Embed presentation

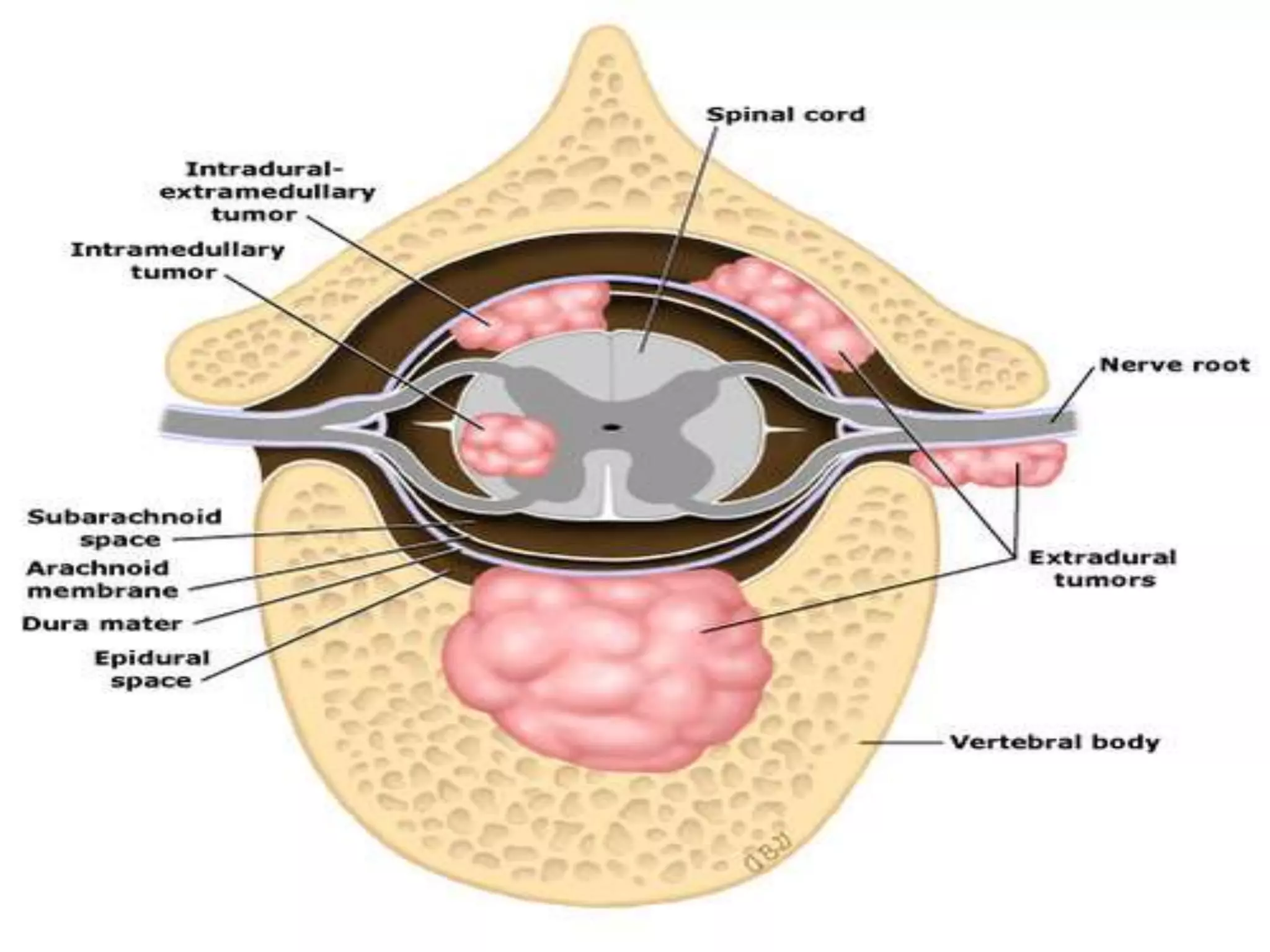
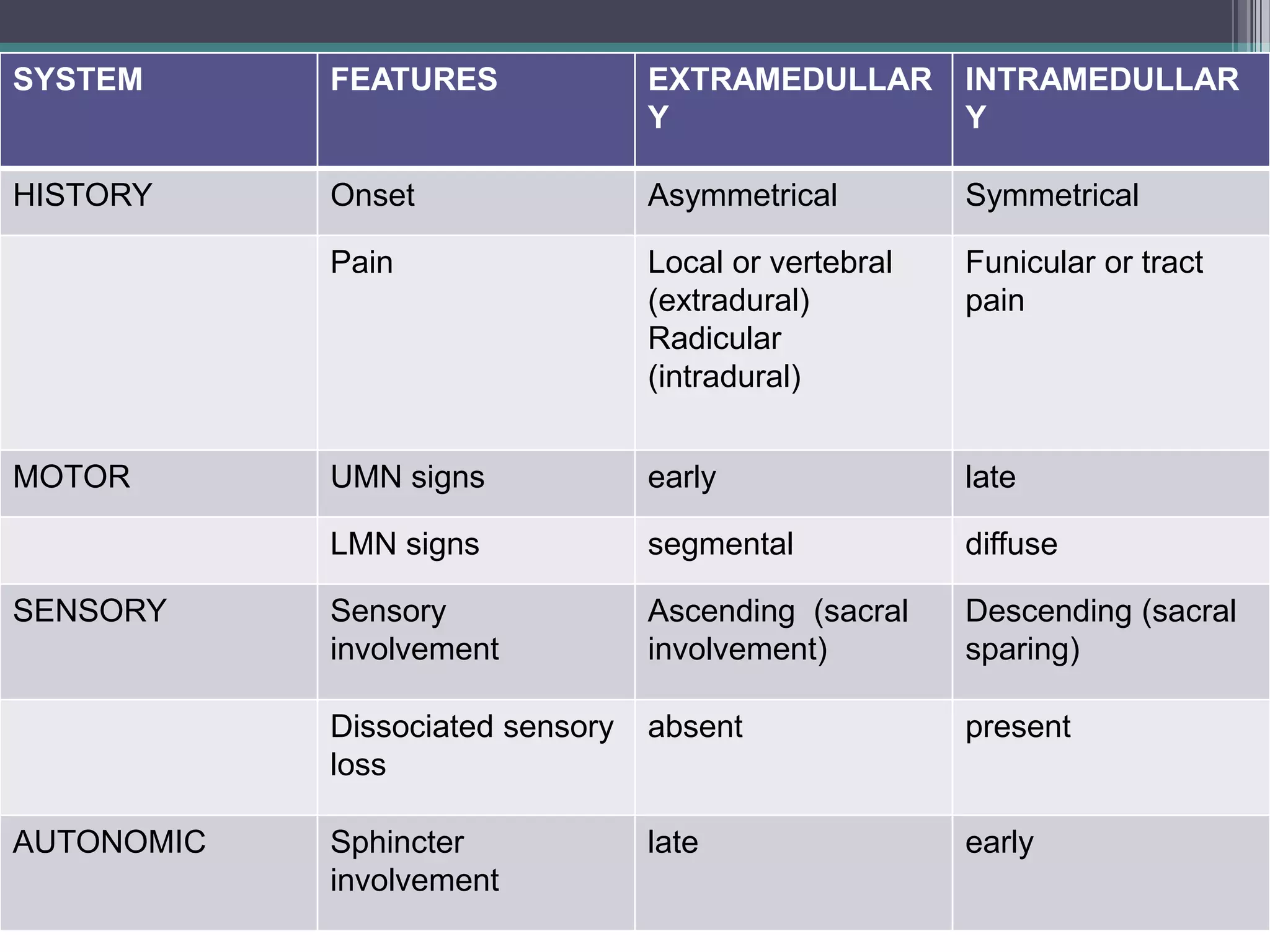


Intramedullary spinal cord lesions occur within the spinal cord itself while extramedullary lesions occur outside the spinal cord. Intramedullary lesions typically cause symmetrical symptoms that affect motor and sensory functions diffusely down the spinal cord, often with early sphincter involvement. In contrast, extramedullary lesions usually cause asymmetrical symptoms, with local or radicular pain and early upper motor neuron signs but later lower motor neuron signs and sensory involvement in the affected segment.



