple process involving the formation of a ceramic core, coating with carbohydrates, and immobilizing drug molecules. They can be evaluated for characteristics like particle size, drug release kinetics, and loading efficiency. Potential applications of aquasomes include delivery of proteins, peptides, vaccines, and other molecules due to their ability to maintain structural integrity of payloads.